|
Sodium Thiocyanate
Sodium thiocyanate (sometimes called sodium sulphocyanide) is the chemical compound with the formula NaSCN. This colorless deliquescent salt is one of the main sources of the thiocyanate anion. As such, it is used as a precursor for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and other specialty chemicals. Thiocyanate salts are typically prepared by the reaction of cyanide with elemental sulfur: :8 NaCN + S8 → 8 NaSCN Sodium thiocyanate crystallizes in an orthorhombic cell. Each Na+ center is surrounded by three sulfur and three nitrogen ligands provided by the triatomic thiocyanate anion. It is commonly used in the laboratory as a test for the presence of Fe3+ ions. Applications in chemical synthesis Sodium thiocyanate is employed to convert alkyl halides into the corresponding alkylthiocyanates. Closely related reagents include ammonium thiocyanate and potassium thiocyanate, which has twice the solubility in water. Silver thiocyanate may be used as well; the precipitation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deliquescent
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption or adsorption from the surrounding environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water molecules become suspended among the substance's molecules, adsorbing substances can become physically changed, e.g., changing in volume, boiling point, viscosity or some other physical characteristic or property of the substance. For example, a finely dispersed hygroscopic powder, such as a salt, may become clumpy over time due to collection of moisture from the surrounding environment. ''Deliquescent'' materials are sufficiently hygroscopic that they absorb so much water that they become liquid and form an aqueous solution. Etymology and pronunciation The word ''hygroscopy'' () uses combining forms of '' hygro-'' and '' -scopy''. Unlike any other ''-scopy'' word, it no longer refers to a viewing or imaging mode. It did begin that way, with the word ''hygroscope'' referring in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanide
Cyanide is a naturally occurring, rapidly acting, toxic chemical that can exist in many different forms. In chemistry, a cyanide () is a chemical compound that contains a functional group. This group, known as the cyano group, consists of a carbon atom triple-bonded to a nitrogen atom. In inorganic cyanides, the cyanide group is present as the anion . Soluble salts such as sodium cyanide (NaCN) and potassium cyanide (KCN) are highly toxic. Hydrocyanic acid, also known as hydrogen cyanide, or HCN, is a highly volatile liquid that is produced on a large scale industrially. It is obtained by acidification of cyanide salts. Organic cyanides are usually called nitriles. In nitriles, the group is linked by a covalent bond to carbon. For example, in acetonitrile (), the cyanide group is bonded to methyl (). Although nitriles generally do not release cyanide ions, the cyanohydrins do and are thus rather toxic. Bonding The cyanide ion is isoelectronic with carbon monoxide a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-Bromopropane
2-Bromopropane, also known as isopropyl bromide and 2-propyl bromide, is the halogenated hydrocarbon with the formula CH3CHBrCH3. It is a colorless liquid. It is used for introducing the isopropyl functional group in organic synthesis. 2-Bromopropane is prepared by heating isopropanol with hydrobromic acid. Preparation 2-Bromopropane is commercially available. It may be prepared in the ordinary manner of alkyl bromides, by reacting isopropanol with phosphorus and bromine, or with phosphorus tribromide. Safety Short-chain alkyl halides are often carcinogenic. The bromine atom is at the secondary position, which allows the molecule to undergo dehydrohalogenation easily to give propene, which escapes as a gas and can rupture closed reaction vessels. When this reagent is used in base catalyzed reactions, potassium carbonate should be used in place of sodium or potassium hydroxide. Further reading *Max Gergel Max G. Gergel (July 24, 1921 - July 5, 2017) was an American chemist and ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Workup (chemistry)
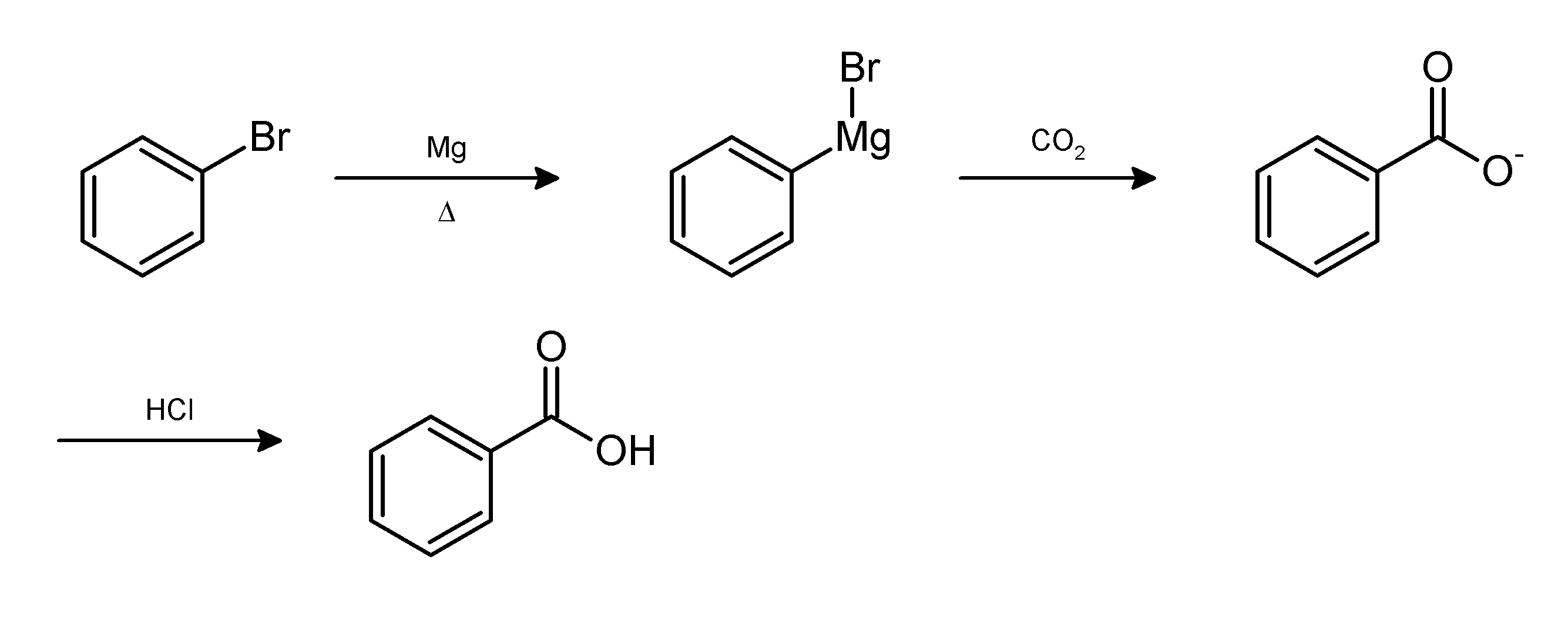
In chemistry, work-up refers to the series of manipulations required to isolate and purify the product(s) of a chemical reaction. Typically, these manipulations may include: * quenching a reaction to deactivate any unreacted reagents. * cooling the reaction mixture or adding an ''antisolvent'' to induce precipitation, and collecting or removing the solids by filtration, decantation, or centrifugation * removal of solvents by evaporation * separating the reaction mixture into organic and aqueous layers by liquid-liquid extraction * purification by chromatography, distillation or recrystallization For example, the Grignard reaction between phenylmagnesium bromide and carbon dioxide in the form of dry ice gives the conjugate base of benzoic acid. The desired product, benzoic acid, is obtained by the following work-up:{{cite book , title = Introduction to Organic Laboratory Techniques: A Small Scale Approach , author = Donald L. Pavia , year = 2004 , publisher = Thomson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Thiocyanate
Silver thiocyanate is the silver salt of thiocyanic acid with the formula AgSCN. Structure AgSCN is monoclinic with 8 molecules per unit cell. Each SCN− group has an almost linear molecular geometry, with bond angle 179.6(5)°. Weak Ag—Ag interactions of length 0.3249(2) nm to 0.3338(2) nm are present in the structure. Production Silver thiocyanate is produced by the reaction between silver nitrate and potassium thiocyanate Potassium thiocyanate is the chemical compound with the molecular formula KSCN. It is an important salt of the thiocyanate anion, one of the pseudohalides. The compound has a low melting point relative to most other inorganic salts. Use in chem .... References {{Silver compounds Thiocyanates Silver compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Thiocyanate
Potassium thiocyanate is the chemical compound with the molecular formula KSCN. It is an important salt of the thiocyanate anion, one of the pseudohalides. The compound has a low melting point relative to most other inorganic salts. Use in chemical synthesis Aqueous KSCN reacts almost quantitatively with Pb(NO3)2 to give Pb(SCN)2, which has been used to convert acyl chlorides to isothiocyanates. KSCN converts ethylene carbonate to ethylenesulfide. For this purpose, the KSCN is first melted under vacuum to remove water. In a related reaction, KSCN converts cyclohexene oxide to the corresponding episulfide. :C6H10O + KSCN → C6H10S + KOCN KSCN is also the starting product for the synthesis of carbonyl sulfide. Other uses Dilute aqueous KSCN is occasionally used for moderately realistic blood effects in film and theater. It can be painted onto a surface or kept as a colorless solution. When in contact with ferric chloride solution (or other solutions containing Fe3+), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium Thiocyanate
Ammonium thiocyanate is an inorganic compound with the formula NH4SCN. It is the salt of the ammonium cation and the thiocyanate anion. Uses Ammonium thiocyanate is used in the manufacture of herbicides, thiourea, and transparent artificial resins; in matches; as a stabilizing agent in photography; in various rustproofing compositions; as an adjuvant in textile dyeing and printing; as a tracer in oil fields; in the separation of hafnium from zirconium (important for the production of hafnium-free zircalloy for use in nuclear fuel cladding), and in titrimetric analyses. In May 1945, USAAF General Victor E. Betrandias advanced a proposal to his superior General Arnold to use of ammonium thiocyanate to reduce rice crops in Japan as part of the bombing raids on their country. Ammonium thiocyanate can also be used to determine the iron content in soft drinks by colorimetry. Ammonium thiocyanate may also be used to separate quinidine, from liquors, after the isolation of quinine f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halide
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a fluoride, chloride, bromide, iodide, astatide, or theoretically tennesside compound. The alkali metals combine directly with halogens under appropriate conditions forming halides of the general formula, MX (X = F, Cl, Br or I). Many salts are halides; the ''hal-'' syllable in ''halide'' and ''halite'' reflects this correlation. All Group 1 metals form halides that are white solids at room temperature. A halide ion is a halogen atom bearing a negative charge. The halide anions are fluoride (), chloride (), bromide (), iodide () and astatide (). Such ions are present in all ionic halide salts. Halide minerals contain halides. All these halides are colourless, high melting crystalline solids having high negative enthalpies of formation. Test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyl
In organic chemistry, an alkyl group is an alkane missing one hydrogen. The term ''alkyl'' is intentionally unspecific to include many possible substitutions. An acyclic alkyl has the general formula of . A cycloalkyl is derived from a cycloalkane by removal of a hydrogen atom from a Ring (chemistry), ring and has the general formula . Typically an alkyl is a part of a larger molecule. In structural formulae, the symbol R is used to designate a generic (unspecified) alkyl group. The smallest alkyl group is methyl, with the formula . Related concepts Alkylation is an important operation in refineries, for example in the production of high-octane gasoline. Alkylating antineoplastic agents are a class of compounds that are used to treat cancer. In such case, the term alkyl is used loosely. For example, nitrogen mustards are well-known alkylating agents, but they are not simple hydrocarbons. In chemistry, alkyl is a group, a substituent, that is attached to other molecular fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferric
In chemistry, iron(III) refers to the element iron in its +3 oxidation state. In ionic compounds (salts), such an atom may occur as a separate cation (positive ion) denoted by Fe3+. The adjective ferric or the prefix ferri- is often used to specify such compounds — as in "ferric chloride" for iron(III) chloride, . The adjective "ferrous" is used instead for iron(II) salts, containing the cation Fe2+. The word ferric is derived from the Latin word ''ferrum'' for iron. Iron(III) metal centres also occur in coordination complexes, such as in the anion ferrioxalate, , where three bidentate oxalate ions surrounding the metal centre; or, in organometallic compounds, such as the ferrocenium cation , where two cyclopentadienyl anions are bound to the FeIII centre. Iron is almost always encountered in the oxidation states 0 (as in the metal), +2, or +3. Iron(III) is usually the most stable form in air, as illustrated by the pervasiveness of rust, an insoluble iron(III)-containing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiocyanate
Thiocyanate (also known as rhodanide) is the anion . It is the conjugate base of thiocyanic acid. Common derivatives include the colourless salts potassium thiocyanate and sodium thiocyanate. Mercury(II) thiocyanate was formerly used in pyrotechnics. Thiocyanate is analogous to the cyanate ion, , wherein oxygen is replaced by sulfur. is one of the pseudohalides, due to the similarity of its reactions to that of halide ions. Thiocyanate used to be known as rhodanide (from a Greek word for rose) because of the red colour of its complexes with iron. Thiocyanate is produced by the reaction of elemental sulfur or thiosulfate with cyanide: : 8 CN- + S8 -> 8 SCN- : CN- + S2O3^2- -> SCN- + SO3^2- The second reaction is catalyzed by thiosulfate sulfurtransferase, a hepatic mitochondrial enzyme, and by other sulfur transferases, which together are responsible for around 80% of cyanide metabolism in the body. Biological chemistry of thiocyanate in medicine Thiocyanate is known to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratory
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physicians' offices, clinics, hospitals, and regional and national referral centers. Overview The organisation and contents of laboratories are determined by the differing requirements of the specialists working within. A physics laboratory might contain a particle accelerator or vacuum chamber, while a metallurgy laboratory could have apparatus for casting or refining metals or for testing their strength. A chemist or biologist might use a wet laboratory, while a psychologist's laboratory might be a room with one-way mirrors and hidden cameras in which to observe behavior. In some laboratories, such as those commonly used by computer scientists, computers (sometimes supercomputers) are used for either simulations or the analysis of data. Scient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


-oxide-sample.jpg)
