|
Siege Of Constantinople (1411)
The siege of Constantinople of 1411 occurred during the Ottoman Interregnum, or Ottoman Civil War, (20 July 1402 – 5 July 1413), when chaos reigned in the Ottoman Empire following the defeat of Sultan Bayezid I by the Central Asian warlord Timur. Although Mehmed Çelebi was confirmed as sultan by Timur after the Battle of Ankara, his brothers İsa Çelebi, Musa Çelebi, Süleyman Çelebi, and later, Mustafa Çelebi, refused to recognize his authority, each claiming the throne for himself. A civil war was the result. The Interregnum lasted until the Battle of Camurlu on 5 July 1413, when Mehmed Çelebi emerged as victor in the strife, crowned himself sultan Mehmed I, and restored peace to the empire. Background Before the Battle of Ankara, the Byzantine Empire was a mere pawn of outside forces for several decades but after the defeat of the Ottomans by Timur, the Empire – for a short while – became a player in Ottoman domestic politics and intrigue. Sultan Bayezid conqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Interregnum
The Ottoman Interregnum, or the Ottoman Civil War ( 20 July 1402 – 5 July 1413; tr, Fetret Devri, , Interregnum Period), was a civil war in the Ottoman Empire between the sons of Sultan Bayezid I following the defeat of their father at the Battle of Ankara on 20 July 1402. Although Mehmed Çelebi was confirmed as sultan by Timur, his brothers İsa Çelebi, Musa Çelebi, Süleyman Çelebi, and later, Mustafa Çelebi, refused to recognize his authority, each claiming the throne for himself. Civil war was the result. The Interregnum lasted a little under 11 years, until the Battle of Çamurlu on 5 July 1413, when Mehmed Çelebi emerged as victor, crowned himself Sultan Mehmed I, and restored the empire. Civil war Isa and Mehmed Civil war broke out among the sons of Sultan Bayezid I upon his death in 1403. His oldest son, Süleyman, with his capital at Edirne, ruled the recently conquered Bulgaria, all of Thrace, Macedonia and northern Greece. The second son, İsa Çelebi, es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Camurlu
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stefan Lazarević
Stefan Lazarević ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Лазаревић, 1377 – 19 July 1427), also known as Stefan the Tall ( sr, Стефан Високи / ''Stefan Visoki''), was the ruler of Serbia as prince (1389–1402) and despot (1402–1427), diplomat, legislator, ktetor, patron of the arts, poet and one of the founding members of the Order of the Dragon. The son of Prince Lazar Hrebeljanović, he was regarded as one of the finest knights and military leaders at that time. After the death of his father at Kosovo (1389), he became ruler of Moravian Serbia and ruled with his mother Milica (a Nemanjić), until he reached adulthood in 1393. Stefan led troops in several battles as an Ottoman vassal, until asserting independence after receiving the title of ''despot'' from the Byzantines in 1402. Becoming a Hungarian ally in 1403–04, he received large possessions, including the important Belgrade and Golubac Fortress. He also held the superior rank in the chivalric Order of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungary to the north, Romania to the northeast, Bulgaria to the southeast, North Macedonia to the south, Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina to the west, and Montenegro to the southwest, and claims a border with Albania through the Political status of Kosovo, disputed territory of Kosovo. Serbia without Kosovo has about 6.7 million inhabitants, about 8.4 million if Kosvo is included. Its capital Belgrade is also the List of cities in Serbia, largest city. Continuously inhabited since the Paleolithic Age, the territory of modern-day Serbia faced Slavs#Migrations, Slavic migrations in the 6th century, establishing several regional Principality of Serbia (early medieval), states in the early Mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of İnceğiz
The Battle of İnceğiz was fought sometime in late 1411 or early 1412 near Constantinople between the rival sons of the Ottoman Sultan Bayezid I, Mehmed Çelebi and Musa Çelebi, during the final stages of the civil war known as the Ottoman Interregnum. Background Musa had become the ruler of the Ottomans' European domains after overthrowing and killing his brother Süleyman Çelebi in 1410–11. Unlike Süleyman, Musa, who relied greatly on the ''akinji'' raiders, followed a policy extremely hostile to his Christian neighbours. The attacks against both the Byzantine Empire and Serbia, that had stopped after the Treaty of Gallipoli in 1403, resumed: in Serbia, Musa besieged Smederovo, while against Byzantium he attacked Thessalonica and Selymbria, and placed Constantinople under blockade in August 1411. Mehmed's alliance with Byzantium and the battle As a result, the Byzantine emperor Manuel II Palaiologos turned to Musa's brother, Mehmed Çelebi, who had established his rule ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Kosmidion
The Battle of Kosmidion ( tr, Eyüp Muharebesi) occurred on 15 June 1410, during the Ottoman Interregnum, and was fought between the forces of the rival brothers, Musa Çelebi and Süleyman Çelebi, at Kosmidion (modern Eyüp) just outside the land walls of Constantinople. Battle The Byzantine emperor Manuel II Palaiologos was allied with Süleyman, whose army was encamped inside Constantinople. Manuel also prepared ships to help evacuate Süleyman's army in case of a defeat, but Musa managed to set them on fire before the battle began. The battle was a victory for Süleyman Çelebi, chiefly due to the defection of many of his vassals, who had previously served Süleyman, defected. Among the defectors was Vuk Lazarević, the brothers' half-uncle. Laonikos Chalkokondyles claims that Vuk's brother Stefan also defected due to the pressure of Süleyman's ally, the Byzantine emperor Manuel II Palaiologos, but the chronicler Constantine of Kostenets reports that he fought alongside M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
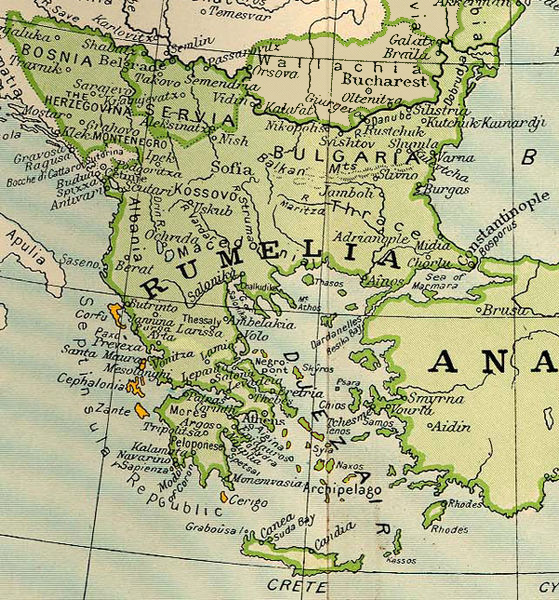
Rumeli
Rumelia ( ota, روم ايلى, Rum İli; tr, Rumeli; el, Ρωμυλία), etymologically "Land of the Romans", at the time meaning Eastern Orthodox Christians and more specifically Christians from the Byzantine rite, was the name of a historical region in Southeastern Europe that was administered by the Ottoman Empire, corresponding to the Balkans. In its wider sense, it was used to refer to all Ottoman possessions and vassals in Europe that would later be geopolitically classified as "the Balkans". During the period of its existence, it was more often known in English as Turkey in Europe. Etymology ''Rûm'' in this context means "Greek", or a Christian Greek speaker and ''ėli'' means "land" and ''Rumelia'' ( ota, روم ايلى, ''Rūm-ėli''; Turkish: ''Rumeli'') means "Land of the Romans" in Ottoman Turkish. It refers to the lands conquered by the Ottoman Empire in the Balkans, which formerly belonged to the Byzantine Empire, known by its contemporaries as the Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edirne
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis (Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, Edirne was the second capital city of the Ottoman Empire from 1369 to 1453, before Constantinople became its capital. The city is a commercial centre for woven textiles, silks, carpets and agricultural products and has a growing tourism industry. In 2019 its estimated population was 185,408. Edirne has an attractive location on the rivers Meriç and Tunca and has managed to withstand some of the unattractive development that mars the outskirts of many Turkish cities. The town is famous in Turkey for its liver. ''Ciğer tava'' (breaded and deep-fried liver) is often served with a side of cacık, a dish of diluted strained yogurt with chopped cucumber. Names and etymology The city was founded and named after the Roman emperor Hadr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be used as the title of certain rulers who claimed almost full sovereignty (i.e., not having dependence on any higher ruler) without claiming the overall caliphate, or to refer to a powerful governor of a province within the caliphate. The adjectival form of the word is "sultanic", and the state and territories ruled by a sultan, as well as his office, are referred to as a sultanate ( '. The term is distinct from king ( '), despite both referring to a sovereign ruler. The use of "sultan" is restricted to Muslim countries, where the title carries religious significance, contrasting the more secular ''king'', which is used in both Muslim and non-Muslim countries. Brunei and Oman are the only independent countries which retain the ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its Thessaloniki metropolitan area, metropolitan area, and the capital city, capital of the geographic regions of Greece, geographic region of Macedonia (Greece), Macedonia, the administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Central Macedonia and the Decentralized Administration of Macedonia and Thrace. It is also known in Greek language, Greek as (), literally "the co-capital", a reference to its historical status as the () or "co-reigning" city of the Byzantine Empire alongside Constantinople. Thessaloniki is located on the Thermaic Gulf, at the northwest corner of the Aegean Sea. It is bounded on the west by the delta of the Vardar, Axios. The Thessaloniki (municipality), municipality of Thessaloniki, the historical center, had a population of 317,778 in 2021, while the Thessaloniki metro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marmara Sea
The Sea of Marmara,; grc, Προποντίς, Προποντίδα, Propontís, Propontída also known as the Marmara Sea, is an inland sea located entirely within the borders of Turkey. It connects the Black Sea to the Aegean Sea via the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits, separating the country's European and Asian sides. The Sea of Marmara is a small sea with an area of , and dimensions of . Its greatest depth is . Name The Sea of Marmara is named after the largest island to its south side which is called Marmara Island because it is rich in marble (Greek (''mármaron'') "marble)." In classical antiquity it was known as the Propontis, which is derived from the Greek words ''pro-'' (before) and ''pontos'' (sea) and reflects the fact that the Ancient Greeks used to sail through it to reach the Black Sea that they called Pontos. Mythology In Greek mythology, a storm on the Propontis brought the Argonauts back to an island they had left, precipitating a battle in which ei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John VII Palaiologos
John VII Palaiologos or Palaeologus ( el, Ἰωάννης Παλαιολόγος, Iōánnēs Palaiológos; 1370 – 22 September 1408) was Byzantine emperor for five months in 1390, from 14 April to 17 September. A handful of sources suggest that John VII sometimes used the name Andronikos (Ἀνδρόνικος), possibly to honour the memory of his father, Andronikos IV Palaiologos, though he reigned under his birth name. Andronikos IV was the firstborn son of Emperor John V Palaiologos (), and had thus been the heir to the throne. After a failed rebellion in 1373, Andronikos IV was imprisoned and partially blinded, the same punishment possibly being carried out on John VII, then only three years old. Andronikos IV escaped in 1376 and successfully took Constantinople, ruling as emperor until 1379. John VII served as co-emperor during this time, possibly being appointed in 1377. Though deposed in 1379 by his brother Manuel II Palaiologos and their father John V, Andronikos IV ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |