|
Senator Schröder (ship)
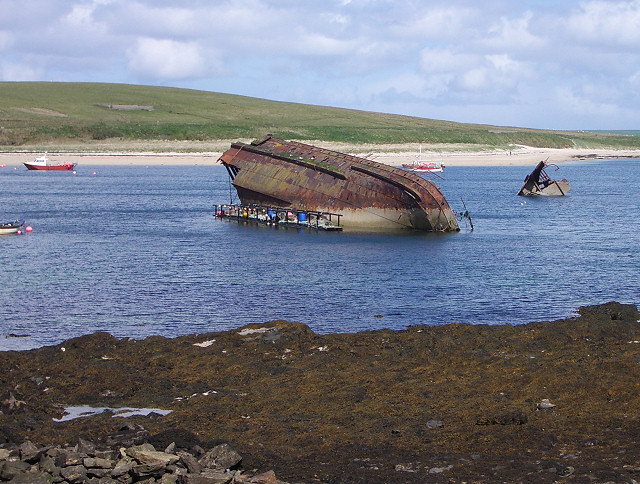
''Senator Schröder'' was a German trawler used as a Vorpostenboot during the First and Second World War. Launched in 1908 as a fishing trawler, she became a research vessel in the inter-war period. Description The ship long, with a beam of . She had a depth of and a draught of . She was assessed at , . She was powered by a triple expansion steam engine, which had cylinders of , and diameter by stroke. The engine was built by Germany._It_was_rated_at_49nominal_horsepower.html" ;"title="Tönning">ider_Werft_AG,_Tönning,_German_Empire.html" "title="Tönning.html" ;"title="ider Werft AG, Tönning">ider Werft AG, Tönning, German Empire">Germany. It was rated at 49nominal horsepower">nhp. It drove a single screw propeller. It could propel the ship at . History ''Senator Schröder'' was built as yard number 81 by Eider Werft AG, Tönning. She was launched on 26 February 1908 and completed on 20 March. Owned by the Cuxhavener Hochseefischerei AG, her port of registry was Cuxh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuxhaven
Cuxhaven (; ) is an independent town and seat of the Cuxhaven district, in Lower Saxony, Germany. The town includes the northernmost point of Lower Saxony. It is situated on the shore of the North Sea at the mouth of the Elbe River. Cuxhaven has a footprint of (east–west) by (north–south). Its town quarters Duhnen, Döse and Sahlenburg are especially popular vacation spots on the North Sea and home to about 52,000 residents. Cuxhaven is home to an important fisherman's wharf and ship registration point for Hamburg as well as the Kiel Canal until 2008. Tourism is also of great importance. The city and its precursor Ritzebüttel belonged to Hamburg from the 13th century until 1937. The island of Neuwerk, a Hamburg dependency, is located just northwest of Cuxhaven in the North Sea. The city's symbol, known as the Kugelbake, is a beacon once used as a lighthouse; the wooden landmark on the mouth of the Elbe marks the boundary between the river and the North Sea and also ador ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blockship
A blockship is a ship deliberately sunk to prevent a river, channel, or canal from being used. It may either be sunk by a navy defending the waterway to prevent the ingress of attacking enemy forces, as in the case of at Portland Harbour in 1914; or it may be brought by enemy raiders and used to prevent the waterway from being used by the defending forces, as in the case of the three old cruisers , and scuttled during the Zeebrugge raid in 1918 to prevent the port from being used by the German navy. An early use was in 1667, during the Dutch Raid on the Medway and their attempts to do likewise in the Thames during the Second Anglo-Dutch War, when a number of warships and merchant ships commandeered by the Royal Navy were sunk in those rivers to attempt to stop the attacking forces. An even earlier use are the six 11th century Skuldelev ships in Roskilde Fjord, sunk to protect Roskilde from northern Vikings. They are now on display in the Viking Ship Museum. The above is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steamships Of Germany
A steamship, often referred to as a steamer, is a type of steam-powered vessel, typically ocean-faring and seaworthy, that is propelled by one or more steam engines that typically move (turn) propellers or paddlewheels. The first steamships came into practical usage during the early 1800s; however, there were exceptions that came before. Steamships usually use the prefix designations of "PS" for ''paddle steamer'' or "SS" for ''screw steamer'' (using a propeller or screw). As paddle steamers became less common, "SS" is assumed by many to stand for "steamship". Ships powered by internal combustion engines use a prefix such as "MV" for ''motor vessel'', so it is not correct to use "SS" for most modern vessels. As steamships were less dependent on wind patterns, new trade routes opened up. The steamship has been described as a "major driver of the first wave of trade globalization (1870–1913)" and contributor to "an increase in international trade that was unprecedented in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ships Built In Germany
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity, and purpose. Ships have supported exploration, trade, warfare, migration, colonization, and science. After the 15th century, new crops that had come from and to the Americas via the European seafarers significantly contributed to world population growth. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce. The word ''ship'' has meant, depending on the era and the context, either just a large vessel or specifically a ship-rigged sailing ship with three or more masts, each of which is square-rigged. As of 2016, there were more than 49,000 merchant ships, totaling almost 1.8 billion dead weight tons. Of these 28% were oil tankers, 43% were bulk carriers, and 13% were con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1908 Ships
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20 * one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album ''63/19'' by Kool A.D. * '' Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle. * "Nineteen", a song by Bad4Good from the 1992 album '' Refugee'' * "Nineteen", a song by Karma to Burn from the 2001 album ''Almost Heathen''. * "Nineteen" (song), a 2007 song by American singer Billy Ray Cyrus. * "Nineteen", a song by Tegan and Sara from the 2007 album '' The Con''. * "XIX" (song), a 2014 song by S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kriegsmarine
The (, ) was the navy of Germany from 1935 to 1945. It superseded the Imperial German Navy of the German Empire (1871–1918) and the inter-war (1919–1935) of the Weimar Republic. The was one of three official branches, along with the and the , of the , the German armed forces from 1935 to 1945. In violation of the Treaty of Versailles, the grew rapidly during German naval rearmament in the 1930s. The 1919 treaty had limited the size of the German navy and prohibited the building of submarines. ships were deployed to the waters around Spain during the Spanish Civil War (1936–1939) under the guise of enforcing non-intervention, but in reality supported the Nationalists against the Spanish Republicans. In January 1939, Plan Z, a massive shipbuilding program, was ordered, calling for surface naval parity with the British Royal Navy by 1944. When World War II broke out in September 1939, Plan Z was shelved in favour of a crash building program for submarines ( U-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Ship
A research vessel (RV or R/V) is a ship or boat designed, modified, or equipped to carry out research at sea. Research vessels carry out a number of roles. Some of these roles can be combined into a single vessel but others require a dedicated vessel. Due to the demanding nature of the work, research vessels may be constructed around an icebreaker hull, allowing them to operate in polar waters. History The research ship had origins in the early voyages of exploration. By the time of James Cook's ''Endeavour'', the essentials of what today we would call a research ship are clearly apparent. In 1766, the Royal Society hired Cook to travel to the Pacific Ocean to observe and record the transit of Venus across the Sun. The ''Endeavour'' was a sturdy vessel, well designed and equipped for the ordeals she would face, and fitted out with facilities for her "research personnel", Joseph Banks. As is common with contemporary research vessels, ''Endeavour'' also carried out more th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million residents within the city limits, over 17 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in the metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's largest cities; being the most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest urban and metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow grew to become a prosperous and powerful city that served as the capital of the Grand Duchy that bears its name. When the Grand Duchy of Moscow evolved into the Tsardom of Russia, Moscow remained the political and economic center for most of the Tsardom's history. Whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist International
The Communist International (Comintern), also known as the Third International, was a Soviet-controlled international organization founded in 1919 that advocated world communism. The Comintern resolved at its Second Congress to "struggle by all available means, including armed force, for the overthrow of the international bourgeoisie and the creation of an international Soviet republic as a transition stage to the complete abolition of the state". The Comintern was preceded by the 1916 dissolution of the Second International. The Comintern held seven World Congresses in Moscow between 1919 and 1935. During that period, it also conducted thirteen Enlarged Plenums of its governing Executive Committee, which had much the same function as the somewhat larger and more grandiose Congresses. Joseph Stalin, leader of the Soviet Union, dissolved the Comintern in 1943 to avoid antagonizing his allies in the later years of World War II, the United States and the United Kingdom. It wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Appel
Jan Appel (pseudonyms: ''Max Hempel'', ''Jan Arndt'', ''Jan Voß''; 22 August 1890, Mecklenburg4 May 1985, Maastricht) was a German revolutionary who participated in the German Revolution of 1918. He became a prominent Left Communist activist and theorist. Early life Appel was born in 1890 in Mecklenburg, Germany. His father was an active socialist and from 1908 he was an active member of the Social Democratic Party of Germany. Although he trained as a shipbuilder, he joined the army in 1911 and served until 1913. Then he saw active service in the First World War. He was demobilised in 1917 and sent to work in the Vulcan Werft Hamburg shipyard. In January 1918 he participated in the strike wave which involved over 400,000 workers across Germany demanding immediate peace without annexation or indemnity, better food, and end to military discipline in the factories and the release of political prisoners. The German Revolution Jan Appel was involved in German Revolution of N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cläre Jung
Cläre Jung (2 February 1892 – 25 March 1981) was a German journalist, writer and political activist. Early life Cläre Otto enjoyed a middle-class upbringing. Her father was a feed merchant. After finishing at her single-sex secondary school she came into contact with the circle of Berlin-based expressionist poets around Georg Heym, Else Lasker-Schüler and, most notably, Franz Pfemfert. Fritz Mierau would later describe her as "the soul and muse of the little circle"."...die Seele und die Muse des kleinen Kreises." Pfemert edited a left-wing political and literary magazine called ''Die Aktion'': Cläre Otto got to know his fellow contributors to ''Die Aktion'', among them the restless anarchist poet Franz Jung whom she would later marry and under whose shadow, according to some evaluations, she would spend much of her life. However, her first marriage was to another ''Die Aktion'' contributor, the writer and political activist Richard Oehring: the two of them were divor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Jung
Franz Josef Johannes Konrad Jung (26 November 1888, Neisse, Upper Silesia – 21 January 1963, Stuttgart) was a writer, economist and political activist in Germany. He also wrote under the names Franz Larsz and Frank Ryberg. He grew up in Neisse (now Nysa) and was a childhood friend of the poet Max Herrmann-Neisse. He studied music, law and economics in Leipzig, Jena, Breslau and Munich. From 1909 he worked as a journalist and soon started writing for ''Der Sturm'' and ''Die Aktion''. The Austrian psychoanalyst Otto Gross was a large influence upon him. He was a member of the League for Proletarian Culture (1919–1920). In 1921 he travelled with Jan Appel to participate in the 3rd World Congress of the Comintern in 1921 as a delegate of the Communist Workers Party of Germany (KAPD). Their clandestine transport involved hijacking the SS Senator Schröder, which was bound for fishing grounds near Iceland, to Murmansk, Russia. He participated in the March Action (March 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |