|
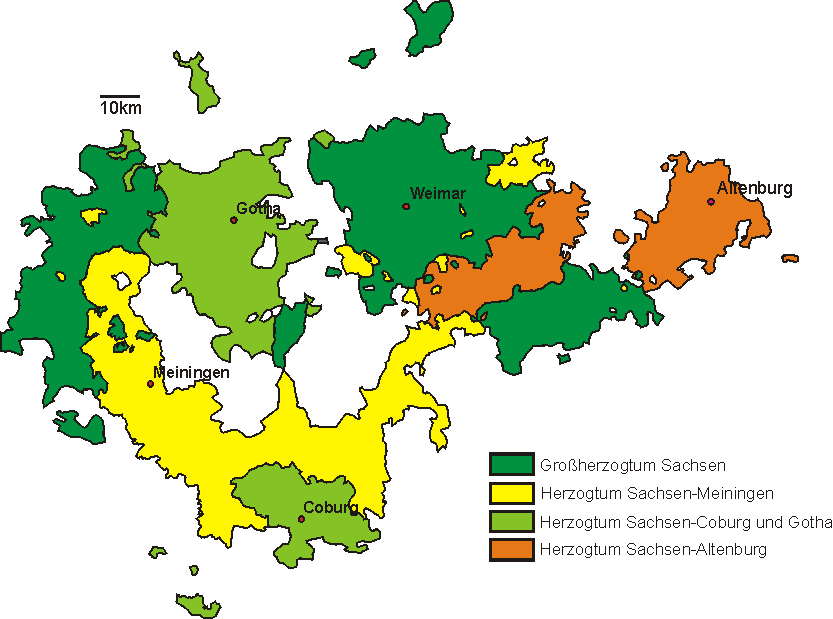
Saxe-Altenburg
Saxe-Altenburg (german: Sachsen-Altenburg, links=no) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the House of Wettin in present-day Thuringia. It was one of the smallest of the German states with an area of 1323 square kilometers and a population of 207,000 (1905) of whom about one fifth resided in the capital, Altenburg. The territory of the duchy consisted of two non-contiguous territories separated by land belonging to the Principality of Reuss. Its economy was based on agriculture, forestry, and small industry. The state had a constitutional monarchical form of government with a parliament composed of thirty members chosen by male taxpayers over 25 years of age. History The duchy had its origins in the medieval Burgraviate of Altenburg in the Imperial Pleissnerland ''(Terra Plisensis)'', a possession of the Wettin Margraves of Meissen since 1243. Upon a partition treaty of 1485, Altenburg fell to Ernst, Elector of Saxony, the progenitor of the Ernestine We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst II, Duke Of Saxe-Altenburg
, image = Ernstii.jpg , image_size = , caption = The Duke in 1915 , succession = Duke of Saxe-Altenburg , reign = 7 February 1908 – , coronation = , predecessor = Ernst I , successor = , spouse = , issue = , house = Wettin , father = Prince Moritz of Saxe-Altenburg , mother = Princess Augusta of Saxe-Meiningen , birth_date = , birth_place = Altenburg, Saxe-Altenburg , death_date = , death_place = Fröhliche Wiederkunft Castle, Trockenborn-Wolfersdorf, East Germany , burial_place = , religion = Lutheranism Ernst II (31 August 1871 in Altenburg – 22 March 1955 in Trockenborn-Wolfersdorf) was the last reigning duke of Saxe-Altenburg and a German general active during World War I. Early life He was the fourth child and only son of Prince Moritz, the youngest son of Georg, Duke of Saxe-Altenburg and Princess Augusta of Saxe-Meiningen. The death of his father, on the 13 May 1907 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg
Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg () was a duchy ruled by the Ernestine branch of the House of Wettin in today's Thuringia, Germany. The extinction of the line in 1825 led to a major re-organisation of the Thuringian states. History In 1640 the sons of the late Ernestine duke John II of Saxe-Weimar divided their paternal heritage (''Ernestinische Teilung'') whereby Duke Ernest the Pious, a younger son, received the newly established Duchy of Saxe-Gotha. In 1636 Ernest had married Elisabeth Sophie, the only child of Duke John Philip of Saxe-Altenburg. Upon her father's death in 1639, the Duchy of Saxe-Altenburg passed to her uncle Duke Frederick William II and her cousin Frederick William III. The Duchy of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg was nominally created in 1672, when Duke Frederick William III of Saxe-Altenburg died at the age of 14 and Ernest the Pious, by his marriage with Elisabeth Sophie, inherited the major part of his possessions. It was common for the Ernestine duchies to merge and spli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Philipp, Duke Of Saxe-Altenburg
Johann Philipp (25 January 1597 – 1 April 1639), was a duke of Saxe-Altenburg. He was born in Torgau, the eldest (but fourth in order of birth) surviving son of Friedrich Wilhelm I, Duke of Saxe-Weimar and Anna Maria of the Palatinate-Neuburg, his second wife. Childhood When his father died (1602), Johann Philipp and his younger brothers Frederick, Johann Wilhelm and Friedrich Wilhelm were underage. Because of this, his uncle Johann (more interested in natural sciences and art than politics) took over his guardianship and the regency of his inheritance; but shortly after he took all the duchy of Saxe-Weimar into his own hands. The next year (1603), the young prince of Saxe-Weimar demanded his own inheritance, but his uncle Johann opposed this. But finally, both parts made a divisionary treaty of the family lands: Johann Philipp and his brothers took Altenburg and some towns, and Johann retained Weimar and Jena. Because they were still underage, the regency of his duchy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernestine Duchies
The Ernestine duchies (), also known as the Saxon duchies (, although the Albertine appanage duchies of Weissenfels, Merseburg and Zeitz were also "Saxon duchies" and adjacent to several Ernestine ones), were a group of small states whose number varied and which were largely located in the present-day German state of Thuringia and governed by dukes of the Ernestine line of the House of Wettin. Overview The Saxon duchy began fragmenting in the 15th century, as a result of the old German succession law that divided inheritances among all sons. In addition, every son of a Saxon duke inherited the title of duke. Brothers sometimes ruled the territory inherited from their father jointly, but sometimes they split it up. Some of the Ernestine duchies retained their separate existence until 1918. Similar events in the houses of Reuss and Schwarzburg led to all of Thuringia becoming a tangle of small states from the late 15th century until the early 20th century. Before the Ernestine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
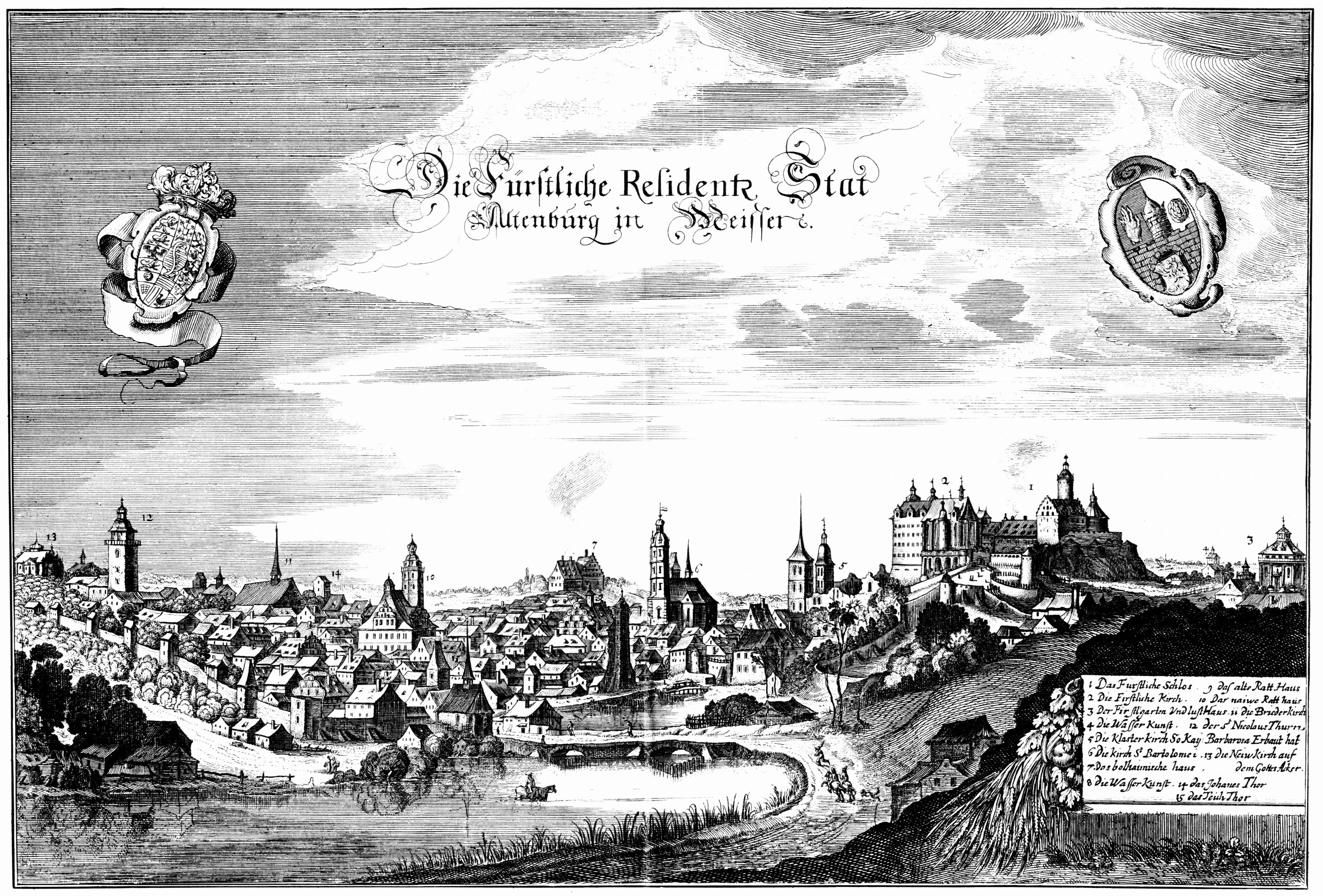
Altenburg
Altenburg () is a city in Thuringia, Germany, located south of Leipzig, west of Dresden and east of Erfurt. It is the capital of the Altenburger Land district and part of a polycentric old-industrial textile and metal production region between Gera, Zwickau and Chemnitz with more than 1 million inhabitants, while the city itself has a population of 33,000. Today, the city and its rural county is part of the Central German Metropolitan Region. Altenburg was first mentioned in 976 and later became one of the first German cities within former Slavic area, east of the Saale river (as part of the medieval Ostsiedlung movement). The emperor Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick Barbarossa visited Altenburg several times between 1165 and 1188, hence the town is named a Barbarossa city, Barbarossa town today. Since the 17th century, Altenburg was the residence of different House of Wettin, Ernestine duchies, of whom the Duchy of Saxe-Altenburg, Saxe-Altenburg persisted until th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Gotha
Saxe-Gotha (german: Sachsen-Gotha) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in the former Landgraviate of Thuringia. The ducal residence was erected at Gotha. History The duchy was established in 1640, when Duke Wilhelm von Saxe-Weimar created a subdivision for his younger brother Ernest I the Pious. Duke Ernest took his residence at Gotha, where he had ''Schloss Friedenstein'' built between 1643 and 1654. At the same time, the Duchy of Saxe-Eisenach was created for the third brother Albert IV. Nevertheless, Albert died in 1644, and Ernest inherited large parts of his duchy, though not the core territory around the residence at Eisenach and the Wartburg, which fell to his elder brother Wilhelm of Saxe-Weimar. Ernest could also incorporate several remaining estates of the extinct House of Henneberg in 1660, which had been vacant since 1583. Finally in 1672 he received the major part of Saxe-Altenburg through his wife Elisabeth Sophie, af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Weimar
Saxe-Weimar (german: Sachsen-Weimar) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in present-day Thuringia. The chief town and capital was Weimar. The Weimar branch was the most genealogically senior extant branch of the House of Wettin. History Division of Leipzig In the late 15th century much of what is now Thuringia, including the area around Weimar, was held by the Wettin Electors of Saxony. According to the 1485 Treaty of Leipzig, the Wettin lands had been divided between Elector Ernest of Saxony and his younger brother Albert III, with the western lands in Thuringia together with the electoral dignity going to the Ernestine branch of the family. Ernest's grandson Elector John Frederick I of Saxony forfeited the electoral dignity in the 1547 Capitulation of Wittenberg, after he had joined the revolt of the Lutheran Schmalkaldic League against the Habsburg emperor Charles V, was defeated, captured and banned. Nevertheless, according ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Coburg-Gotha
Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (german: Sachsen-Coburg und Gotha), or Saxe-Coburg-Gotha (german: Sachsen-Coburg-Gotha, links=no ), was an Ernestine, Thuringian duchy ruled by a branch of the House of Wettin, consisting of territories in the present-day states of Thuringia and Bavaria in Germany. It lasted from 1826 to 1918. In November 1918, Charles Edward, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, was forced to abdicate. In 1920, the northern part of the duchy (since 1918 the Free State of Gotha; culturally and linguistically Thuringian) was merged with six other Thuringian free states to form the Free State of Thuringia: Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (until 1918 a grand duchy), Saxe-Altenburg and Saxe-Meiningen (until 1918 duchies), Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt and Schwarzburg-Sondershausen (until 1918 principalities), as well as the People's State of Reuss (until 1918 the principalities of Reuss-Gera and Reuss-Greiz). The southern part of the duchy (since 1918 the Free State of Coburg; culturally and ling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Wettin
The House of Wettin () is a dynasty of German kings, prince-electors, dukes, and counts that once ruled territories in the present-day German states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. The dynasty is one of the oldest in Europe, and its origins can be traced back to the town of Wettin, Saxony-Anhalt. The Wettins gradually rose to power within the Holy Roman Empire. Members of the family became the rulers of several medieval states, starting with the Saxon Eastern March in 1030. Other states they gained were Meissen in 1089, Thuringia in 1263, and Saxony in 1423. These areas cover large parts of Central Germany as a cultural area of Germany. The family divided into two ruling branches in 1485 by the Treaty of Leipzig: the Ernestine and Albertine branches. The older Ernestine branch played a key role during the Protestant Reformation. Many ruling monarchs outside Germany were later tied to its cadet branch, the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. The Albertine branch, while less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States Of The Weimar Republic
The States of the Weimar Republic were the first-level administrative divisions and constituent states of the German Reich during the Weimar Republic era. The states were established in 1918 following the German Revolution upon the conclusion of World War I, and based on the 22 constituent states of the German Empire that abolished their local monarchies. The new states continued as republics alongside the three pre-existing city-states within the new Weimar Republic, adopting the titles ''Freistaat'' ("Free State") or ''Volksstaat'' ("People's State"). Weimar Republic states Germany suffered significant territorial losses from the Treaty of Versailles following World War I, and some states had their borders altered by international border changes. In 1920, the state of Thuringia was formed from the former Ernestine duchies that continued briefly as republics before merging, except for Saxe-Coburg, which became part of Bavaria. Additionally, the Saar Basin and the city of Danzig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Confederation
The German Confederation (german: Deutscher Bund, ) was an association of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states in Central Europe. It was created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as a replacement of the former Holy Roman Empire, which had been dissolved in 1806. The Confederation had only one organ, the Federal Convention (also Federal Assembly or Confederate Diet). The Convention consisted of the representatives of the member states. The most important issues had to be decided on unanimously. The Convention was presided over by the representative of Austria. This was a formality, however, the Confederation did not have a head of state, since it was not a state. The Confederation, on the one hand, was a strong alliance between its member states because federal law was superior to state law (the decisions of the Federal Convention were binding for the member states). Additionally, the Confederation had been established for eternity and was impossible to dissolve (l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States Of The German Empire
The German Empire consisted of 25 constituent states and an Imperial Territory, the largest of which was Prussia. These states, or ''Staaten'' (or ''Bundesstaaten'', i.e. federal states, a name derived from the previous North German Confederation; they became known as ''Länder'' during the Weimar Republic) each had votes in the Bundesrat, which gave them representation at a federal level. Several of these states had gained sovereignty following the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire. Others were created as sovereign states after the Congress of Vienna in 1815. Territories were not necessarily contiguous, such as Bavaria, or Oldenburg—many existed in several parts (enclaves and exclaves), as a result of historical acquisitions, or, in several cases, divisions of the ruling family trees. Kingdoms *Kingdom of Bavaria *Kingdom of Prussia (itself subdivided into provinces; including the Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg ruled in personal union until annexed 1 July 1876) *Kingdom of Saxo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |