|
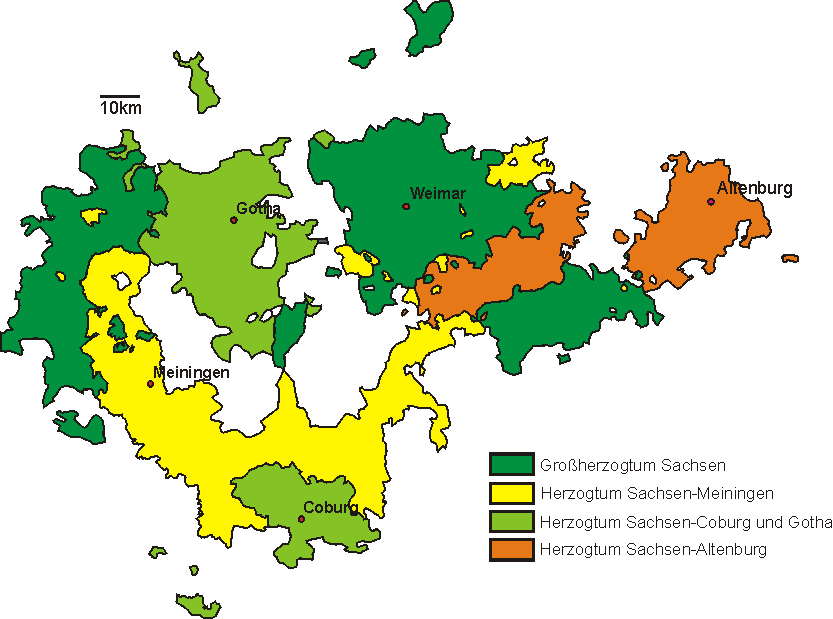
Saxe-Gotha
Saxe-Gotha (german: Sachsen-Gotha) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in the former Landgraviate of Thuringia. The ducal residence was erected at Gotha. History The duchy was established in 1640, when Duke Wilhelm von Saxe-Weimar created a subdivision for his younger brother Ernest I the Pious. Duke Ernest took his residence at Gotha, where he had ''Schloss Friedenstein'' built between 1643 and 1654. At the same time, the Duchy of Saxe-Eisenach was created for the third brother Albert IV. Nevertheless, Albert died in 1644, and Ernest inherited large parts of his duchy, though not the core territory around the residence at Eisenach and the Wartburg, which fell to his elder brother Wilhelm of Saxe-Weimar. Ernest could also incorporate several remaining estates of the extinct House of Henneberg in 1660, which had been vacant since 1583. Finally in 1672 he received the major part of Saxe-Altenburg through his wife Elisabeth Sophie, af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg
Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg () was a duchy ruled by the Ernestine branch of the House of Wettin in today's Thuringia, Germany. The extinction of the line in 1825 led to a major re-organisation of the Thuringian states. History In 1640 the sons of the late Ernestine duke John II of Saxe-Weimar divided their paternal heritage (''Ernestinische Teilung'') whereby Duke Ernest the Pious, a younger son, received the newly established Duchy of Saxe-Gotha. In 1636 Ernest had married Elisabeth Sophie, the only child of Duke John Philip of Saxe-Altenburg. Upon her father's death in 1639, the Duchy of Saxe-Altenburg passed to her uncle Duke Frederick William II and her cousin Frederick William III. The Duchy of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg was nominally created in 1672, when Duke Frederick William III of Saxe-Altenburg died at the age of 14 and Ernest the Pious, by his marriage with Elisabeth Sophie, inherited the major part of his possessions. It was common for the Ernestine duchies to merge and spli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest I, Duke Of Saxe-Gotha
Ernest I, called "Ernest the Pious" (25 December 1601 – 26 March 1675), was a duke of Saxe-Gotha and Saxe-Altenburg. The duchies were later merged into Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg. He was the ninth but sixth surviving son of Johann II, Duke of Saxe-Weimar, and Dorothea Maria of Anhalt. His mother was a granddaughter of Christoph, Duke of Württemberg, and great-granddaughter of Ulrich, Duke of Württemberg. Life Left an orphan early in life (his father died in 1605 and his mother in 1617), he was brought up in a strict manner, and was gifted and precocious but not physically strong. He soon showed traits of the piety of the time. As ruler, by his character and governmental ability as well as by personal attention to matters of state, he introduced a golden age for his subjects after the ravages of the Thirty Years' War. By wise economy, which did not exclude fitting generosity or display on proper occasions, he freed his land from debt, left at his death a considerable sum in the tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schloss Friedenstein
Friedenstein Palace (german: Schloss Friedenstein) is an early Baroque palace built in the mid-17th century by Ernest I, Duke of Saxe-Gotha at Gotha, Thuringia, Germany. In Germany, ''Friedenstein'' was one of the largest palaces of its time and one of the first Baroque palaces ever built. ''Friedenstein'' served as the main seat of the Dukes of Saxe-Gotha and later as one of the residences of the Dukes of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, closely linked with the Royal Family of Great Britain through the marriage of Queen Victoria and Prince Albert. The final two ruling Dukes were both princes of the United Kingdom. The palace complex today houses several museums. It is also notable for hosting the , one of the oldest theatres in operation in Germany, still featuring the original Baroque machinery for changing the scenery. History Earlier structures The site where ''Friedenstein'' stands today, dominating the town of Gotha and its surroundings, was previously occupied by ''Grimmenstein Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princess Elisabeth Sophie Of Saxe-Altenburg
Elisabeth Sophie of Saxe-Altenburg (10 October 1619 – 20 December 1680), was a princess of Saxe-Altenburg and, by marriage, duchess of Saxe-Gotha. She was born in Halle, the only daughter of Johann Philipp, Duke of Saxe-Altenburg, and his wife, Elisabeth of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel. Life In Altenburg on 24 October 1636, Elisabeth Sophie married her kinsman Ernst I, Duke of Saxe-Gotha. As a dowry, she received 20,000 guilders, who were pledged by the town of Roßla. As Widow's seat, the bride obtained the towns of Kapellendorf and Berka, with the called ''Gartenhaus'' in Weimar. Because according to the succession laws of the House of Saxe-Altenburg (which excluded the women from inheritance), after her father died two years later (1 April 1639), he was succeeded by his brother, Frederick Wilhelm II. When her cousin, the duke Frederick Wilhelm III died childless in 1672, Elisabeth Sophie became in the general heiress of all the branch of Saxe-Altenburg on the basis of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Coburg
Saxe-Coburg (german: Sachsen-Coburg) was a duchy held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in today's Bavaria, Germany. History Ernestine Line When Henry IV, Count of Henneberg – Schleusingen, died in 1347, the possessions of the House of Henneberg – Schleusingen were divided between his widow, Jutta of Brandenburg-Salzwedel, and Henry's younger brother, John, and Jutta was given the so-called “''neues Herrschaft''” ("new lordship"), with Coburg among other properties. The death of Jutta six years later was followed by the division of the new ''Herrschaft'' amongst three of her daughters. The second daughter, Catherine of Henneberg, was awarded the southeastern part of the Coburgish land. After their wedding in 1346, Catherine's husband, Frederick III, the Margrave of Meissen from the House of Wettin, asked for his wife's dowry, the Coburgish land called the ''Pflege Coburg''; but his father-in-law resisted the devolution, and Frederick III could not touch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Meiningen
Saxe-Meiningen (; german: Sachsen-Meiningen ) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine line of the Wettin dynasty, located in the southwest of the present-day German state of Thuringia. Established in 1681, by partition of the Ernestine duchy of Saxe-Gotha among the seven sons of deceased Duke Ernst der Fromme (Ernest the Pious), the Saxe-Meiningen line of the House of Wettin lasted until the end of the German monarchies in 1918. History House of Wettin The Wettiner had been the rulers of sizeable holdings in today's states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia since the Middle Ages. In the '' Leipziger Teilung'' of 1485, the Wettiner were split into two branches named after their founding princes Albrecht and Ernst (''albertinisch'' and ''ernestinisch''). Thuringia was part of the Ernestine holdings of ''Kursachsen'' (the Electoral holdings of Saxony). In 1572, the branches Saxe-Coburg-Eisenach and Saxe-Weimar were established there. The senior line again split ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernestine Duchies
The Ernestine duchies (), also known as the Saxon duchies (, although the Albertine appanage duchies of Weissenfels, Merseburg and Zeitz were also "Saxon duchies" and adjacent to several Ernestine ones), were a group of small states whose number varied and which were largely located in the present-day German state of Thuringia and governed by dukes of the Ernestine line of the House of Wettin. Overview The Saxon duchy began fragmenting in the 15th century, as a result of the old German succession law that divided inheritances among all sons. In addition, every son of a Saxon duke inherited the title of duke. Brothers sometimes ruled the territory inherited from their father jointly, but sometimes they split it up. Some of the Ernestine duchies retained their separate existence until 1918. Similar events in the houses of Reuss and Schwarzburg led to all of Thuringia becoming a tangle of small states from the late 15th century until the early 20th century. Before the Ernestine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Römhild
Saxe-Römhild (German: ''Sachsen-Römhild'') was an Ernestine duchy in the southern foothills of the Thuringian Forest. It existed for only 30 years, from 1680 to 1710. History After the Duke of Saxe-Gotha, Ernest the Pious, died on 26 March 1675 in Gotha, the Principality was divided on 24 February 1680 among his seven surviving sons. The lands of Saxe-Römhild went to the fourth son, who became Henry, Duke of Saxe-Römhild (1650–1710). The new Principality included the Districts of Römhild, Königsberg (which was later lost in 1683 to Saxe-Hildburghausen) and Themar, the winery of Behrungen, the monastery estate of Milz, and certain lands of the Echter family of Mespelbrunn that had been lost in 1665 to Saxony. But Duke Henry never had the full sovereignty of his new domains. The actual administration was left to the higher authorities in Gotha – the so-called ''Nexus Gothanus'' – because that was the residence of Henry's oldest brother, who ruled as Frederick I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Altenburg
Saxe-Altenburg (german: Sachsen-Altenburg, links=no) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the House of Wettin in present-day Thuringia. It was one of the smallest of the German states with an area of 1323 square kilometers and a population of 207,000 (1905) of whom about one fifth resided in the capital, Altenburg. The territory of the duchy consisted of two non-contiguous territories separated by land belonging to the Principality of Reuss. Its economy was based on agriculture, forestry, and small industry. The state had a constitutional monarchical form of government with a parliament composed of thirty members chosen by male taxpayers over 25 years of age. History The duchy had its origins in the medieval Burgraviate of Altenburg in the Imperial Pleissnerland ''(Terra Plisensis)'', a possession of the Wettin Margraves of Meissen since 1243. Upon a partition treaty of 1485, Altenburg fell to Ernst, Elector of Saxony, the progenitor of the Ernestine We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Eisenach
Saxe-Eisenach (german: Sachsen-Eisenach) was an Ernestine duchy ruled by the Saxon House of Wettin. The state intermittently existed at three different times in the Thuringian region of the Holy Roman Empire. The chief town and capital of all three duchies was Eisenach. History In the 15th century, much of what is now the German state of Thuringia, including the area around Eisenach, was in the hands of the Wettin dynasty, since 1423 Prince-electors of Saxony. In 1485, the Wettin lands were divided according to the Treaty of Leipzig, with most of the Thuringian lands going to Elector Ernest of Saxony and his descendants. The Ernestine Wettins also retained the title of Elector. However, when Ernest's grandson John Frederick the Magnanimous revolted against Emperor Charles V during the Schmalkaldic War, he was defeated at the 1547 Battle of Mühlberg and deprived of the electorate in favour of his Wettin cousin Maurice. According to the Capitulation of Wittenberg he was only all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gotha (town)
Gotha () is the fifth-largest city in Thuringia, Germany, west of Erfurt and east of Eisenach with a population of 44,000. The city is the capital of the district of Gotha and was also a residence of the Ernestine Wettins from 1640 until the end of monarchy in Germany in 1918. The House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha originating here spawned many European rulers, including the royal houses of the United Kingdom, Belgium, Portugal (until 1910) and Bulgaria (until 1946). In the Middle Ages, Gotha was a rich trading town on the trade route ''Via Regia'' and between 1650 and 1850, Gotha saw a cultural heyday as a centre of sciences and arts, fostered by the dukes of Saxe-Gotha. The first duke, Ernest the Pious, was famous for his wise rule. In the 18th century, the ''Almanach de Gotha'' was first published in the city. The publisher Justus Perthes and the encyclopedist Joseph Meyer made Gotha a leading centre of German publishing around 1800. In the early 19th century, Gotha was a bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Wettin
The House of Wettin () is a dynasty of German kings, prince-electors, dukes, and counts that once ruled territories in the present-day German states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. The dynasty is one of the oldest in Europe, and its origins can be traced back to the town of Wettin, Saxony-Anhalt. The Wettins gradually rose to power within the Holy Roman Empire. Members of the family became the rulers of several medieval states, starting with the Saxon Eastern March in 1030. Other states they gained were Meissen in 1089, Thuringia in 1263, and Saxony in 1423. These areas cover large parts of Central Germany as a cultural area of Germany. The family divided into two ruling branches in 1485 by the Treaty of Leipzig: the Ernestine and Albertine branches. The older Ernestine branch played a key role during the Protestant Reformation. Many ruling monarchs outside Germany were later tied to its cadet branch, the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. The Albertine branch, while less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |