Ernestine Duchies on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Ernestine duchies (), also known as the Saxon duchies (, although the Albertine
The Ernestine duchies (), also known as the Saxon duchies (, although the Albertine
File:Ernst Kurfürst von Sachsen, 1441-1486 (AT KHM GG4795).jpg,
 The Ernestine territories in Thuringia were thus divided and recombined many times as Dukes left more than one son to inherit, and as various lines of the Ducal Ernestines died out in male line. Eventually,
The Ernestine territories in Thuringia were thus divided and recombined many times as Dukes left more than one son to inherit, and as various lines of the Ducal Ernestines died out in male line. Eventually, 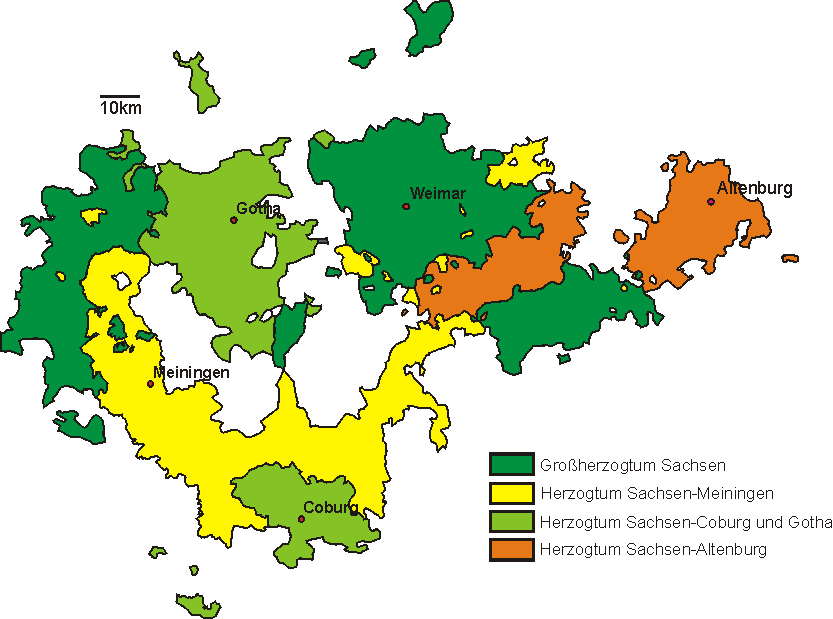 *
*
Ernestine Saxony, 1485(1547
(accessed December 13, 2005)
Wettin Dynasty
(2005). ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Retrieved December 12, 2005, from ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' Premium Service.
(retrieved December 13, 2005)
Chart showing succession of Ernestine duchies
(originally retrieved December 13, 2005, found using Wayback machine November 27, 2006)
appanage
An appanage, or apanage (; french: apanage ), is the grant of an estate, title, office or other thing of value to a younger child of a sovereign, who would otherwise have no inheritance under the system of primogeniture. It was common in much o ...
duchies of Weissenfels, Merseburg
Merseburg () is a town in central Germany in southern Saxony-Anhalt, situated on the river Saale, and approximately 14 km south of Halle (Saale) and 30 km west of Leipzig. It is the capital of the Saalekreis district. It had a diocese ...
and Zeitz
Zeitz ( hsb, Žič) is a town in the Burgenlandkreis district, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is situated on the river White Elster, in the triangle of the federal states Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia and Saxony.
History
Zeitz was first recorded u ...
were also "Saxon duchies" and adjacent to several Ernestine ones), were a group of small states whose number varied and which were largely located in the present-day German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
state of Thuringia
Thuringia (; german: Thüringen ), officially the Free State of Thuringia ( ), is a state of central Germany, covering , the sixth smallest of the sixteen German states. It has a population of about 2.1 million.
Erfurt is the capital and larg ...
and governed by dukes of the Ernestine line of the House of Wettin
The House of Wettin () is a dynasty of German kings, prince-electors, dukes, and counts that once ruled territories in the present-day German states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. The dynasty is one of the oldest in Europe, and its ori ...
.
Overview
The Saxon duchy began fragmenting in the 15th century, as a result of the old German succession law that divided inheritances among all sons. In addition, every son of a Saxon duke inherited the title ofduke
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are ran ...
. Brothers sometimes ruled the territory inherited from their father jointly, but sometimes they split it up. Some of the Ernestine duchies retained their separate existence until 1918. Similar events in the houses of Reuss Reuss may refer to:
*Reuss (surname)
*Reuss (river) in Switzerland
*Reuss (state) or Reuß, several former states or countries in present-day Germany, and the Republic of Reuss
*Reuss Elder Line and Reuss Younger Line (House of Reuss), members incl ...
and Schwarzburg Schwarzburg may refer to:
* Schwarzburg (municipality)
* The House of Schwarzburg
* Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt
* Schwarzburg-Sondershausen
* House of Schwarzburg
* 13th-century fortress built by the Teutonic Order in Transylvania, present day Codlea
...
led to all of Thuringia becoming a tangle of small states from the late 15th century until the early 20th century.
Before the Ernestine branch
Count Bernhard ofAnhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.18 million inhabitants, making it the ...
, youngest son of Albert "the Bear" (1106–1170), inherited parts of the old Saxon duchy, primarily around Lauenburg
Lauenburg (), or Lauenburg an der Elbe ( en, Lauenberg on the Elbe), is a town in the state of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is situated on the northern bank of the river Elbe, east of Hamburg. It is the southernmost town of Schleswig-Holstein ...
and Wittenberg
Wittenberg ( , ; Low Saxon language, Low Saxon: ''Wittenbarg''; meaning ''White Mountain''; officially Lutherstadt Wittenberg (''Luther City Wittenberg'')), is the fourth largest town in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Wittenberg is situated on the Ri ...
, in 1180. He had two sons, Albert and Henry. Albert inherited the Duchy of Saxony
The Duchy of Saxony ( nds, Hartogdom Sassen, german: Herzogtum Sachsen) was originally the area settled by the Saxons in the late Early Middle Ages, when they were subdued by Charlemagne during the Saxon Wars from 772 and incorporated into the C ...
. In 1260 Albert bequeathed the duchy to his sons John I John I may refer to:
People
* John I (bishop of Jerusalem)
* John Chrysostom (349 – c. 407), Patriarch of Constantinople
* John of Antioch (died 441)
* Pope John I, Pope from 523 to 526
* John I (exarch) (died 615), Exarch of Ravenna
* John I o ...
and Albert II, who gradually divided Saxony into the duchies of Saxe-Lauenburg
The Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg (german: Herzogtum Sachsen-Lauenburg, called ''Niedersachsen'' (Lower Saxony) between the 14th and 17th centuries), was a '' reichsfrei'' duchy that existed from 1296–1803 and again from 1814–1876 in the extreme so ...
and Saxe-Wittenberg
The Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg () was a medieval duchy of the Holy Roman Empire centered at Wittenberg, which emerged after the dissolution of the stem duchy of Saxony. The Ascanian dukes prevailed in obtaining the Saxon electoral dignity until th ...
with definite effect of 1296. Saxe-Wittenberg was recognized as the electorate
Electorate may refer to:
* The people who are eligible to vote in an election, especially their number e.g. the term ''size of (the) electorate''
* The dominion of a Prince-elector
The prince-electors (german: Kurfürst pl. , cz, Kurfiřt, ...
of Saxony in the Golden Bull of 1356
The Golden Bull of 1356 (, , , , ) was a decree issued by the Imperial Diet at Nuremberg and Metz ( Diet of Metz, 1356/57) headed by the Emperor Charles IV which fixed, for a period of more than four hundred years, important aspects of the con ...
. When the last duke of Saxe-Wittenberg died without heir in 1422, the Emperor Sigismund Sigismund (variants: Sigmund, Siegmund) is a German proper name, meaning "protection through victory", from Old High German ''sigu'' "victory" + ''munt'' "hand, protection". Tacitus latinises it '' Segimundus''. There appears to be an older form of ...
gave the duchy to Frederick IV of the house of Wettin
The House of Wettin () is a dynasty of German kings, prince-electors, dukes, and counts that once ruled territories in the present-day German states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. The dynasty is one of the oldest in Europe, and its ori ...
, Margrave
Margrave was originally the medieval title for the military commander assigned to maintain the defence of one of the border provinces of the Holy Roman Empire or of a kingdom. That position became hereditary in certain feudal families in the Emp ...
of Meissen
Meissen (in German orthography: ''Meißen'', ) is a town of approximately 30,000 about northwest of Dresden on both banks of the Elbe river in the Free State of Saxony, in eastern Germany. Meissen is the home of Meissen porcelain, the Albrecht ...
and Landgrave
Landgrave (german: Landgraf, nl, landgraaf, sv, lantgreve, french: landgrave; la, comes magnus, ', ', ', ', ') was a noble title used in the Holy Roman Empire, and later on in its former territories. The German titles of ', ' ("margrave"), a ...
of Thuringia, who thereby became Frederick I, Elector of Saxony
Frederick I, the Belligerent or the Warlike (german: Friedrich der Streitbare; 11 April 1370 – 4 January 1428), a member of the House of Wettin, ruled as Margrave of Meissen from 1407 and Elector of Saxony (as Frederick I) from 1423 until ...
. The name Saxony was then generally applied to all of the Wettin's domains, including those in Thuringia, because Saxony was a ducal title, the highest they possessed, and all house members used it, although many of them held lands only in Thuringia. Frederick I was succeeded by his son, Frederick II.
After the death of Frederick II in 1464, his oldest son, Ernest
Ernest is a given name derived from Germanic languages, Germanic word ''ernst'', meaning "serious". Notable people and fictional characters with the name include:
People
*Archduke Ernest of Austria (1553–1595), son of Maximilian II, Holy Roman ...
, became elector, and Ernest and Duke Albert
Albert may refer to:
Companies
* Albert (supermarket), a supermarket chain in the Czech Republic
* Albert Heijn, a supermarket chain in the Netherlands
* Albert Market, a street market in The Gambia
* Albert Productions, a record label
* Alber ...
, the younger son, shared governance of the Wettin lands. In 1485, by the Leipziger division, the brothers split the Wettin possessions, with Ernest receiving northern Meissen, southern Thuringia, and Wittenberg, and Albert receiving northern Thuringia and southern Meissen.
A study of the list of members of the House of Wettin
This is a list of members of the recent House of Wettin. It includes only those who were members of the male-line descent from Ernest, Elector of Saxony, and consequently bore his "surname", ''Wettin''.
Ernestine line
Ernest, Elector of Saxony ...
will reveal many of the different strands of the ducal house and their possessions.
Ernest, Elector of Saxony
Ernest (24 March 144126 August 1486) was Elector of Saxony from 1464 to 1486.
Ernst was the founder and progenitor of the ''Ernestine line'' of Saxon princes.
Biography
Ernst was born in Meissen, the second son (but fourth in order of birth) ...
(1441–1486)
File:Herzog-Albrecht-der-Beherzt.jpg, Albert, Duke of Saxony (1443–1500)
Detailed history of divisions in the Ernestine line
Table
History
Elector Ernest died in 1486, and was succeeded by his son,Frederick the Wise
Frederick III (17 January 1463 – 5 May 1525), also known as Frederick the Wise ( German ''Friedrich der Weise''), was Elector of Saxony from 1486 to 1525, who is mostly remembered for the worldly protection of his subject Martin Luther.
Frede ...
. Leipzig, the economic center of Saxony, as well as the seat of the only university in Saxony, was located in Albertine Saxony. Wanting a university in his lands, for example, to educate civil servants and pastors, Frederick founded the University of Wittenberg in 1502. It was there that Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Order of Saint Augustine, Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Reformation, Protestant Refo ...
posted his 95 Theses. Frederick protected Luther, refusing to extradite him to Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
for trial. Frederick, like other German princes, allowed Lutheran reforms to be implemented in his domain.
Frederick III died in 1525; he was succeeded by his brother, John the Steadfast
Johann (30 June 146816 August 1532), known as Johann the Steadfast or Johann the Constant (''Johann, der Beständige''), was Elector of Saxony from 1525 until 1532 from the House of Wettin.
He is notable for organising the Lutheran Church in the ...
(1525–1532). John was a leader in the Schmalkaldic League
The Schmalkaldic League (; ; or ) was a military alliance of Lutheran princes within the Holy Roman Empire during the mid-16th century.
Although created for religious motives soon after the start of the Reformation, its members later came to ...
of Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
princes in the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
. John died in 1532 and was succeeded by his son John Frederick I
John Frederick I (30 June 1503 in Torgau – 3 March 1554 in Weimar), called the Magnanimous, was the Elector of Saxony (1532–1547) and head of the Schmalkaldic League.
Early years
John Frederick was the eldest son of Elector John by his firs ...
. For the first ten years of his reign, John Frederick shared the rule of Ernestine Saxony with his stepbrother, John Ernest
John Ernest (May 6, 1922 – July 21, 1994) was an American-born constructivist abstract artist. He was born in Philadelphia, in 1922. After living and working in Sweden and Paris from 1946 to 1951, he moved to London, England, where he lived and w ...
, titularly Duke of Saxe-Coburg
Saxe-Coburg (german: Sachsen-Coburg) was a duchy held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in today's Bavaria, Germany.
History
Ernestine Line
When Henry IV, Count of Henneberg – Schleusingen, died in 1347, the possessions of the ...
, who died childless. John Frederick increasingly hardened his support of the Lutheran Reformation, while the Emperor, Charles V Charles V may refer to:
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
* Charles V, Duke of Lorraine (1643–1690)
* Infan ...
, avoided direct confrontation with the Protestant princes, as he needed their support in his struggle with France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
.
Charles eventually came to terms with France, and turned his attention to the Protestant lands of the Holy Roman Empire. In 1546 the Schmalkaldic League raised an army. Elector John Frederick led the league's troops south, but shortly thereafter John Frederick's cousin, Duke Maurice of Albertine Saxony (Meissen), invaded Ernestine Saxony. John Frederick hurried back to Saxony, expelled Maurice from the Ernestine lands, conquered Albertine Saxony and proceeded to invade Bohemia (held directly by Emperor Charles V's brother Ferdinand and that latter's wife Anna of Bohemia and Hungary
Anna of Bohemia and Hungary (23 July 1503 – 27 January 1547), sometimes known as Anna Jagellonica, was Queen of Germany, Bohemia, and Hungary and Archduchess of Austria as the wife of King Ferdinand I (later Holy Roman Emperor).
Ea ...
). Charles' forces drove the Schmalkaldic League troops back and decisively defeated them in the Battle of Mühlberg
The Battle of Mühlberg took place near Mühlberg in the Electorate of Saxony in 1547, during the Schmalkaldic War. The Catholic princes of the Holy Roman Empire led by the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V decisively defeated the Lutheran Schmalka ...
(1547). John Frederick was wounded and taken prisoner. The Emperor condemned him to death as a rebel, but stayed the execution because he did not want to take the time to capture Wittenberg, defended by John Frederick's wife Sybille of Cleves. To save his life, John Frederick conceded in the Capitulation of Wittenberg
{{Campaignbox Schmalkaldic War
The Capitulation of Wittenberg (german: Wittenberger Kapitulation) was a treaty on 19 May 1547 by which John Frederick I, Elector of Saxony, was compelled to resign the title of elector. The Electorate of Saxony ...
to resign the Electorate and the government of his country in favor of Maurice of the Albertine Saxony, and his punishment was changed into imprisonment for life. When the newly minted Elector Maurice, having again changed sides, attacked the Emperor, Duke John Frederick was released from prison, and given back the Landgraviate of Thuringia. He established his capital in Weimar
Weimar is a city in the state of Thuringia, Germany. It is located in Central Germany between Erfurt in the west and Jena in the east, approximately southwest of Leipzig, north of Nuremberg and west of Dresden. Together with the neighbouri ...
, and started a university at Jena
Jena () is a German city and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, while the city itself has a popu ...
(to replace the one in Wittenberg lost to Maurice) before his death in 1554.
The three sons of John Frederick I shared the territory, with John Frederick II becoming head (and briefly, 1554–1556, holding the electoral title) with his seats in Eisenach and Coburg, the middle brother John William staying in Weimar (Saxe-Weimar
Saxe-Weimar (german: Sachsen-Weimar) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in present-day Thuringia. The chief town and capital was Weimar. The Weimar branch was the most genealogically senior extant bra ...
), and the youngest, John Frederick III (namesake of the eldest brother, which has caused much confusion in history writing) establishing residence in Gotha (Saxe-Gotha
Saxe-Gotha (german: Sachsen-Gotha) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in the former Landgraviate of Thuringia. The ducal residence was erected at Gotha.
History
The duchy was established in 1640, when ...
). When John Frederick III of Gotha died unmarried and heirless in 1565, John William of Weimar tried to claim succession to Saxe-Gotha, but the sons of the imprisoned John Frederick II entered their own claim.
The contenders reached agreement in 1572 in the Division of Erfurt
The Ernestine duchies (), also known as the Saxon duchies (, although the Albertine appanage duchies of Weissenfels, Merseburg and Zeitz were also "Saxon duchies" and adjacent to several Ernestine ones), were a group of small states whose numb ...
by which John William added the districts of Altenburg
Altenburg () is a city in Thuringia, Germany, located south of Leipzig, west of Dresden and east of Erfurt. It is the capital of the Altenburger Land district and part of a polycentric old-industrial textile and metal production region betw ...
, Gotha
Gotha () is the fifth-largest city in Thuringia, Germany, west of Erfurt and east of Eisenach with a population of 44,000. The city is the capital of the district of Gotha and was also a residence of the Ernestine Wettins from 1640 until the ...
and Meiningen
Meiningen () is a town in the southern part of the state of Thuringia, Germany. It is located in the region of Franconia and has a population of around 25,000 (2021).
to Saxe-Weimar. When John William died a year later, his older son, Frederick William I received Altenburg, Gotha and Meiningen with the title of Duke of Saxe-Altenburg
Saxe-Altenburg (german: Sachsen-Altenburg, links=no) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the House of Wettin in present-day Thuringia. It was one of the smallest of the German states with an area of 1323 square kilomete ...
, and with his several sons founding the first Saxe-Altenburg line, while Saxe-Weimar
Saxe-Weimar (german: Sachsen-Weimar) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in present-day Thuringia. The chief town and capital was Weimar. The Weimar branch was the most genealogically senior extant bra ...
went to the younger son John II. John Casimir (died heirless 1633), the older son of John Frederick II, and John Ernest
John Ernest (May 6, 1922 – July 21, 1994) was an American-born constructivist abstract artist. He was born in Philadelphia, in 1922. After living and working in Sweden and Paris from 1946 to 1951, he moved to London, England, where he lived and w ...
(died heirless 1638), the younger son of John Frederick II, received together the territory of Saxe-Coburg-Eisenach
Saxe-Coburg-Eisenach was a duchy within the Holy Roman Empire. It existed during two fairly short periods: 1572-1596 and 1633-1638. Its territory was part of the modern states of Bavaria and Thuringia.
History
The duchy was created by the Div ...
, but were appointed a legal guardian because they were minors. In 1596 the brothers agreed to split the duchy into Saxe-Coburg
Saxe-Coburg (german: Sachsen-Coburg) was a duchy held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in today's Bavaria, Germany.
History
Ernestine Line
When Henry IV, Count of Henneberg – Schleusingen, died in 1347, the possessions of the ...
and Saxe-Eisenach
Saxe-Eisenach (german: Sachsen-Eisenach) was an Ernestine duchy ruled by the Saxon House of Wettin. The state intermittently existed at three different times in the Thuringian region of the Holy Roman Empire. The chief town and capital of all th ...
.
Johann II, Duke of Saxe-Weimar
Johann II, Duke of Saxe-Weimar (''Johann Maria Wilhelm''; 22 May 1570 – 18 July 1605) was a Duke of Saxe-Weimar and Jena.
Biography
He was the second son of Johann Wilhelm, Duke of Saxe-Weimar and Dorothea Susanne of Simmern.
His father die ...
(or John II), died young leaving eight surviving sons (including Bernhard of Saxe-Weimar
Bernard of Saxe-Weimar (german: Bernhard von Sachsen-Weimar; 16 August 160418 July 1639) was a German prince and general in the Thirty Years' War.
Biography
Born in Weimar within the Duchy of Saxe-Weimar, Bernard was the eleventh son of Joha ...
, the youngest, the famed general) and a will ordering them to rule jointly. When the eldest of them, John Ernest I, Duke of Saxe-Weimar
Johann Ernst I, Duke of Saxe-Weimar (21 February 1594 in Altenburg – 6 December 1626 in Sankt Martin, Hungary), was a duke of Saxe-Weimar.
Biography
Born as the eldest son of Johann, Duke of Saxe-Weimar and Dorothea Maria of Anhalt, during hi ...
died in action (1626) unmarried, two more of his brothers were already deceased without children, leaving five dukes of Saxe-Weimar, with Wilhelm
Wilhelm may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* William Charles John Pitcher, costume designer known professionally as "Wilhelm"
* Wilhelm (name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name or surname
Other uses
* Mount ...
the eldest. Two more died within fifteen years, including Bernhard in 1639, without heirs. In 1638, the senior Coburg-Eisenach line became extinct and its possessions were divided between the Altenburgs and the Weimars, this doubled the Saxe-Weimar possessions and made it again feasible to be divided. In c. 1640, the remaining brothers finally divided their patrimony, William remaining in Weimar, Albert (Albrecht) receiving seat as Duke of Eisenach and Ernest (by-named "the Pious") also got his share and became known as Duke of Gotha.
Ernest I, Duke of Saxe-Gotha (1601–1675) had married Elisabeth Sophie, the only child of Johann Philipp, Duke of Saxe-Altenburg
Johann Philipp (25 January 1597 – 1 April 1639), was a duke of Saxe-Altenburg.
He was born in Torgau, the eldest (but fourth in order of birth) surviving son of Friedrich Wilhelm I, Duke of Saxe-Weimar and Anna Maria of the Palatinate-Ne ...
and Gotha (1597–1638), the eldest son of Frederick William I. When Elisabeth Sophie's cousin Frederick William III, Duke of Altenburg, died unmarried 1672, the entire first Altenburg line became extinct in male line, opening a succession strife. Ultimately, Ernest and Elisabeth Sophie's sons received the lion's share of Altenburg inheritance, on basis of Duke John Philip's testament (as it was ultimately recognized that the Salic law does not prevent an agnate to will all his possessions to those other agnates of the house he desires to make his heirs, leaving other agnates without; and if those favored agnates also happened to be the testator's son-in-law and maternal grandsons, that is in no way prohibited), but a portion (one-fourth of the original Altenburg moiety) passed to the Saxe-Weimar branch. These two lines: Weimar and Gotha(-Altenburg) form the basis of future Ernestine lines, and both have surviving male lineage up to today. After the division of the inheritance of the first Altenburg line, the senior, Weimar, line held somewhat less than half of the Ernestine lands, and the junior, Gotha-Altenburg, line held more than half. Gotha-Altenburg line subdivided more and Weimar line not so much, and ultimately all the said Weimar line's possessions were concentrated in primogenitural hands in 1741 and in 1815 were raised to grand ducal title of Weimar.
Duke Ernest of Gotha and Duchess Elisabeth Sophie's numerous sons divided the inheritance (five-eighths of all Ernestine lands) initially to seven parts: Gotha-Altenburg, Coburg, Meiningen, Römhild, Eisenberg, Hildburghausen and Saalfeld. Of them, Coburg, Römhild and Eisenberg did not survive past that one generation and were apportioned between the four persevering lines.
 The Ernestine territories in Thuringia were thus divided and recombined many times as Dukes left more than one son to inherit, and as various lines of the Ducal Ernestines died out in male line. Eventually,
The Ernestine territories in Thuringia were thus divided and recombined many times as Dukes left more than one son to inherit, and as various lines of the Ducal Ernestines died out in male line. Eventually, primogeniture
Primogeniture ( ) is the right, by law or custom, of the firstborn legitimate child to inherit the parent's entire or main estate in preference to shared inheritance among all or some children, any illegitimate child or any collateral relativ ...
became the rule for inheritance in the Ernestine duchies, but not before the number of Ernestine duchies had risen to ten at one point. By 1826 the remaining Ernestine duchies were the Grand Duchy of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach
Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (german: Sachsen-Weimar-Eisenach) was a historical German state, created as a duchy in 1809 by the merger of the Ernestine duchies of Saxe-Weimar and Saxe-Eisenach, which had been in personal union since 1741. It was rais ...
(approximately three-eighths of all the Ernestine lands), and the ("Elisabeth-Sophie-line") duchies of Saxe-Gotha
Saxe-Gotha (german: Sachsen-Gotha) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in the former Landgraviate of Thuringia. The ducal residence was erected at Gotha.
History
The duchy was established in 1640, when ...
-Altenburg, Saxe-Meiningen
Saxe-Meiningen (; german: Sachsen-Meiningen ) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine line of the Wettin dynasty, located in the southwest of the present-day German state of Thuringia.
Established in 1681, by partition of the Ernestin ...
, Saxe-Hildburghausen
Saxe-Hildburghausen () was an Ernestine duchy in the southern side of the present State of Thuringia in Germany. It existed from 1680 to 1826 but its name and borders are currently used by the District of Hildburghausen.
History
After the Duk ...
and Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld
Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld () was one of the Saxon Duchies held by the Ernestine line of the Wettin Dynasty. Established in 1699, the Saxe-Coburg-Saalfield line lasted until the reshuffle of the Ernestine territories that occurred following the extinct ...
. In 1826, Ernest the Pious' senior line of Gotha-Altenburg became extinct. The daughter of its penultimate duke had been married with the Duke of Coburg
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are ranke ...
and Saalfeld, and the couple had two sons – the younger of whom was to become Albert, Prince Consort
Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (Franz August Karl Albert Emanuel; 26 August 1819 – 14 December 1861) was the consort of Queen Victoria from their marriage on 10 February 1840 until his death in 1861.
Albert was born in the Saxon duch ...
of the United Kingdom. The patrimony of Gotha-Altenburg was divided between the other three lines stemming from Ernest the Pious and Elisabeth Sophie, causing changes in nomenclature: onwards, they were Saxe-Meiningen
Saxe-Meiningen (; german: Sachsen-Meiningen ) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine line of the Wettin dynasty, located in the southwest of the present-day German state of Thuringia.
Established in 1681, by partition of the Ernestin ...
-Hildburghausen, Saxe-Altenburg
Saxe-Altenburg (german: Sachsen-Altenburg, links=no) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the House of Wettin in present-day Thuringia. It was one of the smallest of the German states with an area of 1323 square kilomete ...
(the former Hildburghausen line) and Saxe-Coburg and Gotha
Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (german: Sachsen-Coburg und Gotha), or Saxe-Coburg-Gotha (german: Sachsen-Coburg-Gotha, links=no ), was an Ernestine, Thuringian duchy ruled by a branch of the House of Wettin, consisting of territories in the present-d ...
– the youngest line (originally Saalfeld line) receiving the "maternal" seat of Gotha which had been the seat of Ernest the Pious, progenitor of all these seven lines. All of the Ernestine duchies ended with the abolition of the monarchy and princely states in Germany shortly after the end of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
.
Five of the Ernestine duchies were members of the Upper Saxon Circle
The Upper Saxon Circle (german: Obersächsischer Reichskreis) was an Imperial Circle of the Holy Roman Empire, created in 1512.
The circle was dominated by the electorate of Saxony (the circle's director) and the electorate of Brandenburg. It f ...
of the Holy Roman Empire:
*Saxe-Weimar
*Saxe-Eisenach
*Saxe-Coburg
*Saxe-Gotha
*Saxe-Altenburg
Membership in the Circle gave the ruler of a state a vote in the Imperial Diet. In the 1792 session of the Imperial Diet, the Duke of Saxe-Weimar was also the Duke of Saxe-Eisenach, and had two votes (as well as three-eights of all the Ernestine lands); the Duke of Saxe-Altenburg was also the Duke of Saxe-Gotha (as senior heir of both Duke John Philip and Duke Ernest the Pious), and had two votes; and the Duke of Saxe-Coburg had one vote.
The other Ernestine duchies were never members of the Imperial Circle, and did not have the right to vote in the Imperial Diet as the five duchies that the other duchies did (for example, the principalities of Meiningen and Hildburghausen were such; that was one reason why Duke of Saxe-Hildburghausen exchanged his patrimony to that of Altenburg). However they were all autonomous and ultimately, with the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
on 6 August 1806, that issue became irrelevant.
 *
* Saxe-Altenburg
Saxe-Altenburg (german: Sachsen-Altenburg, links=no) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the House of Wettin in present-day Thuringia. It was one of the smallest of the German states with an area of 1323 square kilomete ...
(1603 to 1672; 1826 to 1918; extinct in 1991)
* Saxe-Coburg
Saxe-Coburg (german: Sachsen-Coburg) was a duchy held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in today's Bavaria, Germany.
History
Ernestine Line
When Henry IV, Count of Henneberg – Schleusingen, died in 1347, the possessions of the ...
(1596 to 1633; 1681 to 1699)
* Saxe-Coburg-Eisenach
Saxe-Coburg-Eisenach was a duchy within the Holy Roman Empire. It existed during two fairly short periods: 1572-1596 and 1633-1638. Its territory was part of the modern states of Bavaria and Thuringia.
History
The duchy was created by the Div ...
(1572 to 1596)
* Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld
Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld () was one of the Saxon Duchies held by the Ernestine line of the Wettin Dynasty. Established in 1699, the Saxe-Coburg-Saalfield line lasted until the reshuffle of the Ernestine territories that occurred following the extinct ...
(1735 to 1826)
* Saxe-Eisenberg
The Duchy of Saxe-Eisenberg was one of the Saxon Duchies held by the Ernestine line of the Wettin Dynasty.
History
Established in 1680 for Christian, fifth son of Ernest I, Duke of Saxe-Gotha, the Duchy consisted of Eisenberg and the towns ...
(1680 to 1707)
* Saxe-Coburg-Gotha
Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (german: Sachsen-Coburg und Gotha), or Saxe-Coburg-Gotha (german: Sachsen-Coburg-Gotha, links=no ), was an Ernestine, Thuringian duchy ruled by a branch of the House of Wettin, consisting of territories in the present-d ...
(1826 to 1918)
* Saxe-Eisenach
Saxe-Eisenach (german: Sachsen-Eisenach) was an Ernestine duchy ruled by the Saxon House of Wettin. The state intermittently existed at three different times in the Thuringian region of the Holy Roman Empire. The chief town and capital of all th ...
(1596 to 1638; 1640 to 1644; 1672 to 1806)
* Saxe-Gotha
Saxe-Gotha (german: Sachsen-Gotha) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in the former Landgraviate of Thuringia. The ducal residence was erected at Gotha.
History
The duchy was established in 1640, when ...
(1640 to 1680)
* Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg
Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg () was a duchy ruled by the Ernestine branch of the House of Wettin in today's Thuringia, Germany. The extinction of the line in 1825 led to a major re-organisation of the Thuringian states.
History
In 1640 the sons of the l ...
(1681 to 1826)
* Saxe-Hildburghausen
Saxe-Hildburghausen () was an Ernestine duchy in the southern side of the present State of Thuringia in Germany. It existed from 1680 to 1826 but its name and borders are currently used by the District of Hildburghausen.
History
After the Duk ...
(1680 to 1826)
* Saxe-Jena
The Duchy of Saxe-Jena was one of the Saxon Duchies held by the Ernestine line of the Wettin Dynasty. Established in 1672 for Bernhard, fourth son of Wilhelm, Duke of Saxe-Weimar, Saxe-Jena was reincorporated into Saxe-Weimar on the extinction ...
(1672 to 1690)
* Saxe-Marksuhl
The Duchy of Saxe-Marksuhl was one of the Saxon Duchies held by the Ernestine line of the Wettin Dynasty. Established in 1662 for John George I, third son of Wilhelm, Duke of Saxe-Weimar. Originally John George was supposed to share Saxe-Eisen ...
(1662 to 1672)
* Saxe-Meiningen
Saxe-Meiningen (; german: Sachsen-Meiningen ) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine line of the Wettin dynasty, located in the southwest of the present-day German state of Thuringia.
Established in 1681, by partition of the Ernestin ...
(1681 to 1918)
* Saxe-Römhild
Saxe-Römhild (German: ''Sachsen-Römhild'') was an Ernestine duchy in the southern foothills of the Thuringian Forest. It existed for only 30 years, from 1680 to 1710.
History
After the Duke of Saxe-Gotha, Ernest the Pious, died on 26 Marc ...
(1680 to 1710)
* Saxe-Saalfeld
The Duchy of Saxe-Saalfeld was one of the Saxon Duchies held by the Ernestine line of the Wettin Dynasty. Established in 1680 for Johann Ernst, seventh son of Ernest I, Duke of Saxe-Gotha. It remained under this name until 1699, when Albert, D ...
(1680 to 1735)
* Saxe-Weimar
Saxe-Weimar (german: Sachsen-Weimar) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in present-day Thuringia. The chief town and capital was Weimar. The Weimar branch was the most genealogically senior extant bra ...
(1572 to 1806)
* Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach
Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (german: Sachsen-Weimar-Eisenach) was a historical German state, created as a duchy in 1809 by the merger of the Ernestine duchies of Saxe-Weimar and Saxe-Eisenach, which had been in personal union since 1741. It was rais ...
(1806 to 1918)
Ernestine Duchies since 1918
Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach
Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (german: Sachsen-Weimar-Eisenach) was a historical German state, created as a duchy in 1809 by the merger of the Ernestine duchies of Saxe-Weimar and Saxe-Eisenach, which had been in personal union since 1741. It was rais ...
, Saxe-Coburg-Gotha
Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (german: Sachsen-Coburg und Gotha), or Saxe-Coburg-Gotha (german: Sachsen-Coburg-Gotha, links=no ), was an Ernestine, Thuringian duchy ruled by a branch of the House of Wettin, consisting of territories in the present-d ...
, Saxe-Meiningen
Saxe-Meiningen (; german: Sachsen-Meiningen ) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine line of the Wettin dynasty, located in the southwest of the present-day German state of Thuringia.
Established in 1681, by partition of the Ernestin ...
, and Saxe-Altenburg
Saxe-Altenburg (german: Sachsen-Altenburg, links=no) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the House of Wettin in present-day Thuringia. It was one of the smallest of the German states with an area of 1323 square kilomete ...
were the only remaining duchies (Weimar-Eisenach was a Grand Duchy since 1809 and officially Grand Duchy of Saxony since 1903) at the time of the German Revolution of 1918
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
. Their legal privileges and status as Dukes were abolished under the new republican regime and remain so. The four duchies became five constituent states of the Weimar Republic by splitting Gotha and Coburg. On the 1 July 1920 the Free State of Coburg was joined into the Free State of Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
. The other four states were merged on the 1 May 1920 alongside Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt
Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt was a small historic state in present-day Thuringia, Germany, with its capital at Rudolstadt.
History
Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt was established in 1599 in the course of a resettlement of Schwarzburg dynasty lands. Since th ...
and Schwarzburg-Sondershausen
Schwarzburg-Sondershausen was a small principality in Germany, in the present day state of Thuringia, with its capital at Sondershausen.
History
Schwarzburg-Sondershausen was a county until 1697. In that year, it became a principality, which ...
into the Free State of Thuringia
Thuringia (; german: Thüringen ), officially the Free State of Thuringia ( ), is a state of central Germany, covering , the sixth smallest of the sixteen German states. It has a population of about 2.1 million.
Erfurt is the capital and larg ...
.
This reorganisation has remained to the present day, although it was de facto non existent during Nazi Rule, when the Reichsgau
A (plural ) was an administrative subdivision created in a number of areas annexed by Nazi Germany between 1938 and 1945.
Overview
The term was formed from the words (realm, empire) and , the latter a deliberately medieval-sounding word wi ...
system was used instead and Gau Thuringia
The Gau Thuringia (German: ''Gau Thüringen'') formed on 6 April 1925, was an administrative division of Nazi Germany in the Free State of :Thuringia from 1933 to 1945. Before that, from 1925 to 1933, it was the regional subdivision of the Nazi ...
administered the Free State and Gau Bayreuth
Gau Bayreuth (until June 1942, ''Gau Bayerische Ostmark'' (English: Bavarian Eastern March)) was an administrative division of Nazi Germany formed by the 19 January 1933 merger of Gaue in Lower Bavaria, Upper Palatinate and Upper Franconia, Bavari ...
administered northern Bavaria. Between 1945 and 1990 Thuringia was in the Soviet Occupation zone
The Soviet Occupation Zone ( or german: Ostzone, label=none, "East Zone"; , ''Sovetskaya okkupatsionnaya zona Germanii'', "Soviet Occupation Zone of Germany") was an area of Germany in Central Europe that was occupied by the Soviet Union as a c ...
and then East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
while Bavaria was in the American Occupation zone
Germany was already de facto occupied by the Allies from the real fall of Nazi Germany in World War II on 8 May 1945 to the establishment of the East Germany on 7 October 1949. The Allies (United States, United Kingdom, Soviet Union, and Franc ...
and then West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 O ...
.
Surviving Claimants
On 13 February 1991Georg Moritz, Hereditary Prince of Saxe-Altenburg
George Moritz, Hereditary Prince of Saxe-Altenburg (''William George Moritz Ernest Albert Frederick Charles Constantine Edward Maximilian''; 13 May 1900 – 13 February 1991), was the last head of the ducal house of Saxe-Altenburg and nominal ...
died and with him the line of Ernest, Duke of Saxe-Hildburghausen
Ernest, Duke of Saxe-Hildburghausen (12 June 1655 in Gotha – 17 October 1715 in Hildburghausen) was a duke of Saxe-Hildburghausen.
He was the ninth but sixth surviving son of Ernest I, Duke of Saxe-Gotha and Elisabeth Sophie of Saxe-Altenburg ...
and Saxe-Altenburg
Saxe-Altenburg (german: Sachsen-Altenburg, links=no) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the House of Wettin in present-day Thuringia. It was one of the smallest of the German states with an area of 1323 square kilomete ...
went extinct. His claim passed to Michael, Prince of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach
Michael, Prince of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (german: Michael Prinz von Sachsen-Weimar-Eisenach; born 15 November 1946) is the current head of the Grand Ducal House of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, as well as the most senior agnate of the entire House of Wet ...
(b. 15 November 1946). This line is also likely to go extinct soon as Michael only has a daughter and the only other male is his cousin Prince Wilhelm Ernst (b. 10 August 1946), whose son died childless in 2018. These two represent the last non-morganatic
Morganatic marriage, sometimes called a left-handed marriage, is a marriage between people of unequal social rank, which in the context of royalty or other inherited title prevents the principal's position or privileges being passed to the spous ...
descendants of William, Duke of Saxe-Weimar
Wilhelm, Duke of Saxe-Weimar ( Altenburg, 11 April 1598 – Weimar, 17 May 1662), was a duke of Saxe-Weimar.
Wilhelm was the fifth (but third surviving) son of Johann, Duke of Saxe-Weimar, and Dorothea Maria of Anhalt. He was brother to Be ...
. The remaining four males in this line are the Barons of Heygendorff.
The situation is even worse for Konrad, Prince of Saxe-Meiningen (b. 14 April 1952), who is the sole non-morganatic male member of the Saxe-Meiningen
Saxe-Meiningen (; german: Sachsen-Meiningen ) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine line of the Wettin dynasty, located in the southwest of the present-day German state of Thuringia.
Established in 1681, by partition of the Ernestin ...
s and unmarried. His nephew and grandnephew are morganatic as are the Barons von Saalfeld. They are the only remaining descendants of Bernhard I, Duke of Saxe-Meiningen
Bernhard I, Duke of Saxe-Meiningen (Gotha, 10 September 1649 – Meiningen, 27 April 1706) was a duke of Saxe-Meiningen.
He was the sixth but third surviving son of Ernst I, Duke of Saxe-Coburg-Altenburg and Elisabeth Sophie of Saxe-Altenburg ...
.
In the very likely event of the extinction of these two senior branches, the sole represantation of the Ernestine Wettins will pass to the descendants of Francis, Duke of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld en, Francis Frederick Anthony
, house =
, father = Ernest Frederick, Duke of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld
, mother = Princess Sophie Antoinette of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Coburg, S ...
, who are the present Saxe-Coburg-Gothas led by Andreas, Prince of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (b. 21 March 1943), the House of Windsor
The House of Windsor is the reigning royal house of the United Kingdom and the other Commonwealth realms. In 1901, a line of the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (itself a cadet branch of the House of Wettin) succeeded the House of Hanover to t ...
, the Royal Family of Belgium
Belgium is a constitutional, hereditary, and popular monarchy. The monarch is titled king or queen of the Belgians ( nl, Koning(in) der Belgen, french: Roi / Reine des Belges}, german: König(in) der Belgier) and serves as the country's he ...
and the Royal Family of Bulgaria. Francis and his nephew Ludwig Frederick Emil von Coburg are also ancestors to morganatic lines.
Prince Andreas has two sons and a grandson. The line of succession is usually presumed to then go to the former Tsar Simeon II of Bulgaria (b. 16 June 1937), who has three sons and seven grandsons, but his marriage to a daughter of a Marquess is possibly morganatic.
When it became clear that Ernest II, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha
Ernest II (german: Ernst August Karl Johann Leopold Alexander Eduard, link=no; 21 June 181822 August 1893) was Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha from 29 January 1844 to his death in 1893. He was born in Coburg to Ernest I, Duke of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld ...
would die childless, Edward VII
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until his death in 1910.
The second child and eldest son of Queen Victoria an ...
renounced his rights to Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (but only to that duchy) to avert an undesirable personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interlink ...
. The House of Windsor
The House of Windsor is the reigning royal house of the United Kingdom and the other Commonwealth realms. In 1901, a line of the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (itself a cadet branch of the House of Wettin) succeeded the House of Hanover to t ...
(whose original male line includes only the descendants of Edward's son George V
George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until Death and state funeral of George V, his death in 1936.
Born duri ...
since 26 April 1943) and the Royal Family of Belgium
Belgium is a constitutional, hereditary, and popular monarchy. The monarch is titled king or queen of the Belgians ( nl, Koning(in) der Belgen, french: Roi / Reine des Belges}, german: König(in) der Belgier) and serves as the country's he ...
renounced their German titles in 1917 and 1920 respectively. Although whether this actually removed them from all Ernestine successions has been debated. All the surviving agnatic lines however include marriages that are (at least highly likely) morganatic.
If only all the renounciations are ignored this adds Prince Richard Prince Richard may refer to:
* Richard of Shrewsbury, Duke of York (1473–)
* Prince Richard von Metternich (1829–1895), from the German House of Metternich
* Prince Richard of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg (1934–2017), from the German House of ...
, Prince Edward and Prince Michael before Simeon II and Albert II of Belgium
, house = Belgium
, father = Leopold III of Belgium
, mother = Astrid of Sweden
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Stuyvenberg Castle, Laeken, Brussels, Belgium
, death_date =
, death_place =
, signature = Albert II of Belgium Signat ...
after the Bulgarian line. If the equality of marriage is also ignored, this adds a further nine Britons before the Bulgarians and six Belgians after them to the list of Wettins. The most beneficial interpretations give the Saxe-Coburg-Gotha line 33 living non-morganatic agnates and the most restrictive gives it only five, who were born in 1937, 1943, 1975, 1977 and 2015.
The Mountbatten-Windsor
Mountbatten-Windsor is the personal surname used by some of the male-line descendants of Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh. Under a declaration made in Privy Council in 1960, the name '' Mountbatten- Windsor'' applies to ...
s are not considered among the Ernestine Wettins at all due to both their cognatic descent and the fact Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states during ...
was likely a morganatic daughter due to her mother being the daughter of an earl.
See also
*History of Saxony
The history of Saxony began with a small tribe living on the North Sea between the Elbe and Eider River in what is now Holstein. The name of this tribe, the Saxons (Latin: ''Saxones''), was first mentioned by the Greek author Ptolemy. The name ...
* Thuringia
Thuringia (; german: Thüringen ), officially the Free State of Thuringia ( ), is a state of central Germany, covering , the sixth smallest of the sixteen German states. It has a population of about 2.1 million.
Erfurt is the capital and larg ...
* Division of Erfurt in 1572
References
: ''This article includes material translated from the German language Wikipedia article " '' Ernestinische Herzogtümer''" and the Spanish language Wikipedia article " '' Ducados Ernestinos''". * John B. Freed. 1988. Saxony, in Strayer, Joseph R., Ed. in Chief. ''Dictionary of the Middle Ages'', Vol. 10. Charles Scribner's Sons, New York. .Ernestine Saxony, 1485(1547
(accessed December 13, 2005)
Wettin Dynasty
(2005). ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Retrieved December 12, 2005, from ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' Premium Service.
(retrieved December 13, 2005)
Chart showing succession of Ernestine duchies
(originally retrieved December 13, 2005, found using Wayback machine November 27, 2006)
External links
* {{Authority control Upper Saxon Circle House of Wettin