|
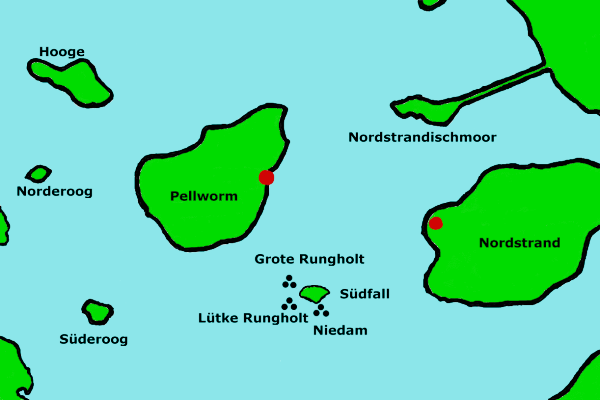
Südfall
Südfall ( da, Sydfald) is a small island in the Wadden Sea off the west coast of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, one of the ten German ''Hallig'' islands. It has a permanent population of two people. It covers an area of and is administratively part of Pellworm Municipality. History Prior to the Grote Mandrenke flood in 1362, the area comprising the present-day island was a part of the former island of Strand in Edoms Hundred. As a result of the flood, which laid waste to much of Strand and submerged the city of Rungholt, three small islands were removed from the area of Strand: Südfall, Nübell (or "Nubel") and Nielandt. Over time, Südfall and Nübell were gradually eroded into the sea, and their inhabitants resettled on Nielandt, renaming it Südfall. In the catastrophic Burchardi flood of 1634, Strand was torn asunder by the sea and its largest settlements were destroyed, causing a great loss of life and property. Nearby Südfall, however, weathered the disaster. Its inhabita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rungholt
Rungholt was a settlement in North Frisia, in what was then the Danish Duchy of Schleswig. The area is today located in Germany. Rungholt reportedly sank beneath the waves of the North Sea when a storm tide (known as ''Grote Mandrenke'' or ''Den Store Manddrukning'') hit the coast on 15 or 16 January 1362. Location The exact location of Rungholt remains unclear. It is likely that Rungholt was situated on the island of Strand, which was overwhelmed by the Burchardi Flood of 1634, and of which the islets of Pellworm and Nordstrandischmoor and the Nordstrand peninsula are the only remaining fragments. One possible location is west of the Hallig Südfall, where in 1921 significant ruins were discovered: wells, trenches and part of a tidal lock. Another theory places Rungholt to the north of the Hallig Südfall. History Today it is widely accepted that Rungholt existed and was not just a local legend. Documents support this, although they mostly date from much later times (16th c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halligen
The ''Halligen'' (German, singular ''Hallig'', ) or the ''halliger'' (Danish, singular ''hallig'') are small islands without protective dikes. They are variously pluralized in English as the Halligen, Halligs, Hallig islands, or Halligen islands. There are ten German ''halligen'' in the North Frisian Islands on Schleswig-Holstein's Wadden Sea-North Sea coast in the district of Nordfriesland and one hallig at the west coast of Denmark (Mandø). The name is cognate to Old-English ''halh'', meaning "slightly raised ground isolated by marsh". The very existence of the ''halligen'' is a result of frequent floods and poor coastal protection. The floods were much more common in the Middle Ages and coastal protection was much poorer. The ''halligen'' have areas ranging from 7 to 956 ha, and are often former parts of the mainland, separated therefrom by storm tide erosion. Some are also parts of once much bigger islands sundered by the same forces. Sometimes, owing to sediment deposition, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schleswig-Holstein Wadden Sea National Park
The Schleswig-Holstein Wadden Sea National Park (german: Nationalpark Schleswig-Holsteinisches Wattenmeer) is a national park in the Schleswig-Holstein area of the German Wadden Sea. It was founded by the Parliament of Schleswig-Holstein on 1 October 1985 by the National Park Act of 22 July 1985 and expanded significantly in 1999. Together with the Lower Saxon Wadden Sea National Park, the Hamburg Wadden Sea National Park and those parts of Elbe estuary which are not nature reserves, it forms the German part of the Wadden Sea. The national park extends from the German-Danish maritime border in the north down to the Elbe estuary in the south. In the North Frisian area, it includes the mudflats around the geest-based and marsh islands and the '' Halligen'' (undyked islands). There, the mudflats are 40 km wide in places. Further south lie areas of mudflats which contain particularly large sandbanks. In addition to the plants and animals that are typical of the entire Wadde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Frisian Islands
The North Frisian Islands (''Öömrang'' and ''Fering'' frr, Nuurdfresk Eilunen, ''Söl'ring'' frr, Nuurđfriisk Ailönen, link=no, da, Nordfrisiske Øer, german: Nordfriesische Inseln) are the Frisian Islands off the coast of North Frisia. The term covers both the North Frisian Islands in the narrow sense (in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany) and the Danish Wadden Sea Islands (in Denmark). However, Cultural geography, culturally and Language geography, linguistically, the Danish islands are usually not reckoned as being part of North Frisia, since they are not inhabited by native speakers of the North Frisian language. Occasionally, the remote island of Heligoland is also included in this group for reasons of political geography, administrative convenience, despite not being located in the Wadden Sea, since the island is home to its Heligolandic dialect, own unique dialect of Frisian. History After the Frisian and Danish colonisation of the islands in the 8th century, the Frisian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Schleswig. Its capital city is Kiel; other notable cities are Lübeck and Flensburg. The region is called ''Slesvig-Holsten'' in Danish and pronounced . The Low German name is ''Sleswig-Holsteen'', and the North Frisian name is ''Slaswik-Holstiinj''. In more dated English, it is also known as ''Sleswick-Holsatia''. Historically, the name can also refer to a larger region, containing both present-day Schleswig-Holstein and the former South Jutland County (Northern Schleswig; now part of the Region of Southern Denmark) in Denmark. It covers an area of , making it the 5th smallest German federal state by area (including the city-states). Schleswig was under Danish control during the Viking Age, but in the 12th century it escaped full control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burchardi Flood
The Burchardi flood (also known as the second Grote Mandrenke) was a storm tide that struck the North Sea coast of North Frisia and Dithmarschen (in modern-day Germany) on the night between 11 and 12 October 1634. Overrunning dikes, it shattered the coastline and caused thousands of deaths (8,000 to 15,000 people drowned) and catastrophic material damage. Much of the island of Strand washed away, forming the islands Nordstrand, Pellworm and several ''halligen''. Background The Burchardi flood hit Schleswig-Holstein during a period of economic weakness. In 1603 a plague epidemic spread across the land, killing many. The flooding occurred during the Thirty Years' War, which also did not spare Schleswig-Holstein. Fighting had occurred between locals and the troops of Frederick III, Duke of Holstein-Gottorp, especially on Strand Island. The people of Strand were resisting changes to their old defence treaties and the forced accommodation of troops. Supported by a Danish expediti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strand (island)
Strand was an island on the west coast of Nordfriesland in Schleswig, which was a fiefdom of the Danish crown. The area now belongs to Schleswig-Holstein in northern Germany. Coastlines along the Dutch-German-Danish coasts were significantly changed during and by a huge storm tide, the Saint Marcellus' flood – also referred to as the Grote Mandrenke – that occurred on 16 January 1362. Many villages and towns were lost. The outlines of Strand changed significantly, nowadays legendary Rungholt reportedly being amongst the now sunken places. The island of Südfall was separated from the mainland. In 1634 the Burchardi flood finally split Strand island into Nordstrand, Pellworm and Nordstrandischmoor Nordstrandischmoor ( da, Nordstrand Mor or Nordstrandmose, North Frisian: ''Lätj Möör''; also known locally as ''Lüttmoor'') is a ''Hallig'' (undyked islet) off the North Frisian coast in Germany and lies within the Schleswig-Holstein Wadden .... References * * Exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wadden Sea
The Wadden Sea ( nl, Waddenzee ; german: Wattenmeer; nds, Wattensee or ; da, Vadehavet; fy, Waadsee, longname=yes; frr, di Heef) is an intertidal zone in the southeastern part of the North Sea. It lies between the coast of northwestern continental Europe and the range of low-lying Frisian Islands, forming a shallow body of water with tidal flats and wetlands. It has a high biological diversity and is an important area for both breeding and migrating birds. In 2009, the Dutch and German parts of the Wadden Sea were inscribed on UNESCO's World Heritage List and the Danish part was added in June 2014. The Wadden Sea stretches from Den Helder, in the northwest of the Netherlands, past the great river estuaries of Germany to its northern boundary at Skallingen in Denmark along a total coastline of some and a total area of about . Within the Netherlands, it is bounded from the IJsselmeer by the Afsluitdijk. Historically, the coastal regions were often subjected to large floods, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verein Jordsand
*
{{disambiguation ...
''Verein'' is a German word, sometimes translated as ''union'', ''club'' or ''association'', and may refer to: * ''Eingetragener Verein'' (e. V.), a registered voluntary association under German law * Swiss Verein, a voluntary association under Swiss law, not necessarily registered See also * Association (other) * Verein für Socialpolitik, a society of economists in the German-speaking area * Voluntary association A voluntary group or union (also sometimes called a voluntary organization, common-interest association, association, or society) is a group of individuals who enter into an agreement, usually as volunteering, volunteers, to form a body (or organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, scientific or other form of significance. The sites are judged to contain " cultural and natural heritage around the world considered to be of outstanding value to humanity". To be selected, a World Heritage Site must be a somehow unique landmark which is geographically and historically identifiable and has special cultural or physical significance. For example, World Heritage Sites might be ancient ruins or historical structures, buildings, cities, deserts, forests, islands, lakes, monuments, mountains, or wilderness areas. A World Heritage Site may signify a remarkable accomplishment of humanity, and serve as evidence of our intellectual history on the planet, or it might be a place of great natural beauty. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It has 193 member states and 12 associate members, as well as partners in the non-governmental, intergovernmental and private sector. Headquartered at the World Heritage Centre in Paris, France, UNESCO has 53 regional field offices and 199 national commissions that facilitate its global mandate. UNESCO was founded in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations's International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation.English summary). Its constitution establishes the agency's goals, governing structure, and operating framework. UNESCO's founding mission, which was shaped by the Second World War, is to advance peace, sustainable development and human rights by facilitating collaboration and dialogue among nations. It pursues this objective t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lock (water Transport)
A lock is a device used for raising and lowering boats, ships and other watercraft between stretches of water of different levels on river and canal waterways. The distinguishing feature of a lock is a fixed chamber in which the water level can be varied; whereas in a caisson lock, a boat lift, or on a canal inclined plane, it is the chamber itself (usually then called a caisson) that rises and falls. Locks are used to make a river more easily navigable, or to allow a canal to cross land that is not level. Later canals used more and larger locks to allow a more direct route to be taken. Pound lock A ''pound lock'' is most commonly used on canals and rivers today. A pound lock has a chamber with gates at both ends that control the level of water in the pound. In contrast, an earlier design with a single gate was known as a flash lock. Pound locks were first used in China during the Song Dynasty (960–1279 AD), having been pioneered by the Song politician and naval en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |