|
System Y
System Y is the terminology used by BT, the main operator of the telephone network in the United Kingdom, to refer to the Ericsson AXE digital switching system. In the mid-1980s, British Telecom chose the well established AXE10 digital switch to provide competition for System X developed by a consortium of Plessey, General Electric Company (GEC) (companies later combined as GPT), STC and BT's state owned predecessor, the GPO. The newly privatised BT brought in Ericsson as a competitive alternative supplier ending Plessey/GEC's monopoly on the provision of switching systems. Initially, the AXE systems installed in the UK were partially locally manufacturered in partnership with Thorn EMI and later directly by Ericsson. While System X exchanges were more widespread in BT's network, AXE10 (and subsequent versions) remain common in the classic BT PSTN until their eventual replacement when the network is closed, which at the time of the writing is expected to be in 2025 AXE10 cove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BT Group
BT Group plc (trading as BT and formerly British Telecom) is a British multinational telecommunications holding company headquartered in London, England. It has operations in around 180 countries and is the largest provider of fixed-line, broadband and mobile services in the UK, and also provides subscription television and IT services. BT's origins date back to the founding in 1846 of the Electric Telegraph Company, the world's first public telegraph company, which developed a nationwide communications network. BT Group as it came to be started in 1912, when the General Post Office, a government department, took over the system of the National Telephone Company becoming the monopoly telecoms supplier in the United Kingdom. The Post Office Act of 1969 led to the GPO becoming a public corporation. The ''British Telecom'' brand was introduced in 1980, and became independent of the Post Office in 1981, officially trading under the name. British Telecommunications was privatised ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorn EMI
Thorn(s) or The Thorn(s) may refer to: Botany * Thorns, spines, and prickles, sharp structures on plants * ''Crataegus monogyna'', or common hawthorn, a plant species Comics and literature * Rose and Thorn, the two personalities of two DC Comics characters * Thorn (Marvel Comics), a fictional character from Marvel Comics * Thornn, a fictional character from Marvel Comics * Thorn (''Inheritance''), a dragon from the ''Inheritance cycle'' * ''Thorns'' (novel), a 1967 science fiction novel by Robert Silverberg * ''Thorn'', a 1982–1986 comic strip by Jeff Smith * Thorn Harvestar, a main character in Jeff Smith's ''Bone'' series * "The Thorn", a poem by William Wordsworth in ''Lyrical Ballads'', 1798 Companies, organisations and teams * Thorn (organization), an anti-human-trafficking organization * Thorn Electrical Industries, an electrical engineering business * Thorn EMI, a major British company involved in consumer electronics, music, defence and retail * Thorn Lighting, lumi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voice Over IP
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), also called IP telephony, is a method and group of technologies for the delivery of speech, voice communications and multimedia sessions over Internet Protocol (IP) networks, such as the Internet. The terms Internet telephony, broadband telephony, and broadband phone service specifically refer to the provisioning of communications services (voice, fax, Short Message Service, SMS, voice-messaging) over the Internet, rather than via the public switched telephone network (PSTN), also known as plain old telephone service (POTS). Overview The steps and principles involved in originating VoIP telephone calls are similar to traditional digital telephony and involve signaling, channel setup, digitization of the analog voice signals, and encoding. Instead of being transmitted over a circuit-switched network, the digital information is packetized and transmission occurs as IP packets over a packet-switched network. They transport media streams using spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time-division Multiplexing
Time-division multiplexing (TDM) is a method of transmitting and receiving independent signals over a common signal path by means of synchronized switches at each end of the transmission line so that each signal appears on the line only a fraction of time in an alternating pattern. This method transmits two or more digital signals or analog signals over a common channel. It can be used when the bit rate of the transmission medium exceeds that of the signal to be transmitted. This form of signal multiplexing was developed in telecommunications for telegraphy systems in the late 19th century, but found its most common application in digital telephony in the second half of the 20th century. History Time-division multiplexing was first developed for applications in telegraphy to route multiple transmissions simultaneously over a single transmission line. In the 1870s, Émile Baudot developed a time-multiplexing system of multiple Hughes telegraph machines. In 1944, the Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Loop
In telephony, the local loop (also referred to as the local tail, subscriber line, or in the aggregate as the last mile) is the physical link or circuit that connects from the demarcation point of the customer premises to the edge of the common carrier or telecommunications service provider's network. At the edge of the carrier access network in a traditional public telephone network, the local loop terminates in a circuit switch housed in an incumbent local exchange carrier or telephone exchange. Infrastructure Traditionally, the local loop was an electrical circuit in the form of a single pair of conductors from the telephone on the customer's premises to the local telephone exchange. Single-wire earth return lines had been used in some countries until the introduction of electric tramways from the 1900s made them unusable. Historically the first section was often an aerial open-wire line, with several conductors attached to porcelain insulators on cross-arms on "telegra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
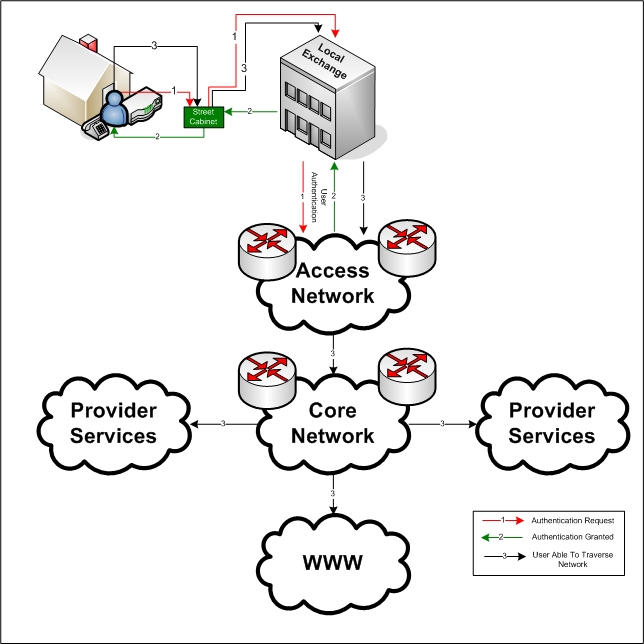
Access Network
An access network is a type of telecommunications network which connects subscribers to their immediate service provider. It is contrasted with the core network, which connects local providers to one another. The access network may be further divided between feeder plant or distribution network, and drop plant or edge network. Telephone heritage An access network, also referred to as an outside plant, refers to the series of wires, cables and equipment lying between a consumer/business telephone termination point (the point at which a telephone connection reaches the customer) and the local telephone exchange. The local exchange contains banks of automated switching equipment which direct a call or connection to the consumer. The access network is perhaps one of the oldest assets a telecoms operator would own. In 2007–2008 many telecommunication operators experienced increasing problems maintaining the quality of the records which describe the network. In 2006, according t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Concentrator
In modern telephony a remote concentrator, remote concentrator unit (RCU), or remote line concentrator (RLC) is a concentrator at the lowest level in the telephone switch hierarchy. Subscribers' analogue telephone/PSTN lines are terminated on concentrators. They have three main functions: * Digitize: convert voice (and sometimes data) from analogue to a digital form. * Connect off-hook lines to the local exchange — the concentration function. * Multiplex, interleaving many calls together on a single wire or optical fiber. via Web Archive Only a few hundred telephone lines attach to each remote concentrator. In North America concentrators are loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Telephony
Telephony ( ) is the field of technology involving the development, application, and deployment of telecommunication services for the purpose of electronic transmission of voice, fax, or data, between distant parties. The history of telephony is intimately linked to the invention and development of the telephone. Telephony is commonly referred to as the construction or operation of telephones and telephonic systems and as a system of telecommunications in which telephonic equipment is employed in the transmission of speech or other sound between points, with or without the use of wires. The term is also used frequently to refer to computer hardware, software, and computer network systems, that perform functions traditionally performed by telephone equipment. In this context the technology is specifically referred to as Internet telephony, or voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP). Overview The first telephones were connected directly in pairs. Each user had a separate telephone wired ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Switched Telephone Network
The public switched telephone network (PSTN) provides Communications infrastructure, infrastructure and services for public Telecommunications, telecommunication. The PSTN is the aggregate of the world's circuit-switched telephone networks that are operated by national, regional, or local telephony operators. These consist of telephone lines, fiber optic cables, microwave transmission links, Routing in cellular networks, cellular networks, communications satellites, and undersea telephone cables, all interconnected by switching centers which allow most telephones to communicate with each other. Originally a network of fixed-line Analog signal processing, analog telephone systems, the PSTN is now almost entirely digital in its core network and includes mobile and other networks, as well as fixed telephones. The technical operation of the PSTN adheres to the standards created by the ITU-T. These standards allow different networks in different countries to interconnect seamlessly. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Post Office
The General Post Office (GPO) was the state postal system and telecommunications carrier of the United Kingdom until 1969. Before the Acts of Union 1707, it was the postal system of the Kingdom of England, established by Charles II in 1660. Similar General Post Offices were established across the British Empire. In 1969 the GPO was abolished and the assets transferred to The Post Office, changing it from a Department of State to a statutory corporation. In 1980, the telecommunications and postal sides were split prior to British Telecommunications' conversion into a totally separate publicly owned corporation the following year as a result of the British Telecommunications Act 1981. For the more recent history of the postal system in the United Kingdom, see the articles Royal Mail and Post Office Ltd. Originally, the GPO was a state monopoly covering the dispatch of items from a specific sender to a specific receiver, which was to be of great importance when new forms of co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 170 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Telephones And Cables
Standard Telephones and Cables Ltd (later STC plc) was a British manufacturer of telephone, telegraph, radio, telecommunications, and related equipment. During its history, STC invented and developed several groundbreaking new technologies including pulse-code modulation (PCM) and optical fibres. The company was founded in 1883 in London as International Western Electric by the Western Electric Company, shortly after Western Electric became the telephone equipment supplier for the American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T) in the United States. In 1925, Western Electric divested itself of all foreign operations and sold International Western Electric to International Telephone and Telegraph (ITT), in part to thwart antitrust actions by the American government. In mid-1982, STC became an independent company and was listed on the London Stock Exchange; for a time it was a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. It was bought by Nortel in 1991. History Early days The company was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |