access network on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An access network is a type of
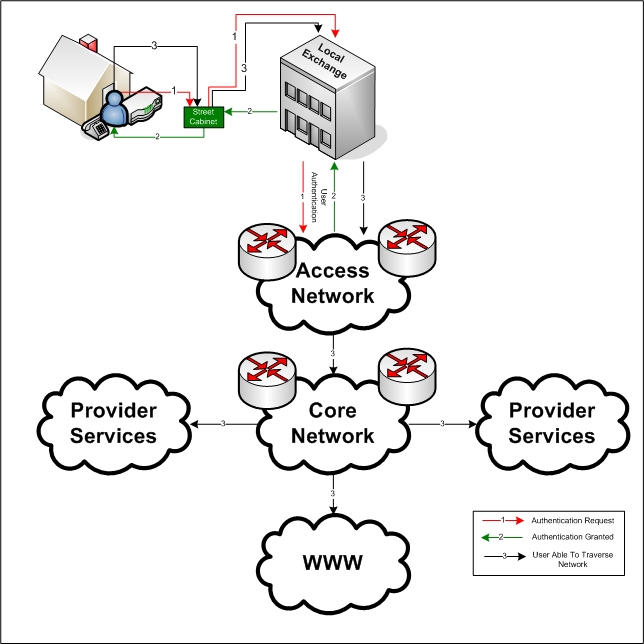 The process of communicating with a network begins with an access attempt, in which one or more users interact with a communications system to enable initiation of user information transfer. An access attempt itself begins with issuance of an access request by an access originator.
An access attempt ends either in successful access or in access failure - an unsuccessful access that results in termination of the attempt in any manner other than initiation of user
The process of communicating with a network begins with an access attempt, in which one or more users interact with a communications system to enable initiation of user information transfer. An access attempt itself begins with issuance of an access request by an access originator.
An access attempt ends either in successful access or in access failure - an unsuccessful access that results in termination of the attempt in any manner other than initiation of user
telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than tha ...
s network which connects subscribers to their immediate service provider
A service provider (SP) is an organization that provides services, such as consulting, legal, real estate, communications, storage, and processing services, to other organizations. Although a service provider can be a sub-unit of the organization t ...
. It is contrasted with the core network, which connects local providers to one another. The access network may be further divided between feeder plant or distribution network, and drop plant or edge network.
Telephone heritage
An access network, also referred to as an outside plant, refers to the series of wires, cables and equipment lying between a consumer/business telephone termination point (the point at which a telephone connection reaches the customer) and the local telephone exchange. The local exchange contains banks of automated switching equipment which direct a call or connection to the consumer. The access network is perhaps one of the oldest assets a telecoms operator would own. In 2007–2008 many telecommunication operators experienced increasing problems maintaining the quality of the records which describe the network. In 2006, according to an independent Yankee Group report, globally operators experience profit leakage in excess of $17 billion each year. The access network is also perhaps the most valuable asset an operator owns since this is what physically allows them to offer a service. Access networks consist largely of pairs ofcopper wires
Copper has been used in electrical wiring since the invention of the electromagnet and the telegraph in the 1820s. The invention of the telephone in 1876 created further demand for copper wire as an electrical conductor.
Copper is the electri ...
, each traveling in a direct path between the exchange and the customer. In some instances, these wires may even consist of aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It h ...
, which was commonly used in the 1960s and 1970s following a massive increase in the cost of copper. The price increase was temporary, but the effects of this decision are still felt today as electromigration within the aluminum wires can cause an increase in on-state resistance. This resistance causes degradation which can eventually lead to the complete failure of the wire to transport data.
Access is essential to the future profitability of operators who are experiencing massive reductions in revenue from plain old telephone service
Plain old telephone service (POTS), or plain ordinary telephone system, is a retronym for voice-grade telephone service employing analog signal transmission over copper loops. POTS was the standard service offering from telephone companies from ...
s, due in part to the opening of historically nationalized companies to competition, and in part to increased use of mobile phone
A mobile phone, cellular phone, cell phone, cellphone, handphone, hand phone or pocket phone, sometimes shortened to simply mobile, cell, or just phone, is a portable telephone that can make and receive telephone call, calls over a radio freq ...
s and voice over IP
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), also called IP telephony, is a method and group of technologies for the delivery of voice communications and multimedia sessions over Internet Protocol (IP) networks, such as the Internet. The terms Interne ...
(VoIP) services. Operators offered additional services such as xDSL based broadband and IPTV ( Internet Protocol television) to guarantee profit. The access network is again the main barrier to achieving these profits since operators worldwide have accurate records of only 40% to 60% of the network. Without understanding or even knowing the characteristics of these enormous copper spider webs, it is very difficult, and expensive to 'provision' (connect) new customers and assure the data rates required to receive next-generation services.
Access networks around the world evolved to include more and more optical fiber technology. Optical fiber already makes up the majority of core networks and will start to creep closer and closer to the customer, until a full transition is achieved, delivering value-added services over fiber to the home (FTTH).
Access process
 The process of communicating with a network begins with an access attempt, in which one or more users interact with a communications system to enable initiation of user information transfer. An access attempt itself begins with issuance of an access request by an access originator.
An access attempt ends either in successful access or in access failure - an unsuccessful access that results in termination of the attempt in any manner other than initiation of user
The process of communicating with a network begins with an access attempt, in which one or more users interact with a communications system to enable initiation of user information transfer. An access attempt itself begins with issuance of an access request by an access originator.
An access attempt ends either in successful access or in access failure - an unsuccessful access that results in termination of the attempt in any manner other than initiation of user information transfer
In telecommunications, information transfer is the process of moving messages containing user information from a source to a sink via a communication channel. In this sense, information transfer is equivalent to data transmission which highlights ...
between the intended source and destination ( sink) within the specified maximum access time.
Access time is the time delay or latency between a requested access attempt and successful access being completed. In a telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than tha ...
s system, access time values are measured only on access attempts that result in successful access.
Access failure can be the result of access outage, user blocking, incorrect access, or access denial. Access denial (system blocking) can include:
*Access failure caused by the issuing of a system blocking signal by a communications system that does not have a camp-on busy signal feature.
*Access failure caused by exceeding the maximum access time and nominal system access time fraction during an access attempt.
Charging for access
An access charge is a charge made by a local exchange carrier for use of its local exchange facilities for a purpose such as the origination or termination of network traffic that is carried to or from a distant exchange by an interexchange carrier. Although some access charges are billed directly to interexchange carriers, a significant percentage of all access charges are paid by the local end users.Mobile access networks
* GERAN * UTRAN * E-UTRAN * CDMA2000 * GSM * UMTS *1xEVDO
Evolution-Data Optimized (EV-DO, EVDO, etc.) is a telecommunications standard for the wireless transmission of data through radio signals, typically for broadband Internet access. EV-DO is an evolution of the CDMA2000 (IS-2000) standard which su ...
* voLTE
* Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi () is a family of wireless network protocols, based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio w ...
in* WiMAX
Optical distribution network
A passive optical distribution network (PON) uses single-mode optical fiber in the outside plant, optical splitters andoptical distribution frame
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviole ...
s, duplexed so that both upstream and downstream signals share the same fiber on separate wavelengths. Faster PON standards generally support a higher split ratio of users per PON, but may also use reach extenders/amplifiers where extra coverage is needed. Optical splitters creating a point to multipoint topology are also the same technology regardless of the type of PON system, making any PON network upgradable by changing the optical network terminals (ONT) and optical line terminal (OLT) terminals at each end, with minimal change to the physical network.
Access networks usually also must support point-to-point technologies such as Ethernet
Ethernet () is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in ...
, which bypasses any outside plant splitter to achieve a dedicated link to the telephone exchange. Some PON networks use a "home run" topology where roadside cabinets only contain patch panels so that all splitters are located centrally. While a 20% higher capital cost could be expected, home run networks may encourage a more competitive wholesale market since providers' equipment can achieve higher use.
See also
* Edge device * Hierarchical internetworking model * Internet access * IP connectivity access network *Local loop
In telephony, the local loop (also referred to as the local tail, subscriber line, or in the aggregate as the last mile) is the physical link or circuit that connects from the demarcation point of the customer premises to the edge of the comm ...
* Passive Optical Network
References
External links
* {{cite web, title=The Network Story , publisher=British Telecom , url=http://www.btplc.com/Thegroup/Networkstory/html/slide.aspx_slide=1.html , year=2005 , url-status=dead , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100505215237/http://www.btplc.com/Thegroup/Networkstory/html/slide.aspx_slide%3D1.html , archive-date=5 May 2010 Interactive presentation introducing the technology and design of access networks Telecommunications infrastructure Network access Fiber to the premises