|
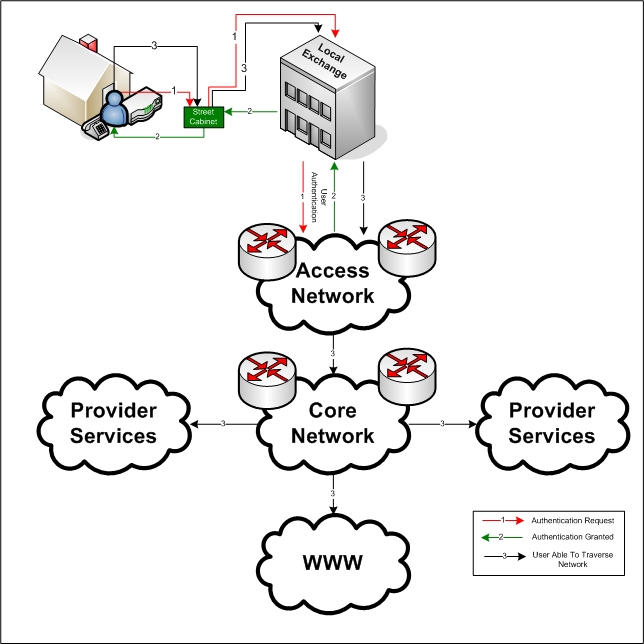
Access Network
An access network is a type of telecommunications network which connects subscribers to their immediate service provider. It is contrasted with the core network, which connects local providers to one another. The access network may be further divided between feeder plant or distribution network, and drop plant or edge network. Telephone heritage An access network, also referred to as an outside plant, refers to the series of wires, cables and equipment lying between a consumer/business telephone termination point (the point at which a telephone connection reaches the customer) and the local telephone exchange. The local exchange contains banks of automated switching equipment which direct a call or connection to the consumer. The access network is perhaps one of the oldest assets a telecoms operator would own. In 2007–2008 many telecommunication operators experienced increasing problems maintaining the quality of the records which describe the network. In 2006, accordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than that feasible with the human voice, but with a similar scale of expediency; thus, slow systems (such as postal mail) are excluded from the field. The transmission media in telecommunication have evolved through numerous stages of technology, from beacons and other visual signals (such as smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs), to electrical cable and electromagnetic radiation, including light. Such transmission paths are often divided into communication channels, which afford the advantages of multiplexing multiple concurrent communication sessions. ''Telecommunication'' is often used in its plural form. Other examples of pre-modern long-distance communication included audio messages, such as code ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
User (telecommunications)
In telecommunications, a user is a person, organization, or other entity that employs the services provided by a telecommunication system, or by an information processing system, for transfer of information. A user functions as a source or final destination of user information, or both. A user ''may'' also be the subscriber, i.e. the customer paying for the service. User is also a person or process accessing an AIS by direct connections (e.g., via terminals) or indirect connections. "Indirect connection" relates to persons who prepare input data or receive output that is not reviewed for content or classification by a responsible individual. Sources * {{FS1037C MS188 * National Information Systems Security Glossary See also * User (computing) A user is a person who utilizes a computer or network service. A user often has a user account and is identified to the system by a username (or user name). Other terms for username include login name, screenname (or scree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-UTRAN
E-UTRA is the air interface of 3rd Generation Partnership Project ( 3GPP) Long Term Evolution (LTE) upgrade path for mobile networks. It is an acronym for Evolved Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) Terrestrial Radio Access, also referred to as the 3GPP work item on the Long Term Evolution (LTE) also known as the Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) in early drafts of the 3GPP LTE specification. E-UTRAN is the initialism of Evolved UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network and is the combination of E-UTRA, user equipment (UE), and E-UTRAN Node B or Evolved Node B ( eNodeB). It is a radio access network (RAN) which is referred to under the name EUTRAN standard meant to be a replacement of the UMTS and HSDPA/ HSUPA technologies specified in 3GPP releases 5 and beyond. Unlike HSPA, LTE's E-UTRA is an entirely new air interface system, unrelated to and incompatible with W-CDMA. It provides higher data rates, lower latency and is optimized for packet data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UTRAN
UTRAN (short for "UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network''") is a collective term for the network and equipment that connects mobile handsets to the public telephone network or the Internet. It contains the base stations, which are called Node B's and Radio Network Controllers (RNCs) which make up the UMTS radio access network. This communications network, commonly referred to as 3G (for 3rd Generation Wireless Mobile Communication Technology), can carry many traffic types from real-time Circuit Switched to IP based Packet Switched. The UTRAN allows connectivity between the UE (user equipment) and the core network. The RNC provides control functionalities for one or more Node Bs. A Node B and an RNC can be the same device, although typical implementations have a separate RNC located in a central office serving multiple Node Bs. Despite the fact that they do not have to be physically separated, there is a logical interface between them known as the Iub. The RNC and its correspondi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GERAN
GERAN is an abbreviation for GSM EDGE Radio Access Network. The standards for GERAN are maintained by the 3GPP (Third Generation Partnership Project). GERAN is a key part of GSM, and also of combined UMTS/GSM networks. GERAN is the radio part of GSM/EDGE together with the network that joins the base stations (the Ater and Abis interfaces) and the base station controllers (A interfaces, etc.) The network represents the core of a GSM network, through which phone calls and packet data are routed from and to the PSTN and Internet to and from subscriber handsets. A mobile phone operator's network comprises one or more GERANs, coupled with UTRANs in the case of a UMTS/GSM network. A GERAN without EDGE is a GRAN, but is otherwise identical in concept. A GERAN without GSM is an ERAN. See also *UTRAN UTRAN (short for "UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network''") is a collective term for the network and equipment that connects mobile handsets to the public telephone network or the In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interexchange Carrier
An interexchange carrier (IXC), in U.S. legal and regulatory terminology, is a type of telecommunication company, commonly called a long-distance telephone company. It is defined as any carrier that provides services across multiple local access and transport areas (interLATA). Calls made on telephone circuits within the local geographic area covered by one local network are handled only by that intraLATA carrier, commonly called a local telephone exchange carrier. Local calls are usually defined by connections made without additional charge whether the connected call is in the same LATA or connects to another LATA with no charge. IntraLATA usually refers to rated or toll calls between LATA within state boundaries, as opposed to interstate, or calls between LATAs in different states. Call handling An interexchange carrier handles traffic between telephone exchanges. Telephone exchanges are identified in the United States by the three-digit area code (NPA) and the central office pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Access Time
Access time is the time delay or latency between a request to an electronic system, and the access being completed or the requested data returned * In a computer, it is the time interval between the instant at which an instruction control unit initiates a call for data or a request to store data, and the instant at which delivery of the data is completed or the storage is started. See also * Memory latency * Mechanical latency * Rotational latency * Seek time Higher performance in hard disk drives comes from devices which have better performance characteristics. These performance characteristics can be grouped into two categories: access time and data transfer time (or rate). Access time The ''acce ... References Network access {{compu-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camp-on Busy Signal
In telecommunication, the term camp-on busy signal has the following meanings: *A signal that informs a busy telephone user that another call originator is waiting for a connection. Synonym: ''call waiting'' *A teleprinter exchange facility Facility may refer to: * A place for doing something, or a place that facilitates an activity: ** A commercial or institutional building, such as a hotel, resort, school, office complex, sports arena, or convention center ** Medical facili ... signal that automatically causes a calling station to retry the call-receiver number after a given interval when the call-receiver teleprinter is occupied or the circuits are busy. Synonym: ''speed-up tone'' {{FS1037C Telephony signals Telegrams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications System
A communications system or communication system is a collection of individual telecommunications networks, transmission systems, relay stations, tributary stations, and terminal equipment usually capable of interconnection and interoperation to form an integrated whole. The components of a communications system serve a common purpose, are technically compatible, use common procedures, respond to controls, and operate in union. Telecommunications is a method of communication (e.g., for sports broadcasting, mass media, journalism, etc.). Communication is the act of conveying intended meanings from one entity or group to another through the use of mutually understood signs and semiotic rules. Types By media An optical communication system is any form of telecommunication that uses light as the transmission medium. Equipment consists of a transmitter, which encodes a ''message'' into an optical '' signal'', a ''communication channel'', which carries the signal to its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denial Of Service
In computing, a denial-of-service attack (DoS attack) is a cyber-attack in which the perpetrator seeks to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users by temporarily or indefinitely disrupting services of a host connected to a network. Denial of service is typically accomplished by flooding the targeted machine or resource with superfluous requests in an attempt to overload systems and prevent some or all legitimate requests from being fulfilled. In a distributed denial-of-service attack (DDoS attack), the incoming traffic flooding the victim originates from many different sources. More sophisticated strategies are required to mitigate this type of attack, as simply attempting to block a single source is insufficient because there are multiple sources. A DoS or DDoS attack is analogous to a group of people crowding the entry door of a shop, making it hard for legitimate customers to enter, thus disrupting trade. Criminal perpetrators of DoS attacks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Block (Internet)
On the Internet, a block or ban is a technical measure intended to restrict access to information or resources. Blocking and its inverse, unblocking, may be implemented by the owners of computers using software. Some countries, notably China and Singapore, block access to certain news information. In the United States, the Children's Internet Protection Act requires schools receiving federal funded discount rates for Internet access to install filter software that blocks obscene content, pornography, and, where applicable, content "harmful to minors". Blocking may also refer to denying access to a web server based on the IP address of the client machine. In certain websites, including social networks such as Facebook or editable databases like wikis, users can apply blocks (based in either IP number or account) on other users deemed undesirable to prevent them from performing certain actions. Blocks of this kind may occur for several reasons and produce different effe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |