|
Surprize (1780 Ship)
''Surprize'' was a three-deck merchant vessel launched in 1780 that made five voyages as a packet ship under charter to the British East India Company (EIC). The fourth of which was subsequent to her participating in the notorious Second Fleet transporting convicts to Port Jackson (EIC). Her fifth voyage for the EIC was subsequent to her second voyage transporting convicts to Australia. In 1799 a French frigate captured her in the Bay of Bengal. First EIC voyage (1783) Under the command of Captain David Asquith, ''Surprize'' left Bengal on 22 April 1783 and reached the River Shannon on 11 September. She arrived at The Downs on 17 October. Second EIC voyage (1785) Captain Asquith sailed for Bengal, leaving Britain on 23 January 1784. She may have left as late as 29 April. She arrived at Calcutta by 9 September, bringing with her "a variety of articles, as well useful as curious". ''Surprize'' arrived back in Britain on 16 May 1785. Third EIC voyage Captain Asquith left the Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Bradley (Royal Navy Officer)
William Bradley (14 November 1758–13 March 1833) was a British naval officer and cartographer who was one of the officers who participated in the First Fleet to Australia. During this expedition, Bradley undertook extensive surveys and became one of the first of the settlers to establish relations with the aborigines, with whom he struck up a dialogue and whose customs and nature he studied extensively. He later however fell out with his aboriginal contacts and instead undertook a mission to gather food which ended with an eleven-month stay on Norfolk Island after a shipwreck. Bradley's later career was overshadowed by his steadily deteriorating mental state. Although a successful small ship commander, Bradley became increasingly erratic and was eventually retired as a result. A few years later, suffering serious mental problems, Bradley committed a highly unusual case of postal fraud and was ultimately exiled. He never returned to Britain but lived in quiet disgrace in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic period, but takes its name from the Angles, a Germanic tribe deriving its name from the Anglia peninsula, who settled during the 5th and 6th centuries. England became a unified state in the 10th century and has had a significant cultural and legal impact on the wider world since the Age of Discovery, which began during the 15th century. The English language, the Anglican Church, and Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
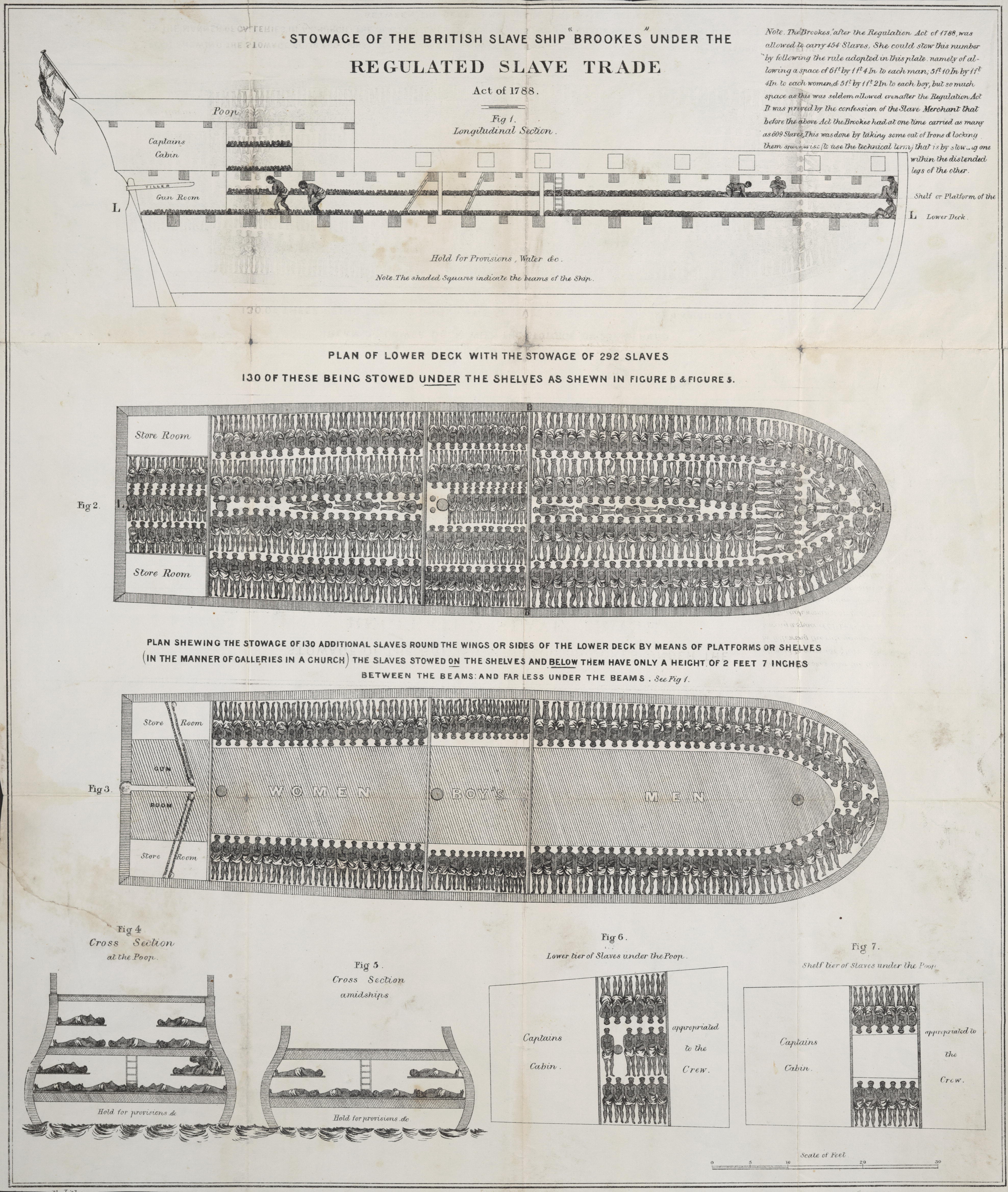
Slave Ship
Slave ships were large cargo ships specially built or converted from the 17th to the 19th century for transporting slaves. Such ships were also known as "Guineamen" because the trade involved human trafficking to and from the Guinea coast in West Africa. Atlantic slave trade In the early 1600s, more than a century after the arrival of Europeans to the Americas, demand for unpaid labor to work plantations made slave-trading a profitable business. The Atlantic slave trade peaked in the last two decades of the 18th century, during and following the Kongo Civil War. To ensure profitability, the owners of the ships divided their hulls into holds with little headroom, so they could transport as many slaves as possible. Unhygienic conditions, dehydration, dysentery and scurvy led to a high mortality rate, on average 15% and up to a third of captives. Often the ships carried hundreds of slaves, who were chained tightly to plank beds. For example, the slave ship ''Henrietta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Helena
Saint Helena () is a British overseas territory located in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is a remote volcanic tropical island west of the coast of south-western Africa, and east of Rio de Janeiro in South America. It is one of three constituent parts of the British Overseas Territory of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha. Saint Helena measures about and has a population of 4,439 per the 2021 census. It was named after Helena, mother of Constantine I. It is one of the most remote islands in the world and was uninhabited when discovered by the Portuguese enroute to the Indian subcontinent in 1502. For about four centuries the island was an important stopover for ships from Europe to Asia and back, while sailing around the African continent, until the opening of the Suez canal. St Helena is the United Kingdom's second-oldest overseas territory after Bermuda. Saint Helena is known for being the site of Napoleon's second exile, following his final defeat in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anyer
Anyer, also known as Anjer or Angier, is a coastal town in Banten, formerly West Java, Indonesia, west of Jakarta and south of Merak. A significant coastal town late 18th-century, Anyer faces the Sunda Strait. History The town was a considerable port in the 19th century, but was completely destroyed by a 100-foot-high tsunami which was caused by the 1883 eruption of Krakatoa. The present settlement still houses the Cikoneng Lighthouse built by Dutch government two years later as a memorial for the townspeople killed by the eruption. It was also the starting point of the Great Post Road, built by the Dutch in the nineteenth century, which ran around to the eastern tip of Java. Off the coast of Anyer is the island Pulau Sangiang, an uninhabited island with vast areas of untouched jungle. The area is also known for coral formations swarming with tropical fish. Anyer Beach is a tourist attraction with hot swimming water, a hotel and rental of resting sheds, boats, four-wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whampoa Anchorage
Pazhou is a subdistrict of Haizhu in southeastern Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, in China. , formerly Whampoa Island, has a total area of and is the site of Pazhou Pagoda. Its eastern bay was formerly the chief anchorage for ships participating in Guangzhou's foreign trade. Traders from the "Southern Sea", including Indians, Arabians, and most Europeans, were required to keep their ships at Pazhou while smaller craft ferried goods to and from the Thirteen Factories area of Guangzhou's western suburbs. Traders rented storage for ships supplies and repair shops on Whampoa Island. Images of the anchorage were a common theme in 18th-century art. With the expansion of Guangzhou, the subdistrict is now part of its downtown area, with many commercial and recreational facilities. The Guangzhou International Convention and Exhibition Center is the current site of the annual Canton Fair. Names The English, French, and Danish ''Whampoa'' and Swedish ' are irregular romani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Montagu-Dunk, 2nd Earl Of Halifax
George Montagu-Dunk, 2nd Earl of Halifax, (6 October 1716 – 8 June 1771) was a British statesman of the Georgian era. Due to his success in extending commerce in the Americas, he became known as the "father of the colonies". President of the Board of Trade from 1748 to 1761, he aided the foundation of Nova Scotia, 1749, the capital Halifax being named after him. When Canada was ceded to the King of Great Britain by the King of France, following the Treaty of Paris of 1763, he restricted its boundaries and renamed it "Province of Quebec". Early life The son of the 1st Earl of Halifax, he was styled Viscount Sunbury until succeeding his father as Earl of Halifax in 1739 (thus also styled in common usage Lord Halifax). Educated at Eton College and at Trinity College, Cambridge, he was married in 1741 to Anne Richards (died 1753), who had inherited a great fortune from Sir Thomas Dunk, whose name Halifax took. Career After having been an official in the household of Frederi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montague Island (Australia)
Montague Island (Barunguba) is a continental island contained within the Montague Island Nature Reserve, a protected nature reserve that is located offshore from the South Coast region of New South Wales, in eastern Australia. The nearest town located onshore from the reserve and island is , situated approximately to the northwest. History The island has been known to the local group of Yuin people, an Aboriginal nation, as Barunguba, and there are Aboriginal sites of significance across the island. It features in Aboriginal mythology, as the eldest son of Gulaga (Mount Dromedary), the mother. Her younger son, Najanuka (Little Dromedary), was not allowed to go far from home as Barunguba did, but Gulaga can still see her both her sons in the distance. Text may have been copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)licence. The island was first sighted by Europeans in 1770 by James Cook and named Cape Dromedary, then identif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kong and north of Macau, Guangzhou has a history of over 2,200 years and was a major terminus of the maritime Silk Road; it continues to serve as a major port and transportation hub as well as being one of China's three largest cities. For a long time, the only Chinese port accessible to most foreign traders, Guangzhou was captured by the British during the First Opium War. No longer enjoying a monopoly after the war, it lost trade to other ports such as Hong Kong and Shanghai, but continued to serve as a major transshipment port. Due to a high urban population and large volumes of port traffic, Guangzhou is classified as a Large-Port Megacity, the largest type of port-city in the world. Due to worldwide travel restrictions at the beg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norfolk Island
Norfolk Island (, ; Norfuk: ''Norf'k Ailen'') is an external territory of Australia located in the Pacific Ocean between New Zealand and New Caledonia, directly east of Australia's Evans Head and about from Lord Howe Island. Together with the neighbouring Phillip Island and Nepean Island, the three islands collectively form the Territory of Norfolk Island. At the 2021 census, it had inhabitants living on a total area of about . Its capital is Kingston. The first known settlers in Norfolk Island were East Polynesians but they had already departed when Great Britain settled it as part of its 1788 settlement of Australia. The island served as a convict penal settlement from 6 March 1788 until 5 May 1855, except for an 11-year hiatus between 15 February 1814 and 6 June 1825, when it lay abandoned. On 8 June 1856, permanent civilian residence on the island began when descendants of the ''Bounty'' mutineers were relocated from Pitcairn Island. In 1914 the UK handed Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( af, Kaap die Goeie Hoop ) ;''Kaap'' in isolation: pt, Cabo da Boa Esperança is a rocky headland on the Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa. A common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is the southern tip of Africa, based on the misbelief that the Cape was the dividing point between the Atlantic and Indian oceans, and have nothing to do with north or south. In fact, by looking at a map, the southernmost point of Africa is Cape Agulhas about to the east-southeast. The currents of the two oceans meet at the point where the warm-water Agulhas current meets the cold-water Benguela current and turns back on itself. That oceanic meeting point fluctuates between Cape Agulhas and Cape Point (about east of the Cape of Good Hope). When following the western side of the African coastline from the equator, however, the Cape of Good Hope marks the point where a ship begins to travel more eastward than southward. Thus, the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Waters (surgeon)
William Waters may refer to: * William Waters (mayor) (died 1881), mayor in Nelson, New Zealand *William Waters (architect), American architect * W. F. Waters (1897–1968), Victorian Rover Scouting notable in Australia *Joe Waters (musician) (William Joseph Waters, 1947–2008), American country music singer * Billy Waters (busker) (c. 1778–1823), black man who busked in London * Billy Waters (footballer, born 1994), English football forward * Billy Waters (footballer, born 1931) William Anthony Waters (born 19 September 1931) is a Welsh former footballer who played as a goalkeeper. He made appearances in the English Football League with Wrexham and Millwall. Career Waters first signed for Blackpool in 1950, however, ..., Welsh football goalkeeper See also * William Walters (other) {{hndis, Waters, William ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |