|
SuperDish
The Super Dish is a satellite dish that was deployed by the DISH Network in November 2003 as a means to provide more channels for their subscribers. Its elliptical reflector (The part that gives the SuperDish its "dish" shape) is 36" x 20" - more than 50% larger than the round 20" Dish 500. The Super Dish receives signals from three orbiting satellites, as opposed to a Dish 500 which only receives signals from two satellites. The Super Dish's three satellites are at 110°W, 119°W, and either 105°W or 121°W depending on customer requirements. The 105-degree orbital slot provided local channels via Ku band from SES Americom's AMC-15 satellite. The other, 121-degree orbital slot provided local channels and international packages via Ku band from EchoStar 9, which is also known as Galaxy 23/EchoStar 9 due to a joint partnership with Intelsat. Technology These two satellite services, and their older Fixed Service Satellite technology, were provided to add additional capacity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed Service Satellite
Fixed-satellite service (short: FSS | also: fixed-satellite radiocommunication service) is – according to ''article 1.21'' of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as ''A radiocommunication service between earth stations at given positions, when one or more satellites are used; the given position may be a specified fixed point or any fixed point within specified areas; in some cases this service includes satellite-to-satellite links, which may also be operated in the inter-satellite service; the fixed-satellite service may also include feeder links for other space radiocommunication services.'' Classification This ''radiocommunication service'' is classified in accordance with ''ITU Radio Regulations'' (article 1) as follows: Fixed service (article 1.20) * (article 1.21) * Inter-satellite service (article 1.22) * Earth exploration-satellite service (article 1.51) ** Meteorological-satellite service (article 1.52) ; Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy 23
Galaxy 23 is the name given to the C-band service of the Galaxy 23/EchoStar 9 communications satellite jointly owned by Intelsat and EchoStar located at 121° W longitude, serving the North American market. It was built by Space Systems/Loral, as part of its FS-1300 line. Galaxy 23 was formerly known as Intelsat Americas 13. The "Galaxy 23" portion of the service provides transponders in the C band. The "EchoStar 9" portion broadcasts Ku band, and Ka band transponders. While the satellite itself is jointly owned through a partnership between Intelsat and Echostar, the Ku band payload is owned and operated by Echostar for international television programming and local television channels. That service is intended for Dish Network customers using a SuperDish system. The C-band payload is owned and operated by Intelsat. The Ka band payload is owned and operated by Echostar for as-yet-undisclosed purposes. Current clients for Galaxy 23/EchoStar 9 include Dish Network, Dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Broadcast Satellite
Satellite television is a service that delivers television programming to viewers by relaying it from a communications satellite orbiting the Earth directly to the viewer's location. The signals are received via an outdoor parabolic antenna commonly referred to as a satellite dish and a low-noise block downconverter. A satellite receiver then decodes the desired television program for viewing on a television set. Receivers can be external set-top boxes, or a built-in television tuner. Satellite television provides a wide range of channels and services. It is usually the only television available in many remote geographic areas without terrestrial television or cable television service. Modern systems signals are relayed from a communications satellite on the X band (8–12 GHz) or Ku band (12–18 GHz) frequencies requiring only a small dish less than a meter in diameter. The first satellite TV systems were an obsolete type now known as television receive-only. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Frequency Antenna Types
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates the waves, and received by another antenna connected to a radio receiver. Radio is very widely used in modern technology, in radio communication, radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications. In radio communication, used in radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, two-way radios, wireless networking, and satellite communication, among numerous other uses, radio waves are used to carry information across space from a transmitter to a receiver, by modulating the radio signal (impressing an information signal on the radio wave by varying some aspect of the wave) in the transmitter. In radar, used to locate and track objects like aircraft, ships, spacecraft an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wells Fargo
Wells Fargo & Company is an American multinational financial services company with corporate headquarters in San Francisco, California; operational headquarters in Manhattan; and managerial offices throughout the United States and internationally. The company has operations in 35 countries with over 70 million customers globally. It is considered a systemically important financial institution by the Financial Stability Board. The firm's primary subsidiary is Wells Fargo Bank, N.A., a national bank which designates its Sioux Falls, South Dakota site as its main office. It is the fourth largest bank in the United States by total assets and is also one of the largest as ranked by bank deposits and market capitalization. Along with JPMorgan Chase, Bank of America and Citigroup. Wells Fargo is one of the " Big Four Banks" of the United States. It has 8,050 branches and 13,000 ATMs. It is one of the most valuable bank brands. Wells Fargo, in its present form, is a resu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wachovia Bank
Wachovia was a diversified financial services company based in Charlotte, North Carolina. Before its acquisition by Wells Fargo and Company in 2008, Wachovia was the fourth-largest bank holding company in the United States, based on total assets. Wachovia provided a broad range of banking, asset management, wealth management, and corporate and investment banking products and services. At its height, it was one of the largest providers of financial services in the United States, operating financial centers in 21 states and Washington, D.C., with locations from Connecticut to Florida and west to California. Wachovia provided global services through more than 40 offices around the world. The acquisition of Wachovia by Wells Fargo was completed on December 31, 2008, after a government-forced sale to avoid Wachovia's failure. The Wachovia brand was absorbed into the Wells Fargo brand in a process that lasted three years. On October 15, 2011, the last Wachovia branches in North Carol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anik(satellite) , American mixed martial arts commentator
{{Disambiguation, geo ...
Anik may refer to: * Anik (satellite), satellites launched by Canadian telecommunications company Telesat * Anik, Iran, a village in South Khorasan Province, Iran * Anik Mountain * Anik Bissonnette, a Canadian ballet dancer * Anik Jean (born 1977), Canadian pop and rock singer, actress and screenwriter * Anik Matern, a Canadian actress and founder of the Dynamic Theater Factory * Jon Anik Jon Anik (born July 3, 1978) is an American mixed martial arts commentator who currently works for the Ultimate Fighting Championship (UFC). He was an anchor with ESPN for more than 5 years before moving to the UFC as a play-by-play commentator i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-definition Television
High-definition television (HD or HDTV) describes a television system which provides a substantially higher image resolution than the previous generation of technologies. The term has been used since 1936; in more recent times, it refers to the generation following standard-definition television (SDTV), often abbreviated to HDTV or HD-TV. It is the current de facto standard video format used in most broadcasts: terrestrial broadcast television, cable television, satellite television and Blu-ray Discs. Formats HDTV may be transmitted in various formats: * 720p (1280 horizontal pixels × 720 lines): 921,600 pixels * 1080i (1920×1080) interlaced scan: 1,036,800 pixels (~1.04 MP). * 1080p (1920×1080) progressive scan: 2,073,600 pixels (~2.07 MP). ** Some countries also use a non-standard CEA resolution, such as 1440×1080i: 777,600 pixels (~0.78 MP) per field or 1,555,200 pixels (~1.56 MP) per frame When transmitted at two megapixels per frame, HDTV provides about five times ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
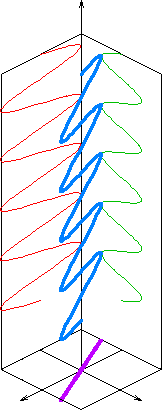
Linear Polarization
In electrodynamics, linear polarization or plane polarization of electromagnetic radiation is a confinement of the electric field vector or magnetic field vector to a given plane along the direction of propagation. The term ''linear polarization'' (French: ''polarisation rectiligne'') was coined by Augustin-Jean Fresnel in 1822.A. Fresnel, "Mémoire sur la double réfraction que les rayons lumineux éprouvent en traversant les aiguilles de cristal de roche suivant les directions parallèles à l'axe", read 9 December 1822; printed in H. de Senarmont, E. Verdet, and L. Fresnel (eds.), ''Oeuvres complètes d'Augustin Fresnel'', vol. 1 (1866), pp.731–51; translated as "Memoir on the double refraction that light rays undergo in traversing the needles of quartz in the directions parallel to the axis", , 2021 (open access); §9. See '' polarization'' and '' plane of polarization'' for more information. The orientation of a linearly polarized electromag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Polarization
In electrodynamics, circular polarization of an electromagnetic wave is a polarization state in which, at each point, the electromagnetic field of the wave has a constant magnitude and is rotating at a constant rate in a plane perpendicular to the direction of the wave. In electrodynamics, the strength and direction of an electric field is defined by its electric field vector. In the case of a circularly polarized wave, as seen in the accompanying animation, the tip of the electric field vector, at a given point in space, relates to the phase of the light as it travels through time and space. At any instant of time, the electric field vector of the wave indicates a point on a helix oriented along the direction of propagation. A circularly polarized wave can rotate in one of two possible senses: clockwise or ''right-handed circular polarization (RHCP)'' in which the electric field vector rotates in a right-hand sense with respect to the direction of propagation, and counter-cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Must-carry
In cable television, governments apply a must-carry regulation stating that locally licensed television stations must be carried on a cable provider's system. North America Canada Under current CRTC regulations, the lowest tier of service on all Canadian television providers may not be priced higher than $25 per-month, and must include all local Canadian broadcast television channels, local legislative and educational services, and all specialty services that have 9(1)(h) must-carry status. All specialty channels licensed by the CRTC as a mainstream news channel must also be offered by all television providers, although they do not necessarily have to be on the lowest tier of service. In the mid-to-late 1970s, the CRTC implemented a rule that a cable system must carry a broadcast television station at no cost to the broadcaster so long as the transmitter emitted an equivalent isotropically radiated power of at least 5 watts. This CRTC rule may have changed over the years, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)