Linear polarization on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
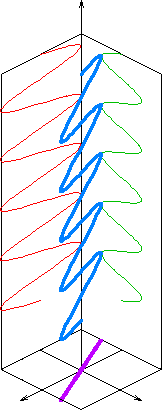 In
In
Animation of Linear Polarization (on YouTube)Comparison of Linear Polarization with Circular and Elliptical Polarizations (YouTube Animation)
{{FS1037C Polarization (waves) ja:直線偏光 pl:Polaryzacja_fali#Polaryzacja_liniowa
 In
In electrodynamics
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge via electromagnetic fields. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental forces of nature. It is the dominant force in the interacti ...
, linear polarization or plane polarization of electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a self-propagating wave of the electromagnetic field that carries momentum and radiant energy through space. It encompasses a broad spectrum, classified by frequency or its inverse, wavelength ...
is a confinement of the electric field
An electric field (sometimes called E-field) is a field (physics), physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles such as electrons. In classical electromagnetism, the electric field of a single charge (or group of charges) descri ...
vector or magnetic field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
vector to a given plane along the direction of propagation. The term ''linear polarization'' (French: ''polarisation rectiligne'') was coined by Augustin-Jean Fresnel
Augustin-Jean Fresnel (10 May 1788 – 14 July 1827) was a French civil engineer and physicist whose research in optics led to the almost unanimous acceptance of the wave theory of light, excluding any remnant of Isaac Newton, Newton's c ...
in 1822.A. Fresnel, "Mémoire sur la double réfraction que les rayons lumineux éprouvent en traversant les aiguilles de cristal de roche suivant les directions parallèles à l'axe", read 9 December 1822; printed in H. de Senarmont, E. Verdet, and L. Fresnel (eds.), ''Oeuvres complètes d'Augustin Fresnel'', vol. 1 (1866), pp.731–51; translated as "Memoir on the double refraction that light rays undergo in traversing the needles of quartz in the directions parallel to the axis", , 2021 (open access); §9. See '' polarization'' and ''plane of polarization
For light and other electromagnetic radiation, the plane of polarization is the plane (geometry), plane spanned by the direction of propagation and either the electric vector or the magnetic vector, depending on the convention. It can be defined ...
'' for more information.
The orientation of a linearly polarized electromagnetic wave is defined by the direction of the electric field
An electric field (sometimes called E-field) is a field (physics), physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles such as electrons. In classical electromagnetism, the electric field of a single charge (or group of charges) descri ...
vector. For example, if the electric field vector is vertical (alternately up and down as the wave travels) the radiation is said to be vertically polarized.
Mathematical description
The classicalsinusoidal
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or sinusoid (symbol: ∿) is a periodic wave whose waveform (shape) is the trigonometric sine function. In mechanics, as a linear motion over time, this is '' simple harmonic motion''; as rotation, it correspond ...
plane wave solution of the electromagnetic wave equation
The electromagnetic wave equation is a second-order partial differential equation that describes the propagation of electromagnetic waves through a medium or in a vacuum. It is a three-dimensional form of the wave equation. The homogeneous for ...
for the electric
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
and magnetic
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that occur through a magnetic field, which allows objects to attract or repel each other. Because both electric currents and magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, m ...
fields is (cgs units)
:
:
for the magnetic field, where k is the wavenumber
In the physical sciences, the wavenumber (or wave number), also known as repetency, is the spatial frequency of a wave. Ordinary wavenumber is defined as the number of wave cycles divided by length; it is a physical quantity with dimension of ...
,
:
is the angular frequency
In physics, angular frequency (symbol ''ω''), also called angular speed and angular rate, is a scalar measure of the angle rate (the angle per unit time) or the temporal rate of change of the phase argument of a sinusoidal waveform or sine ...
of the wave, and is the speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted , is a universal physical constant exactly equal to ). It is exact because, by international agreement, a metre is defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time i ...
.
Here is the amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of am ...
of the field and
:
is the Jones vector
In optics, polarized light can be described using the Jones calculus, invented by R. C. Jones in 1941. Polarized light is represented by a Jones vector, and linear optical elements are represented by ''Jones matrices''. When light crosses an opt ...
in the x-y plane.
The wave is linearly polarized when the phase angles are equal,
:.
This represents a wave polarized at an angle with respect to the x axis. In that case, the Jones vector can be written
:.
The state vectors for linear polarization in x or y are special cases of this state vector.
If unit vectors are defined such that
:
and
:
then the polarization state can be written in the "x-y basis" as
:.
See also
* Sinusoidal plane-wave solutions of the electromagnetic wave equation * Polarization **Circular polarization
In electrodynamics, circular polarization of an electromagnetic wave is a polarization state in which, at each point, the electromagnetic field of the wave has a constant magnitude and is rotating at a constant rate in a plane perpendicular to ...
** Elliptical polarization
**Plane of polarization
For light and other electromagnetic radiation, the plane of polarization is the plane (geometry), plane spanned by the direction of propagation and either the electric vector or the magnetic vector, depending on the convention. It can be defined ...
* Photon polarization
References
*External links
Animation of Linear Polarization (on YouTube)
{{FS1037C Polarization (waves) ja:直線偏光 pl:Polaryzacja_fali#Polaryzacja_liniowa