|
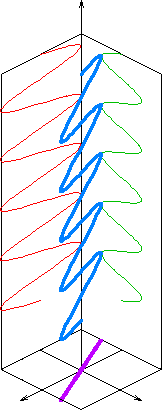
Linear Polarization
In electrodynamics, linear polarization or plane polarization of electromagnetic radiation is a confinement of the electric field vector or magnetic field vector to a given plane along the direction of propagation. The term ''linear polarization'' (French: ''polarisation rectiligne'') was coined by Augustin-Jean Fresnel in 1822.A. Fresnel, "Mémoire sur la double réfraction que les rayons lumineux éprouvent en traversant les aiguilles de cristal de roche suivant les directions parallèles à l'axe", read 9 December 1822; printed in H. de Senarmont, E. Verdet, and L. Fresnel (eds.), ''Oeuvres complètes d'Augustin Fresnel'', vol. 1 (1866), pp.731–51; translated as "Memoir on the double refraction that light rays undergo in traversing the needles of quartz in the directions parallel to the axis", , 2021 (open access); §9. See '' polarization'' and ''plane of polarization'' for more information. The orientation of a linearly polarized electromagn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Polarization Schematic
In mathematics, the term ''linear'' is used in two distinct senses for two different properties: * linearity of a ''function'' (or '' mapping''); * linearity of a ''polynomial''. An example of a linear function is the function defined by f(x)=(ax,bx) that maps the real line to a line in the Euclidean plane R2 that passes through the origin. An example of a linear polynomial in the variables X, Y and Z is aX+bY+cZ+d. Linearity of a mapping is closely related to '' proportionality''. Examples in physics include the linear relationship of voltage and current in an electrical conductor (Ohm's law), and the relationship of mass and weight. By contrast, more complicated relationships, such as between velocity and kinetic energy, are ''nonlinear''. Generalized for functions in more than one dimension, linearity means the property of a function of being compatible with addition and scaling, also known as the superposition principle. Linearity of a polynomial means that its degree i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavenumber
In the physical sciences, the wavenumber (or wave number), also known as repetency, is the spatial frequency of a wave. Ordinary wavenumber is defined as the number of wave cycles divided by length; it is a physical quantity with dimension of reciprocal length, expressed in SI units of cycles per metre or reciprocal metre (m−1). Angular wavenumber, defined as the wave phase divided by time, is a quantity with dimension of angle per length and SI units of radians per metre. They are analogous to temporal frequency, respectively the '' ordinary frequency'', defined as the number of wave cycles divided by time (in cycles per second or reciprocal seconds), and the ''angular frequency'', defined as the phase angle divided by time (in radians per second). In multidimensional systems, the wavenumber is the magnitude of the '' wave vector''. The space of wave vectors is called ''reciprocal space''. Wave numbers and wave vectors play an essential role in optics and the physics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photon Polarization
Photon polarization is the quantum mechanical description of the classical polarized sinusoidal plane electromagnetic wave. An individual photon can be described as having right or left circular polarization, or a superposition of the two. Equivalently, a photon can be described as having horizontal or vertical linear polarization, or a superposition of the two. The description of photon polarization contains many of the physical concepts and much of the mathematical machinery of more involved quantum descriptions, such as the quantum mechanics of an electron in a potential well. Polarization is an example of a qubit degree of freedom, which forms a fundamental basis for an understanding of more complicated quantum phenomena. Much of the mathematical machinery of quantum mechanics, such as state vectors, probability amplitudes, unitary operators, and Hermitian operators, emerge naturally from the classical Maxwell's equations in the description. The quantum polarizatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plane Of Polarization
For light and other electromagnetic radiation, the plane of polarization is the plane (geometry), plane spanned by the direction of propagation and either the electric vector or the magnetic vector, depending on the convention. It can be defined for polarization (physics), polarized light, remains fixed in space for ''linear polarization, linearly-polarized'' light, and undergoes axial rotation for ''circular polarization, circularly-polarized'' light. Unfortunately the two conventions are contradictory. As originally defined by Étienne-Louis Malus in 1811,Buchwald, 1989, p.54. the plane of polarization coincided (although this was not known at the time) with the plane containing the direction of propagation and the ''magnetic'' vector. In modern literature, the term ''plane of polarization'', if it is used at all, is likely to mean the plane containing the direction of propagation and the ''electric'' vector, because the electric field has the greater propensity to interact with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elliptical Polarization
In electrodynamics, elliptical polarization is the polarization of electromagnetic radiation such that the tip of the electric field vector describes an ellipse in any fixed plane intersecting, and normal to, the direction of propagation. An elliptically polarized wave may be resolved into two linearly polarized waves in phase quadrature, with their polarization planes at right angles to each other. Since the electric field can rotate clockwise or counterclockwise as it propagates, elliptically polarized waves exhibit chirality. ''Circular polarization'' and ''linear polarization'' can be considered to be special cases of ''elliptical polarization''. This terminology was introduced by Augustin-Jean Fresnel in 1822,A. Fresnel, "Mémoire sur la double réfraction que les rayons lumineux éprouvent en traversant les aiguilles de cristal de roche suivant les directions parallèles à l'axe", read 9 December 1822; printed in H. de Senarmont, E. Verdet, and L. Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Polarization
In electrodynamics, circular polarization of an electromagnetic wave is a polarization state in which, at each point, the electromagnetic field of the wave has a constant magnitude and is rotating at a constant rate in a plane perpendicular to the direction of the wave. In electrodynamics, the strength and direction of an electric field is defined by its electric field vector. In the case of a circularly polarized wave, the tip of the electric field vector, at a given point in space, relates to the phase of the light as it travels through time and space. At any instant of time, the electric field vector of the wave indicates a point on a helix oriented along the direction of propagation. A circularly polarized wave can rotate in one of two possible senses: ''right-handed circular polarization (RHCP)'' in which the electric field vector rotates in a right-hand sense with respect to the direction of propagation, and ''left-handed circular polarization (LHCP)'' in which the vecto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinusoidal Plane-wave Solutions Of The Electromagnetic Wave Equation
Sinusoidal plane-wave solutions are particular solutions to the wave equation. The general solution of the electromagnetic wave equation in homogeneous, linear, time-independent media can be written as a linear superposition of plane-waves of different frequencies and polarizations. The treatment in this article is classical but, because of the generality of Maxwell's equations for electrodynamics, the treatment can be converted into the quantum mechanical treatment with only a reinterpretation of classical quantities (aside from the quantum mechanical treatment needed for charge and current densities). The reinterpretation is based on the theories of Max Planck and the interpretations by Albert Einstein of those theories and of other experiments. The quantum generalization of the classical treatment can be found in the articles on photon polarization and photon dynamics in the double-slit experiment. Explanation Experimentally, every light signal can be decomposed int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jones Vector
In optics, polarized light can be described using the Jones calculus, invented by R. C. Jones in 1941. Polarized light is represented by a Jones vector, and linear optical elements are represented by ''Jones matrices''. When light crosses an optical element the resulting polarization of the emerging light is found by taking the product of the Jones matrix of the optical element and the Jones vector of the incident light. Note that Jones calculus is only applicable to light that is already fully polarized. Light which is randomly polarized, partially polarized, or incoherent must be treated using Mueller calculus. Jones vector The Jones vector describes the polarization of light in free space or another homogeneous isotropic non-attenuating medium, where the light can be properly described as transverse waves. Suppose that a monochromatic plane wave of light is travelling in the positive ''z''-direction, with angular frequency ''ω'' and wave vector k = (0,0,''k''), where th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of amplitude (see below), which are all functions of the magnitude of the differences between the variable's extreme values. In older texts, the phase of a periodic function is sometimes called the amplitude. Definitions Peak amplitude and semi-amplitude For symmetric periodic waves, like sine waves or triangle waves, ''peak amplitude'' and ''semi amplitude'' are the same. Peak amplitude In audio system measurements, telecommunications and others where the measurand is a signal that swings above and below a reference value but is not sinusoidal, peak amplitude is often used. If the reference is zero, this is the maximum absolute value of the signal; if the reference is a mean value ( DC component), the peak amplitude is the maximum ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed Of Light
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted , is a universal physical constant exactly equal to ). It is exact because, by international agreement, a metre is defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of second. The speed of light is invariant (physics), the same for all observers, no matter their relative velocity. It is the upper limit for the speed at which Information#Physics_and_determinacy, information, matter, or energy can travel through Space#Relativity, space. All forms of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, travel at the speed of light. For many practical purposes, light and other electromagnetic waves will appear to propagate instantaneously, but for long distances and sensitive measurements, their finite speed has noticeable effects. Much starlight viewed on Earth is from the distant past, allowing humans to study the history of the universe by viewing distant objects. When Data communication, comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Frequency
In physics, angular frequency (symbol ''ω''), also called angular speed and angular rate, is a scalar measure of the angle rate (the angle per unit time) or the temporal rate of change of the phase argument of a sinusoidal waveform or sine function (for example, in oscillations and waves). Angular frequency (or angular speed) is the magnitude of the pseudovector quantity '' angular velocity''. (UP1) Angular frequency can be obtained multiplying '' rotational frequency'', ''ν'' (or ordinary ''frequency'', ''f'') by a full turn (2 radians): . It can also be formulated as , the instantaneous rate of change of the angular displacement, ''θ'', with respect to time, ''t''. (11 pages) Unit In SI[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, electric currents, and electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function (mathematics), function assigning a Euclidean vector, vector to each point of space, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |