|
Stylus Records
A stylus (plural styli or styluses) is a writing utensil or a small tool for some other form of marking or shaping, for example, in pottery. It can also be a computer accessory that is used to assist in navigating or providing more precision when using touchscreens. It usually refers to a narrow elongated staff, similar to a modern ballpoint pen. Many styluses are heavily curved to be held more easily. Another widely used writing tool is the stylus used by blind users in conjunction with the slate for punching out the dots in Braille. Etymology The English word ''stylus'' has two plurals: ''styli'' and ''styluses''. The original Latin word was spelled ; the spelling ''stylus'' arose from an erroneous connection with Greek (), 'pillar'.''Oxford Latin Dictionary'', s.v. "stilus" (2012). The Latin word had several meanings, including "a long, sharply pointed piece of metal; the stem of a plant; a pointed instrument for incising letters; the stylus (as used in literary composi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Table With Was And Stylus Roman Times
Table may refer to: * Table (furniture), a piece of furniture with a flat surface and one or more legs * Table (landform), a flat area of land * Table (information), a data arrangement with rows and columns * Table (database), how the table data arrangement is used within databases * Calligra Tables, a spreadsheet application * Mathematical table * Table (parliamentary procedure) * Tables (board game) * Table, surface of the sound board (music) of a string instrument * ''Al-Ma'ida'', the fifth ''surah'' of the Qur'an, usually translated as “The Table” * Water table See also * Spreadsheet, a computer application * Table cut, a type of diamond cut * The Table (other) * Table Mountain (other) * Table Rock (other) * Tabler (other) * Tablet (other) Tablet may refer to: Medicine * Tablet (pharmacy), a mixture of pharmacological substances pressed into a small cake or bar, colloquially called a "pill" Computing * Tablet computer, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and Corsica. Crete rests about south of the Greek mainland, and about southwest of Anatolia. Crete has an area of and a coastline of 1,046 km (650 mi). It bounds the southern border of the Aegean Sea, with the Sea of Crete (or North Cretan Sea) to the north and the Libyan Sea (or South Cretan Sea) to the south. Crete and a number of islands and islets that surround it constitute the Region of Crete ( el, Περιφέρεια Κρήτης, links=no), which is the southernmost of the 13 top-level administrative units of Greece, and the fifth most populous of Greece's regions. Its capital and largest city is Heraklion, on the north shore of the island. , the region had a population of 636,504. The Dodecanese are located to the no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embossing (paper)
Embossing and debossing are the processes of creating either raised or recessed relief images and designs in paper and other materials. An embossed pattern is raised against the background, while a debossed pattern is sunken into the surface of the material but might protrude somewhat on the reverse side. Techniques Often used in combination with foil stamping, embossing alters the surface of paper stock or other substrates by providing a three-dimensional or raised effect on selected areas. The procedure requires the use of two dies: one that is raised and one that is recessed. The dies fit into each other so that when the paper is pressed between them, the raised die forces the stock into the recessed die and creates the embossed impression. A specific level of pressure is applied to the dies in order to squeeze the fibers of the paper, which results in a permanently raised area in the paper. When the dies are produced, a die maker engraves the desired image into several me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Paper
Carbon paper (originally carbonic paper) consists of sheets of paper which create one or more copies simultaneously with the creation of an original document when inscribed by a typewriter or ballpoint pen. History In 1801, Pellegrino Turri, an Italian inventor, invented carbon paper to provide the ink for his mechanical typing machine, one of the first typewriters. Ralph Wedgwood obtained the first patent for carbon paper in 1806. Carbon paper in its original form was paper coated on one side with a layer of a loosely bound dry ink or pigmented coating, bound with wax. The manufacture of carbon paper was formerly the largest consumer of montan wax. In 1954 the Columbia Ribbon & Carbon Manufacturing Company filed a patent for what became known in the trade as solvent carbon paper: the coating was changed from wax-based to polymer-based. The manufacturing process changed from a hot-melt method to a solvent-applied coating or set of coatings. It was then possible to use po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Transfer
Dry transfers (also called rub-ons or rubdowns) are decals that can be applied without the use of water or other solvent. The decal itself is on a backing material such as paper or plastic sheeting much like a transparency. The dry transfer is placed in the desired location with the backing side up. The decal is then applied by burnishing the backing with a stylus or similar object such as a ballpoint pen. The contact side of the decal includes a pressure-sensitive adhesive; the combination of heat and pressure causes the decal to stick more strongly to the new surface than to the backing. When the backing is removed, the decal remains. This allows for ink only where needed even if the pattern is delicate, because the backing supports the decal while it is being applied. Dry transfers are used in manual technical drawing when standard graphic elements such as title blocks, forms, patterned lines, shading, piping or electronic schematic symbols need to be repetitively used. Use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
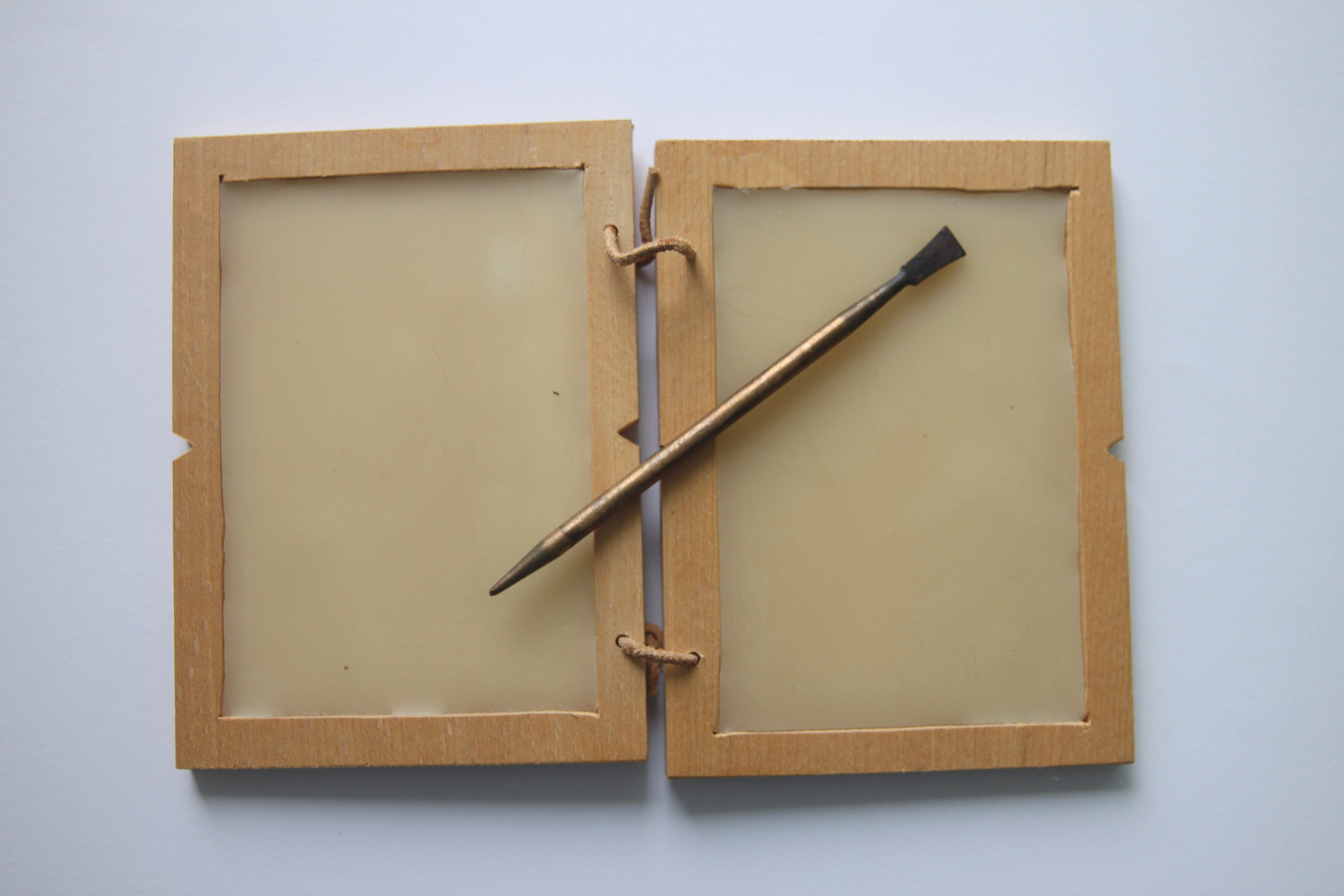
Wax Tablet
A wax tablet is a tablet made of wood and covered with a layer of wax, often linked loosely to a cover tablet, as a "double-leaved" diptych. It was used as a reusable and portable writing surface in Antiquity and throughout the Middle Ages. Cicero's letters make passing reference to the use of ''cerae'', and some examples of wax-tablets have been preserved in waterlogged deposits in the Roman fort at Vindolanda on Hadrian's Wall. Medieval wax tablet books are on display in several European museums. Writing on the wax surface was performed with a pointed instrument, a stylus. A straight-edged spatula-like implement (often placed on the opposite end of the stylus tip) would be used as an eraser. The modern expression of ''"a clean slate"'' equates to the Latin expression ''"tabula rasa"''. Wax tablets were used for a variety of purposes, from taking down students' or secretaries' notes to recording business accounts. Early forms of shorthand were used too. Use in antiquity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
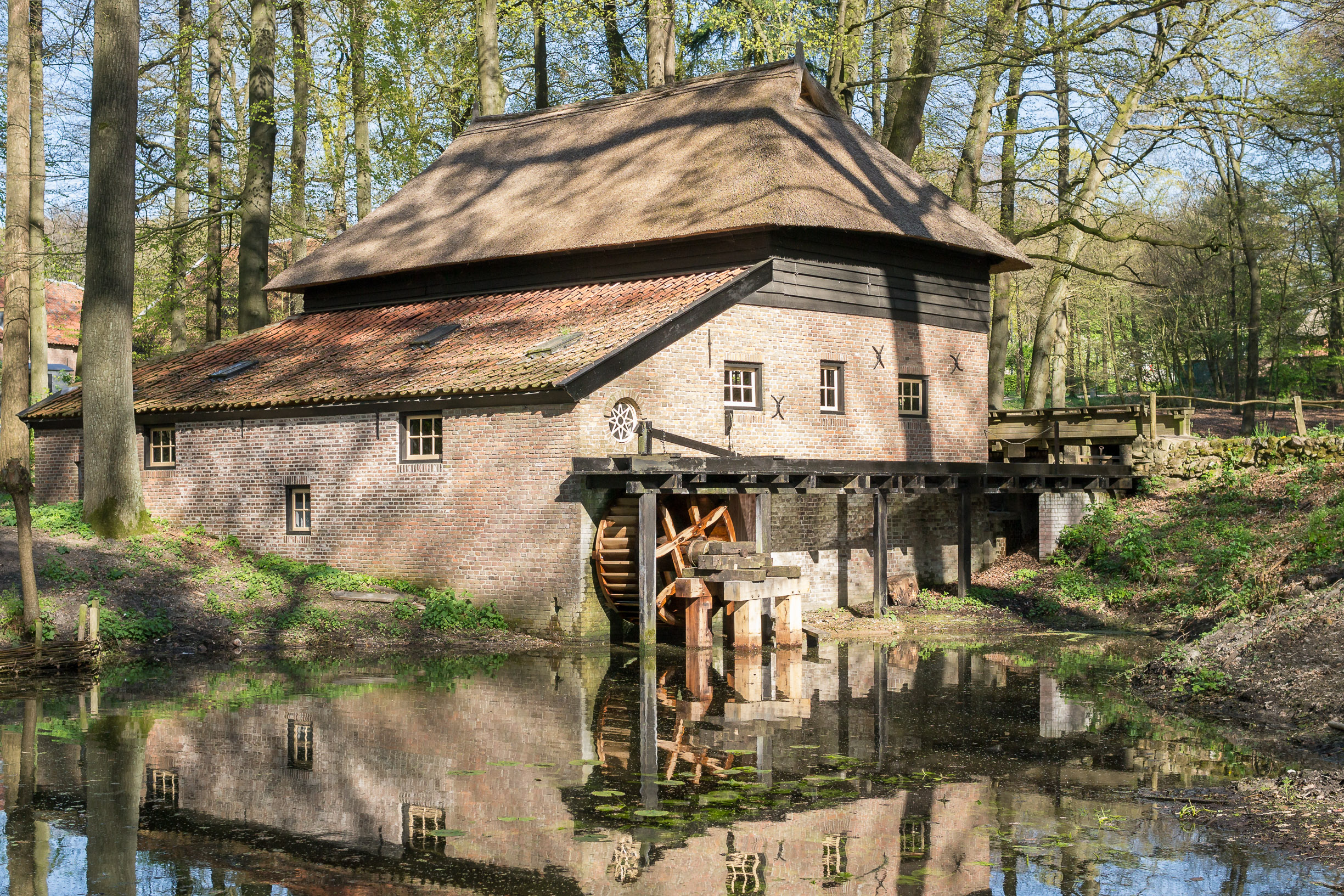
Paper Mill
A paper mill is a factory devoted to making paper from vegetable fibres such as wood pulp, old rags, and other ingredients. Prior to the invention and adoption of the Fourdrinier machine and other types of paper machine that use an endless belt, all paper in a paper mill was made by hand, one sheet at a time, by specialized laborers. History Historical investigations into the origin of the paper mill are complicated by differing definitions and loose terminology from modern authors: Many modern scholars use the term to refer indiscriminately to all kinds of mills, whether powered by humans, by animals or by water. Their propensity to refer to any ancient paper manufacturing center as a "mill", without further specifying its exact power source, has increased the difficulty of identifying the particularly efficient and historically important water-powered type. Human and animal-powered mills The use of human and animal powered mills was known to Muslim and Chinese paperma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slate (writing)
A slate is a thin piece of hard flat material, historically slate stone, which is used as a medium for writing. Composition The writing slate consisted of a piece of slate, typically either 4x6 inches or 7x10 inches, encased in a wooden frame. A slate pencil was used to write on the slate board. It was made from a softer and lighter coloured stone such as shale or chalk. Usually, a piece of cloth or slate sponge was used to clean it and this was sometimes attached with a string to the bottom of the writing slate. History The exact origins of the writing slate remain unclear. References to its use can be found in the fourteenth century and evidence suggests that it was used in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. The central time period for the writing slate, however, "appears to begin in the later eighteenth century, when developments in sea and land transport permitted the gradual expansion of slate quarrying in Wales and the growth of a substantial slate workshop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the Periodization, period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Renaissance). Around 1300, centuries of prosperity and growth in Europe came to a halt. A series of famines and Plague (disease), plagues, including the Great Famine of 1315–1317 and the Black Death, reduced the population to around half of what it had been before the calamities. Along with depopulation came social unrest and endemic warfare. France and England experienced serious peasant uprisings, such as the Jacquerie and the Peasants' Revolt, as well as over a century of intermittent conflict, the Hundred Years' War. To add to the many problems of the period, the unity of the Catholic Church was temporarily shattered by the Western Schism. Collectively, those events are sometimes called the Crisis of the Late Middle Ages. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
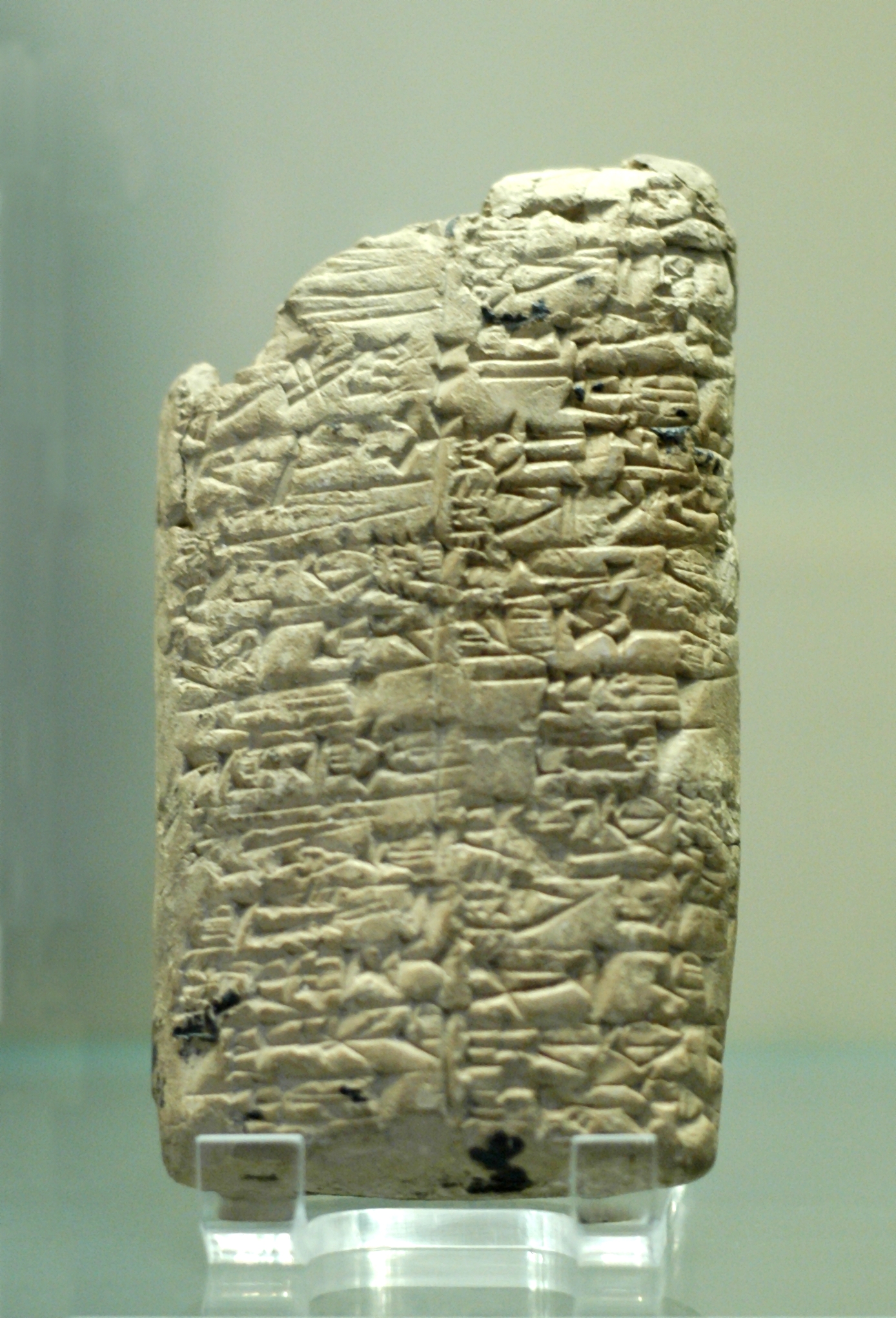
Clay Tablet
In the Ancient Near East, clay tablets (Akkadian ) were used as a writing medium, especially for writing in cuneiform, throughout the Bronze Age and well into the Iron Age. Cuneiform characters were imprinted on a wet clay tablet with a stylus often made of reed (reed pen). Once written upon, many tablets were dried in the sun or air, remaining fragile. Later, these unfired clay tablets could be soaked in water and recycled into new clean tablets. Other tablets, once written, were either deliberately fired in hot kilns, or inadvertently fired when buildings were burnt down by accident or during conflict, making them hard and durable. Collections of these clay documents made up the first archives. They were at the root of the first libraries. Tens of thousands of written tablets, including many fragments, have been found in the Middle East. Surviving tablet-based documents from the Minoan/ Mycenaean civilizations, are mainly those which were used for accounting. Tablets servin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
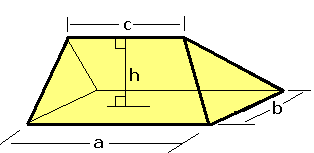
Wedge (geometry)
In solid geometry, a wedge is a polyhedron defined by two triangles and three trapezoid faces. A wedge has five faces, nine edges, and six vertices. A wedge is a subclass of the prismatoids with the base and opposite ridge in two parallel planes. A wedge can also be classified as a digonal cupola. Comparisons: * A wedge is a parallelepiped where a face has collapsed into a line. * A quadrilaterally-based pyramid is a wedge in which one of the edges between two trapezoid faces has collapsed into a point. Volume For a rectangle based wedge, the volume is :V = bh\left(\frac+\frac\right), where the base rectangle is ''a'' by ''b'', ''c'' is the apex edge length parallel to ''a'', and ''h'' the height from the base rectangle to the apex edge. Examples Wedges can be created from decomposition of other polyhedra. For instance, the dodecahedron can be divided into a central cube with 6 wedges covering the cube faces. The orientations of the wedges are such that the triangle and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |