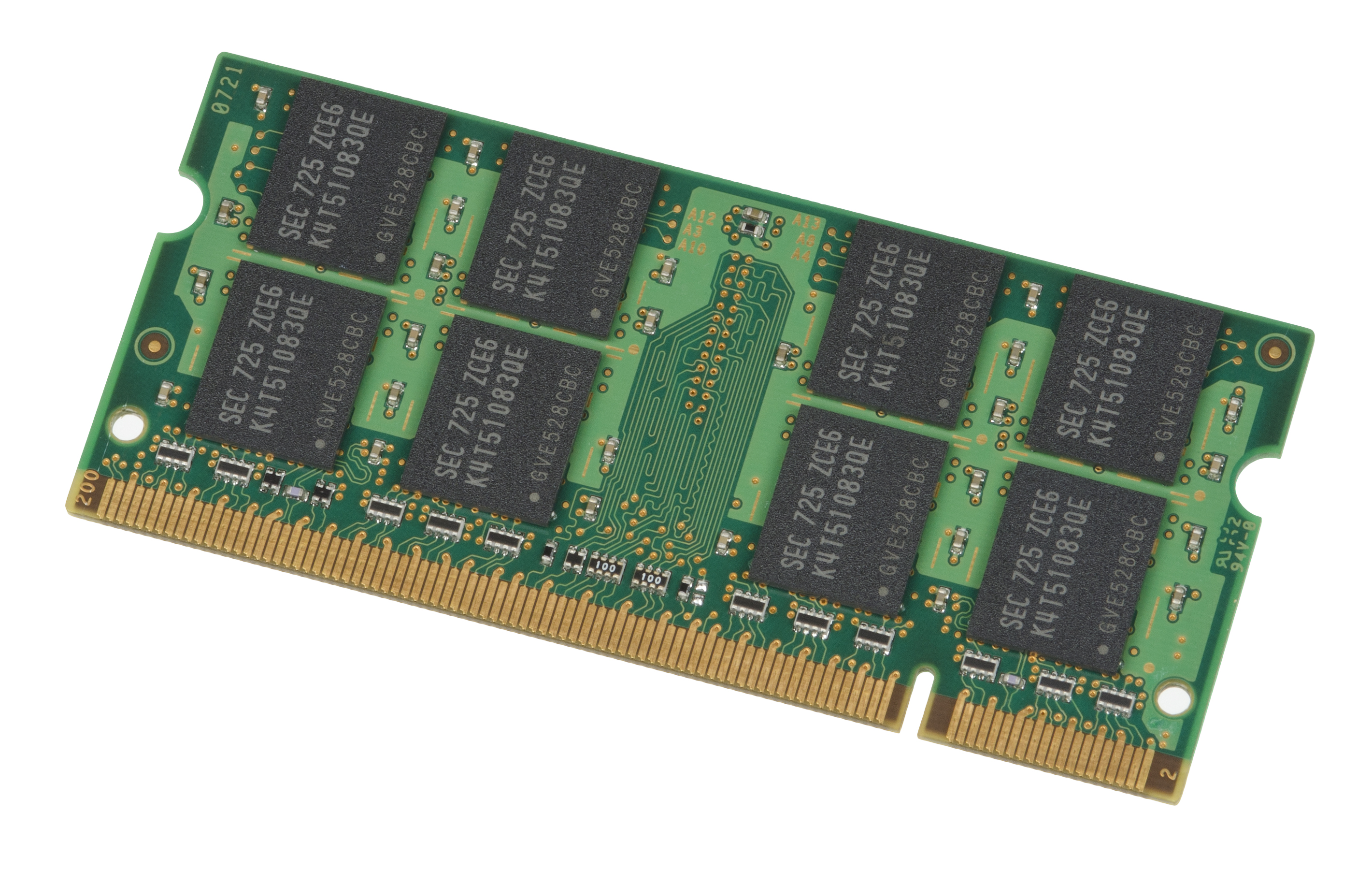
|
Stub Series Terminated Logic
Stub Series Terminated Logic (SSTL) is a group of electrical standards for driving transmission lines commonly used with DRAM based DDR memory IC's and memory modules. SSTL is primarily designed for driving the DDR (double-data-rate) SDRAM modules used in computer memory; however, it is also used in other applications, notably some PCI Express PHYs and other high-speed devices. Four voltage levels for SSTL are defined: *SSTL_3, 3.3 V, defined in EIA/JESD8-8 1996 *SSTL_2, 2.5 V, defined in EIA/JESD8-9B 2002 used in DDR among other things. *SSTL_18, 1.8 V, defined in EIA/JESD8-15A, used in DDR2 among other things. *SSTL_15, 1.5 V, used in DDR3 Double Data Rate 3 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR3 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) with a high bandwidth (" double data rate") interface, and has been in use since 2007. It is the higher-spee ... among other things. SSTL_3 uses a reference of 0.45 * VDDQ (1.5 V). SSTL_2 and SSTL_18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission Line
In electrical engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable or other structure designed to conduct electromagnetic waves in a contained manner. The term applies when the conductors are long enough that the wave nature of the transmission must be taken into account. This applies especially to radio-frequency engineering because the short wavelengths mean that wave phenomena arise over very short distances (this can be as short as millimetres depending on frequency). However, the theory of transmission lines was historically developed to explain phenomena on very long telegraph lines, especially submarine telegraph cables. Transmission lines are used for purposes such as connecting radio transmitters and receivers with their antennas (they are then called feed lines or feeders), distributing cable television signals, trunklines routing calls between telephone switching centres, computer network connections and high speed computer data buses. RF engineers commonly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DRAM
Dynamic random-access memory (dynamic RAM or DRAM) is a type of random-access semiconductor memory that stores each bit of data in a memory cell, usually consisting of a tiny capacitor and a transistor, both typically based on metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) technology. While most DRAM memory cell designs use a capacitor and transistor, some only use two transistors. In the designs where a capacitor is used, the capacitor can either be charged or discharged; these two states are taken to represent the two values of a bit, conventionally called 0 and 1. The electric charge on the capacitors gradually leaks away; without intervention the data on the capacitor would soon be lost. To prevent this, DRAM requires an external ''memory refresh'' circuit which periodically rewrites the data in the capacitors, restoring them to their original charge. This refresh process is the defining characteristic of dynamic random-access memory, in contrast to static random-access memory (SRA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Data Rate
In computing, a computer bus operating with double data rate (DDR) transfers data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal. This is also known as double pumped, dual-pumped, and double transition. The term toggle mode is used in the context of NAND flash memory. Overview The simplest way to design a clocked electronic circuit is to make it perform one transfer per full cycle (rise and fall) of a clock signal. This, however, requires that the clock signal changes twice per transfer, while the data lines change at most once per transfer. When operating at a high bandwidth, signal integrity limitations constrain the clock frequency. By using both edges of the clock, the data signals operate with the same limiting frequency, thereby doubling the data transmission rate. This technique has been used for microprocessor front-side busses, Ultra-3 SCSI, expansion buses ( AGP, PCI-X), graphics memory (GDDR), main memory (both RDRAM and DDR1 through DDR5), and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DDR SDRAM
Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR SDRAM) is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) class of memory integrated circuits used in computers. DDR SDRAM, also retroactively called DDR1 SDRAM, has been superseded by DDR2 SDRAM, DDR3 SDRAM, DDR4 SDRAM and DDR5 SDRAM. None of its successors are forward or backward compatible with DDR1 SDRAM, meaning DDR2, DDR3, DDR4 and DDR5 memory modules will not work in DDR1-equipped motherboards, and vice versa. Compared to single data rate ( SDR) SDRAM, the DDR SDRAM interface makes higher transfer rates possible by more strict control of the timing of the electrical data and clock signals. Implementations often have to use schemes such as phase-locked loops and self-calibration to reach the required timing accuracy. The interface uses double pumping (transferring data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal) to double data bus bandwidth without a corresponding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Memory
In computing, memory is a device or system that is used to store information for immediate use in a computer or related computer hardware and digital electronic devices. The term ''memory'' is often synonymous with the term ''primary storage'' or '' main memory''. An archaic synonym for memory is store. Computer memory operates at a high speed compared to storage that is slower but less expensive and higher in capacity. Besides storing opened programs, computer memory serves as disk cache and write buffer to improve both reading and writing performance. Operating systems borrow RAM capacity for caching so long as not needed by running software. If needed, contents of the computer memory can be transferred to storage; a common way of doing this is through a memory management technique called ''virtual memory''. Modern memory is implemented as semiconductor memory, where data is stored within memory cells built from MOS transistors and other components on an integrated c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
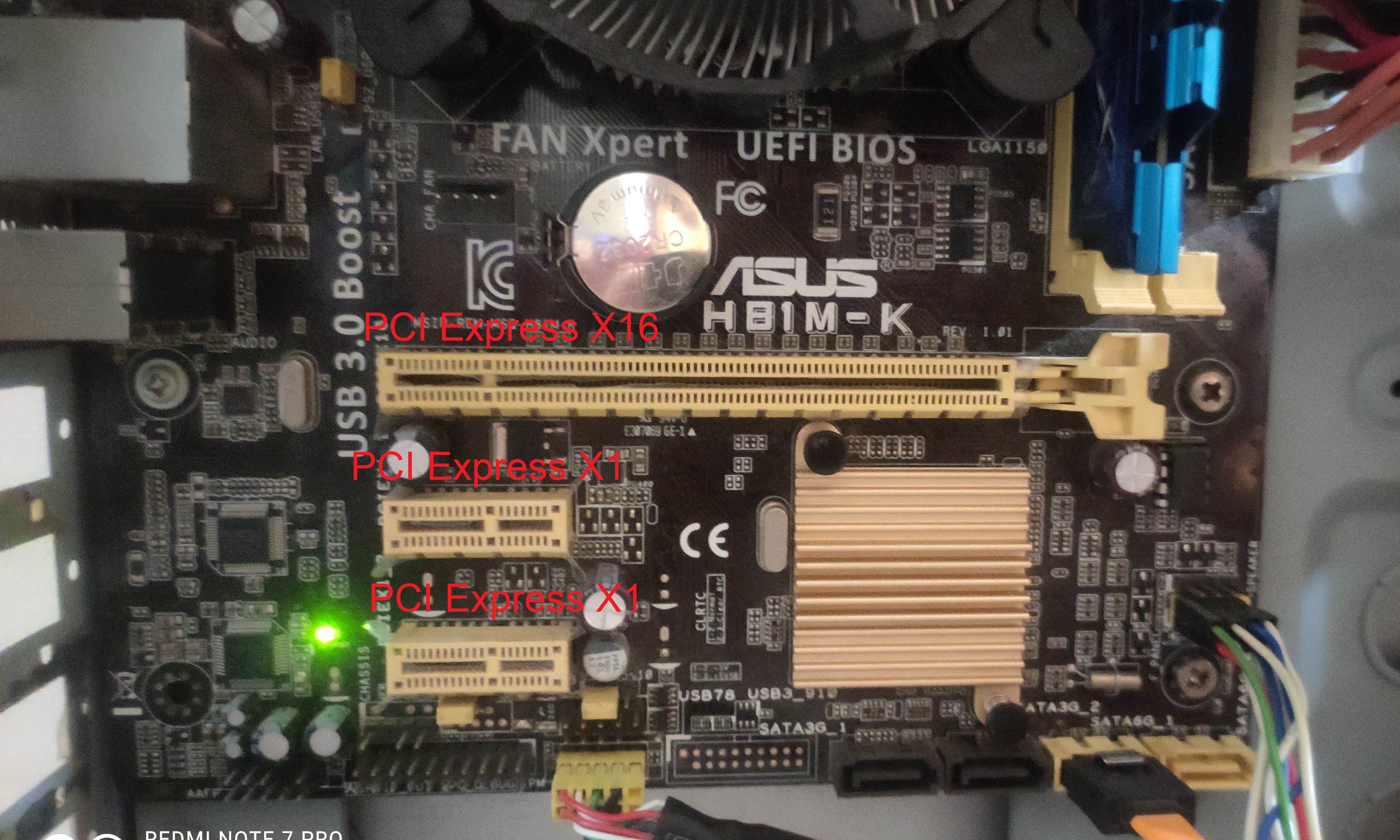
PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common motherboard interface for personal computers' graphics cards, hard disk drive host adapters, SSDs, Wi-Fi and Ethernet hardware connections. PCIe has numerous improvements over the older standards, including higher maximum system bus throughput, lower I/O pin count and smaller physical footprint, better performance scaling for bus devices, a more detailed error detection and reporting mechanism (Advanced Error Reporting, AER), and native hot-swap functionality. More recent revisions of the PCIe standard provide hardware support for I/O virtualization. The PCI Express electrical interface is measured by the number of simultaneous lanes. (A lane is a single send/receive line of data. The analogy is a highway with traffic in both directions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DDR2 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 2 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR2 SDRAM) is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) interface. It superseded the original DDR SDRAM specification, and was itself superseded by DDR3 SDRAM (launched in 2007). DDR2 DIMMs are neither forward compatible with DDR3 nor backward compatible with DDR. In addition to double pumping the data bus as in DDR SDRAM (transferring data on the rising and falling edges of the bus clock signal), DDR2 allows higher bus speed and requires lower power by running the internal clock at half the speed of the data bus. The two factors combine to produce a total of four data transfers per internal clock cycle. Since the DDR2 internal clock runs at half the DDR external clock rate, DDR2 memory operating at the same external data bus clock rate as DDR results in DDR2 being able to provide the same bandwidth but with better latency. Alternatively, DDR2 memory operating at twice the external data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DDR3
Double Data Rate 3 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR3 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) with a high bandwidth ("double data rate") interface, and has been in use since 2007. It is the higher-speed successor to DDR and DDR2 and predecessor to DDR4 synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) chips. DDR3 SDRAM is neither forward nor backward compatible with any earlier type of random-access memory (RAM) because of different signaling voltages, timings, and other factors. DDR3 is a DRAM interface specification. The actual DRAM arrays that store the data are similar to earlier types, with similar performance. The primary benefit of DDR3 SDRAM over its immediate predecessor DDR2 SDRAM, is its ability to transfer data at twice the rate (eight times the speed of its internal memory arrays), enabling higher bandwidth or peak data rates. The DDR3 standard permits DRAM chip capacities of up to 8 gigabits (Gbit), and up to four ranks o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Memory
In computing, memory is a device or system that is used to store information for immediate use in a computer or related computer hardware and digital electronic devices. The term ''memory'' is often synonymous with the term ''primary storage'' or '' main memory''. An archaic synonym for memory is store. Computer memory operates at a high speed compared to storage that is slower but less expensive and higher in capacity. Besides storing opened programs, computer memory serves as disk cache and write buffer to improve both reading and writing performance. Operating systems borrow RAM capacity for caching so long as not needed by running software. If needed, contents of the computer memory can be transferred to storage; a common way of doing this is through a memory management technique called ''virtual memory''. Modern memory is implemented as semiconductor memory, where data is stored within memory cells built from MOS transistors and other components on an integrated c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)