|
Storflaket
Storflaket is a permafrost plateau peat bog on the southern shore of Torneträsk lake, in northern Sweden. Storflaket together with Stordalen is one of the main sites of studying palsas and methane emissions in Scandinavia. The bog received its name, Storflaket, due to its relatively large extent and flat surface during the buildings works of Malmbanan The Iron Ore Line ( sv, Malmbanan) is a long railway line between Riksgränsen and Boden in Norrbotten County, Sweden, owned by Trafikverket (the Swedish Transport Administration). The line also contains two branches, from Kiruna to Svappav ... railroad in early 20th century. See also * Abisko Scientific Research Station * Stordalen Kiruna Bogs of Sweden Palsas Patterned grounds Landforms of Norrbotten County {{sweden-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palsa
Palsas are peat mounds with a permanently frozen peat and mineral soil core. They are a typical phenomenon in the polar and subpolar zone of discontinuous permafrost. One of their characteristics is having steep slopes that rises above the mire surface. This leads to the accumulation of large amounts of snow around them. The summits of the palsas are free of snow even in winter, because the wind carries the snow and deposits on the slopes and elsewhere on the flat mire surface. Palsas can be up to 150 m in diameter and can reach a height of 12 m. Permafrost is found on palsa mires only in the palsas themselves, and its formation is based on the physical properties of peat. Dry peat is a good insulator, but wet peat conducts heat better, and frozen peat is even better at conducting heat. This means that cold can penetrate deep into the peat layers, and that heat can easily flow from deeper wet layers in winter. Whereas the dry peat on the palsa surface insulates the frozen c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abisko Scientific Research Station
The Abisko Scientific Research Station (ANS) is a field research station managed by the Swedish Polar Research Secretariat. Situated on the south shore of Lake Torneträsk, it lies at the edge of the Abisko National Park. The station conducts ecological, geological, geomorphological and meteorological research in subarctic environments and each year about 500 scientists visit from all over the world. The varied geological, topographical and climatic conditions of the area allow it to be inhabited by a range of flora and fauna. These features, which have caused the area to be given National Park status, also make it an important place for scientific research, particularly of alpine and subalpine ecosystems. The station The first proper field station to be established in the area dates back to 1903, however the official station has only been affiliated with the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences since 1935. The station holds meteorological datasets extending back to 1913, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palsas
Palsas are peat mounds with a permanently frozen peat and mineral soil core. They are a typical phenomenon in the polar and subpolar zone of discontinuous permafrost. One of their characteristics is having steep slopes that rises above the mire surface. This leads to the accumulation of large amounts of snow around them. The summits of the palsas are free of snow even in winter, because the wind carries the snow and deposits on the slopes and elsewhere on the flat mire surface. Palsas can be up to 150 m in diameter and can reach a height of 12 m. Permafrost is found on palsa mires only in the palsas themselves, and its formation is based on the physical properties of peat. Dry peat is a good insulator, but wet peat conducts heat better, and frozen peat is even better at conducting heat. This means that cold can penetrate deep into the peat layers, and that heat can easily flow from deeper wet layers in winter. Whereas the dry peat on the palsa surface insulates the frozen c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peat Bog
A bog or bogland is a wetland that accumulates peat as a deposit of dead plant materials often mosses, typically sphagnum moss. It is one of the four main types of wetlands. Other names for bogs include mire, mosses, quagmire, and muskeg; alkaline mires are called fens. A baygall is another type of bog found in the forest of the Gulf Coast states in the United States.Watson, Geraldine Ellis (2000) ''Big Thicket Plant Ecology: An Introduction'', Third Edition (Temple Big Thicket Series #5). University of North Texas Press. Denton, Texas. 152 pp. Texas Parks and Wildlife. Ecological Mapping systems of Texas: West Gulf Coastal Plain Seepage Swamp and Baygall'. Retrieved 7 July 2020 They are often covered in heath or heather shrubs rooted in the sphagnum moss and peat. The gradual accumulation of decayed plant material in a bog functions as a carbon sink. Bogs occur where the water at the ground surface is acidic and low in nutrients. In contrast to fens, they derive most of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torneträsk
Torneträsk or Torne träsk (; Saami: ; Finnish and fit, Tornio or ) is a lake in Kiruna Municipality, Lapland, Norrbotten County in Sweden, in the Scandinavian Mountains. ''Träsk'' is the local word for ''lake'' (in Standard Swedish it means "swamp"). It is the sixth-largest lake in Sweden, with a total area of and a length of . The lake drains to the south-east through Torne river. South-west of the lake lies the Abisko National Park and the UNESCO World Heritage Site Laponian area. Torneträsk originated from the remnant of a glacier, which has given the lake its depth of , making it the second-deepest lake in Sweden. It is usually ice-covered from December through June, with variations dependent on temperature variations. Permafrost Permafrost is ground that continuously remains below 0 °C (32 °F) for two or more years, located on land or under the ocean. Most common in the Northern Hemisphere, around 15% of the Northern Hemisphere or 11% of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweden
Sweden, ; fi, Ruotsi; fit, Ruotti; se, Ruoŧŧa; smj, Svierik; sje, Sverji; sju, Sverje; sma, Sveerje or ; yi, שוועדן, Shvedn; rmu, Svedikko; rmf, Sveittiko. formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic country and the List of European countries by area, fifth-largest country in Europe. The Capital city, capital and largest city is Stockholm. Sweden has a population of 10.5 million, and a low population density of ; around 87% of Swedes reside in urban areas in the central and southern half of the country. Sweden’s urban areas together cover 1.5% of its land area. Because the country is so long, ranging from 55th parallel north, 55°N to 69th parallel north, 69°N, the climate of Sweden is diverse. Sweden has been inhabited since Prehistoric Sweden, prehistoric times, . T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stordalen, Sweden
Stordalen Mire (elevation 351 m) is a mire which lies in the subarctic region in northernmost Sweden. It is 10 km east of the town of Abisko close to Lake Torneträsk. It is a 25 ha palsa mire, which is common in the discontinuous permafrost zone. The mire has two major topographical features: elevated palsas and depressions. The palsas are dry, ombrotrophic plateaus (or hummocks) with permafrost cores that raise the peat surface above its surroundings that is the wet minerotrophic depressions, largely permafrost free and water saturated. The small-scale topography is often very patchy in its structure, creating an environment where localities nearby each other have distinct differences in moisture, permafrost and nutrient status, which creates differences in vegetation types. Of these subhabitats the vegetation in the dry parts consists mainly of mosses, lichens and dwarf shrubs, whereas the wet parts are dominated by sphagnum or tall graminoids. A peat layer up to 3 m de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methane Emissions
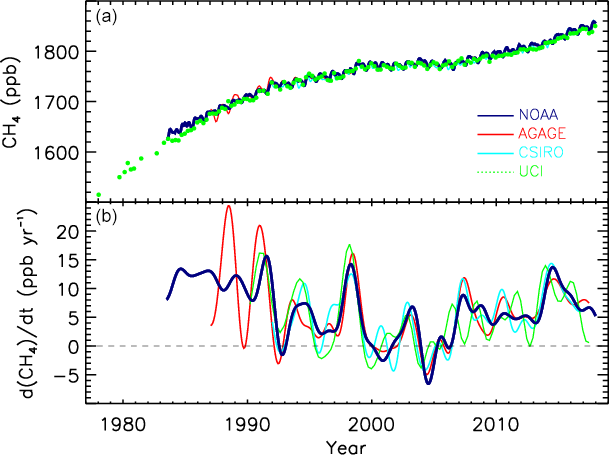
Increasing methane emissions are a major contributor to the rising concentration of greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere, and are responsible for up to one-third of near-term global heating. During 2019, about 60% (360 million tons) of methane released globally was from human activities, while natural sources contributed about 40% (230 million tons). Reducing methane emissions by capturing and utilizing the gas can produce simultaneous environmental and economic benefits. Since the Industrial Revolution, methane concentrations in the atmosphere have more than doubled, and about 20 percent of the warming the planet has experienced can be attributed to the gas. About one-third (33%) of anthropogenic emissions are from gas release during the extraction and delivery of fossil fuels; mostly due to gas venting and gas leaks from both active fossil fuel infrastructure and orphan wells. Russia is the world's top methane emitter from oil and gas. Animal agriculture is a similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malmbanan
The Iron Ore Line ( sv, Malmbanan) is a long railway line between Riksgränsen and Boden in Norrbotten County, Sweden, owned by Trafikverket (the Swedish Transport Administration). The line also contains two branches, from Kiruna to Svappavaara and from Gällivare to Koskullskulle. The term is often colloquially used to also include the Ofoten Line, from Riksgränsen to Narvik in Norway, and the northernmost part of the Main Line Through Upper Norrland from Boden to Luleå. The railway from Narvik to Luleå is long. The line is dominated by the ore freight trains operated by LKAB's subsidiary Malmtrafik from their mines to the Port of Narvik and the Port of Luleå. In addition, SJ operates passenger trains and CargoNet operates container freight trains. The Iron Ore Line is single track, electrified at and has a permitted axle load of . The Swedish part of the line is the northernmost railway in Sweden and the Norwegian part outside Narvik is the northernmost r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stordalen (Sweden)
Stordalen Mire (elevation 351 m) is a mire which lies in the subarctic region in northernmost Sweden. It is 10 km east of the town of Abisko close to Lake Torneträsk. It is a 25 ha palsa mire, which is common in the discontinuous permafrost zone. The mire has two major topographical features: elevated palsas and depressions. The palsas are dry, ombrotrophic plateaus (or hummocks) with permafrost cores that raise the peat surface above its surroundings that is the wet minerotrophic depressions, largely permafrost free and water saturated. The small-scale topography is often very patchy in its structure, creating an environment where localities nearby each other have distinct differences in moisture, permafrost and nutrient status, which creates differences in vegetation types. Of these subhabitats the vegetation in the dry parts consists mainly of mosses, lichens and dwarf shrubs, whereas the wet parts are dominated by sphagnum or tall graminoids. A peat layer up to 3 m deep c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiruna
(; se, Giron ; fi, Kiiruna ) is the northernmost city in Sweden, situated in the province of Lapland. It had 17,002 inhabitants in 2016 and is the seat of Kiruna Municipality (population: 23,167 in 2016) in Norrbotten County. The city was originally built in the 1890s to serve the Kiruna Mine. The Esrange Space Center was established in Kiruna in the 1960s. Also in Kiruna are the Institute of Space Physics and Luleå University of Technology's Department of Space Science. History Origins Archaeological findings have shown that the region around Kiruna has been inhabited for at least 6,000 years. Centuries before Kiruna was founded in 1900, the presence of iron ore at Kiirunavaara and Luossavaara had been known by the local Sami population. In 1696, Samuel Mört, a bookkeeper of the Kengis works, wrote on rumours about the presence of iron in the two hills.Kummu 1997, p. 96. The ore became better known after it was reported by Mangi, a Sami man, in 1736 to Swedish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)
