|
Stordalen (Sweden)
Stordalen Mire (elevation 351 m) is a mire which lies in the subarctic region in northernmost Sweden. It is 10 km east of the town of Abisko close to Lake Torneträsk. It is a 25 ha palsa mire, which is common in the discontinuous permafrost zone. The mire has two major topographical features: elevated palsas and depressions. The palsas are dry, ombrotrophic plateaus (or hummocks) with permafrost cores that raise the peat surface above its surroundings that is the wet minerotrophic depressions, largely permafrost free and water saturated. The small-scale topography is often very patchy in its structure, creating an environment where localities nearby each other have distinct differences in moisture, permafrost and nutrient status, which creates differences in vegetation types. Of these subhabitats the vegetation in the dry parts consists mainly of mosses, lichens and dwarf shrubs, whereas the wet parts are dominated by sphagnum or tall graminoids. A peat layer up to 3 m deep c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mire
A mire, peatland, or quagmire is a wetland area dominated by living peat-forming plants. Mires arise because of incomplete decomposition of organic matter, usually litter from vegetation, due to water-logging and subsequent anoxia. All types of mires share the common characteristic of being saturated with water, at least seasonally with actively forming peat, while having their own ecosystem. Like coral reefs, mires are unusual landforms that derive mostly from biological rather than physical processes, and can take on characteristic shapes and surface patterning. A quagmire is a floating (quaking) mire, bog, or any peatland being in a stage of hydrosere or hydrarch (hydroseral) succession, resulting in pond-filling yields underfoot. Ombrotrophic types of quagmire may be called quaking bog (quivering bog). Minerotrophic types can be named with the term quagfen. There are four types of mire: bog, fen, marsh and swamp. A bog is a mire that, due to its location relative to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abisko
Abisko (; se, Ábeskovvu) is a village in Sápmi (Lapland (Sweden), Lapland), in northern Sweden, roughly 250 km within the Arctic Circle, and near Abisko National Park, located 4 km west of the village. It had 85 inhabitants as of 2005. Permafrost is common around the village albeit this low altitude permafrost is disappearing because of global warming and increased snowfall. Transportation Daily passenger electric trains run by SJ AB connect Stockholm with the Norwegian city of Narvik, stopping at both the Abisko village (the name of that railway station is ''Abisko Östra'' [east]) and the Abisko Turiststation. Additional regional trains provide links along the Kiruna-Narvik stretch. Abisko is also reachable by car via the highway E10 which has linked Kiruna and Narvik since the early 1980s. Other local forms of transportation include hiking and dog-sledding in winter. A chair-lift provides access to a point below the summit of nearby Mt. Nuolja. Tourism The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torneträsk
Torneträsk or Torne träsk (; Saami: ; Finnish and fit, Tornio or ) is a lake in Kiruna Municipality, Lapland, Norrbotten County in Sweden, in the Scandinavian Mountains. ''Träsk'' is the local word for ''lake'' (in Standard Swedish it means " swamp"). It is the sixth-largest lake in Sweden, with a total area of and a length of . The lake drains to the south-east through Torne river. South-west of the lake lies the Abisko National Park and the UNESCO World Heritage Site Laponian area. Torneträsk originated from the remnant of a glacier, which has given the lake its depth of , making it the second-deepest lake in Sweden. It is usually ice-covered from December through June, with variations dependent on temperature variations. Permafrost is common in the land around the lake. This low elevation permafrost is disappearing because of global warming and increased snowfall. During the 1944 Operation Obviate of WWII, British bombers seeking to destroy the German battlesh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palsa
Palsas are peat mounds with a permanently frozen peat and mineral soil core. They are a typical phenomenon in the polar and subpolar zone of discontinuous permafrost. One of their characteristics is having steep slopes that rises above the mire surface. This leads to the accumulation of large amounts of snow around them. The summits of the palsas are free of snow even in winter, because the wind carries the snow and deposits on the slopes and elsewhere on the flat mire surface. Palsas can be up to 150 m in diameter and can reach a height of 12 m. Permafrost is found on palsa mires only in the palsas themselves, and its formation is based on the physical properties of peat. Dry peat is a good insulator, but wet peat conducts heat better, and frozen peat is even better at conducting heat. This means that cold can penetrate deep into the peat layers, and that heat can easily flow from deeper wet layers in winter. Whereas the dry peat on the palsa surface insulates the frozen co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permafrost
Permafrost is ground that continuously remains below 0 °C (32 °F) for two or more years, located on land or under the ocean. Most common in the Northern Hemisphere, around 15% of the Northern Hemisphere or 11% of the global surface is underlain by permafrost, with the total area of around 18 million km2. This includes substantial areas of Alaska, Greenland, Canada and Siberia. It can also be located on mountaintops in the Southern Hemisphere and beneath ice-free areas in the Antarctic. Permafrost does not have to be the first layer that is on the ground. It can be from an inch to several miles deep under the Earth's surface. It frequently occurs in ground ice, but it can also be present in non-porous bedrock. Permafrost is formed from ice holding various types of soil, sand, and rock in combination. Permafrost contains large amounts of biomass and decomposed biomass that has been stored as methane and carbon dioxide, making tundra soil a carbon sink. As global war ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ombrotrophic
Ombrotrophic ("cloud-fed"), from Ancient Greek ὄμβρος (''ómvros'') meaning "rain" and τροφή (''trofí'') meaning "food"), refers to Soil, soils or vegetation which receive all of their water and nutrients from precipitation, rather than from streams or springs. Such environments are hydrology, hydrologically isolated from the surrounding landscape, and since rain is acidic and very low in Plant nutrition, nutrients, they are home to organisms tolerant of acidic, low-nutrient environments. The vegetation of ombrotrophic peatlands is often bog, dominated by ''Sphagnum'' mosses. The hydrology of these environments are directly related to their climate, as precipitation is the water and nutrient source, and temperatures dictate how quickly water evaporates from these systems. Ombrotrophic circumstances may occur even in landscapes composed of limestone or other nutrient-rich substrates – for example, in high-rainfall areas, limestone boulders may be capped by acidic om ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minerotrophic
Minerotrophic refers to environments that receive nutrients primarily through groundwater that flows through mineral-rich soils or rock,Environment Canada (2014). Ontario wetland evaluation system: Northern Manual, 1st edition, version 3.2. Queen’s printer for Ontario. or surface water flowing over land. Minerotrophic, “minerogenous”, and “geogenous” are now often used interchangeably, although the latter two terms refer primarily to hydrological systems, while the former refers to nutrient dynamics. The hydrologic process behind minerotrophic wetlands results in water that has acquired dissolved chemicals which raise the nutrient levels and reduce the acidity. This in turn affects vegetation assemblages and diversity in the wetland in question.Brinson, M. M. (1993). A Hydrogeomorphic Classification for Wetlands. ''Environmental Laboratory (U.S.) & Engineer Research and Development Center (U.S.).'' Retrieved from https://erdc-library.erdc.dren.mil/jspui/bitstream/11681/6483/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2019 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 42.778), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in autumn 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander Macmillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the journal; ''Nature'' redoubled its efforts in exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
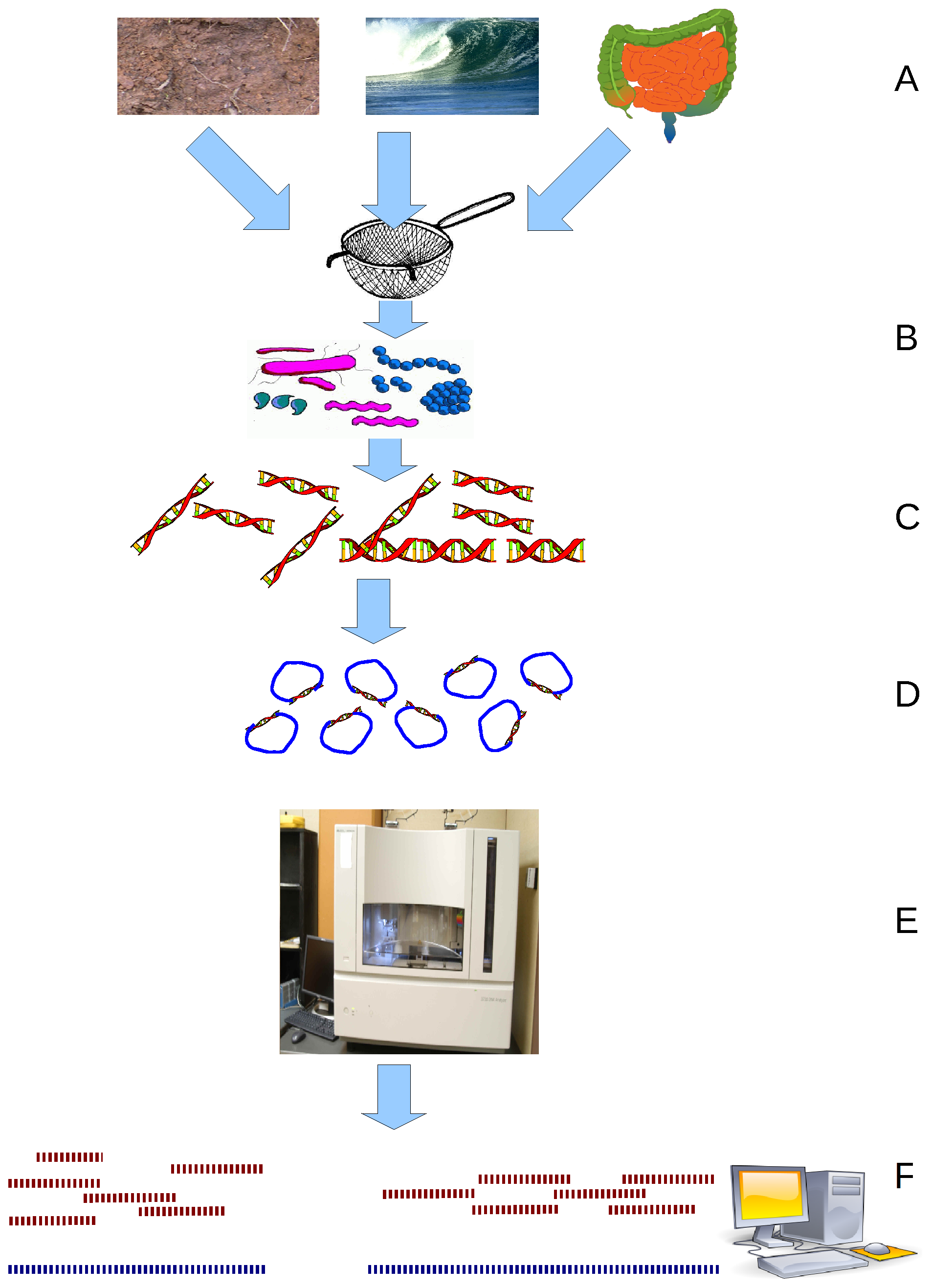
Metagenomics
Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental or clinical samples by a method called sequencing. The broad field may also be referred to as environmental genomics, ecogenomics, community genomics or microbiomics. While traditional microbiology and microbial genome sequencing and genomics rely upon cultivated clonal cultures, early environmental gene sequencing cloned specific genes (often the 16S rRNA gene) to produce a profile of diversity in a natural sample. Such work revealed that the vast majority of microbial biodiversity had been missed by cultivation-based methods. Because of its ability to reveal the previously hidden diversity of microscopic life, metagenomics offers a powerful lens for viewing the microbial world that has the potential to revolutionize understanding of the entire living world. As the price of DNA sequencing continues to fall, metagenomics now allows microbial ecology to be investigated at a much greater scale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binning (metagenomics)
In metagenomics, binning is the process of grouping reads or contigs and assigning them to individual genome. Binning methods can be based on either compositional features or alignment (similarity), or both. Introduction Metagenomic samples can contain reads from a huge number of organisms. For example, in a single gram of soil, there can be up to 18000 different types of organisms, each with its own genome. Metagenomic studies sample DNA from the whole community, and make it available as nucleotide sequences of certain length. In most cases, the incomplete nature of the obtained sequences makes it hard to assemble individual genes, much less recovering the full genomes of each organism. Thus, binning techniques represent a "best effort" to identify reads or contigs within certain genome known as Metagenome Assembled Genome (MAG). Taxonomy of MAGs can be inferred through placement into reference phylogenetic tree using algorithms like GTDB-Tk. The first studies that sampled DN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiruna
(; se, Giron ; fi, Kiiruna ) is the northernmost Stad (Sweden), city in Sweden, situated in the province of Lapland, Sweden, Lapland. It had 17,002 inhabitants in 2016 and is the seat of Kiruna Municipality (population: 23,167 in 2016) in Norrbotten County. The city was originally built in the 1890s to serve the Kiruna Mine. The Esrange Space Center was established in Kiruna in the 1960s. Also in Kiruna are the Institute of Space Physics (Sweden), Institute of Space Physics and Luleå University of Technology's Department of Space Science. History Origins Archaeological findings have shown that the region around Kiruna has been inhabited for at least 6,000 years. Centuries before Kiruna was founded in 1900, the presence of iron ore at Kiirunavaara and Luossavaara had been known by the local Sami people, Sami population. In 1696, Samuel Mört, a bookkeeper of the Kengis works, wrote on rumours about the presence of iron in the two hills.Kummu 1997, p. 96. The ore became b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bogs Of Sweden
A bog or bogland is a wetland that accumulates peat as a deposit of dead plant materials often mosses, typically sphagnum moss. It is one of the four main types of wetlands. Other names for bogs include mire, mosses, quagmire, and muskeg; alkaline mires are called fens. A baygall is another type of bog found in the forest of the Gulf Coast states in the United States.Watson, Geraldine Ellis (2000) ''Big Thicket Plant Ecology: An Introduction'', Third Edition (Temple Big Thicket Series #5). University of North Texas Press. Denton, Texas. 152 pp. Texas Parks and Wildlife. Ecological Mapping systems of Texas: West Gulf Coastal Plain Seepage Swamp and Baygall'. Retrieved 7 July 2020 They are often covered in heath or heather shrubs rooted in the sphagnum moss and peat. The gradual accumulation of decayed plant material in a bog functions as a carbon sink. Bogs occur where the water at the ground surface is acidic and low in nutrients. In contrast to fens, they derive most of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |