|
Steam Museums In The United States
Steam is a substance containing water in the gas phase, and sometimes also an aerosol of liquid water droplets, or air. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporization. Steam that is saturated or superheated is invisible; however, "steam" often refers to wet steam, the visible mist or aerosol of water droplets formed as water vapor condenses. Water increases in volume by 1,700 times at standard temperature and pressure; this change in volume can be converted into mechanical work by steam engines such as reciprocating piston type engines and steam turbines, which are a sub-group of steam engines. Piston type steam engines played a central role in the Industrial Revolution and modern steam turbines are used to generate more than 80% of the world's electricity. If liquid water comes in contact with a very hot surface or depressurizes quickly below its vapor pressure, it can create a steam explosion. Types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
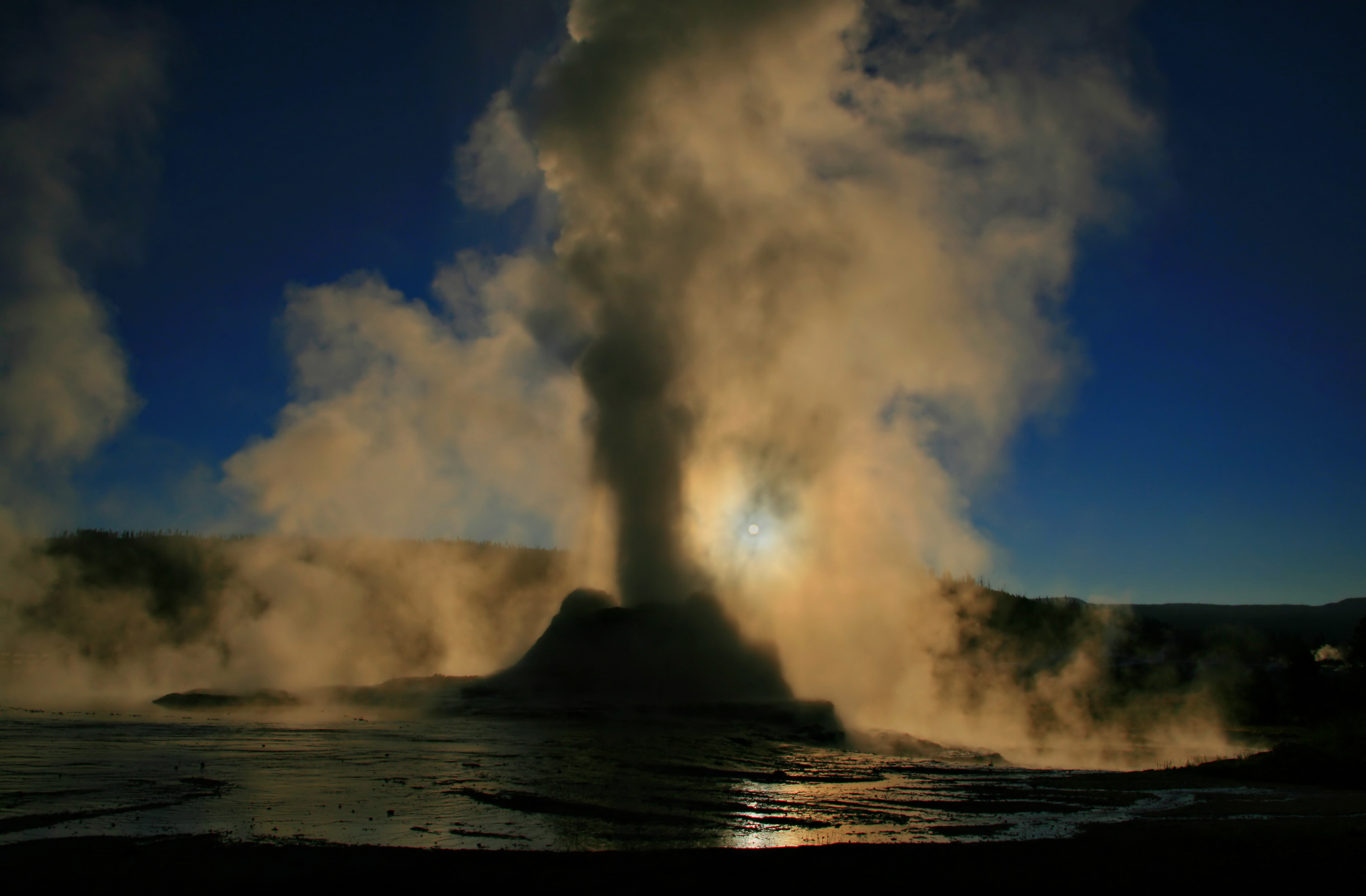
Steam Phase Eruption Of Castle Geyser
Steam is a substance containing water in the gas phase, and sometimes also an aerosol of liquid water droplets, or air. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporization. Steam that is saturated or superheated steam, superheated is invisible; however, "steam" often refers to wet steam, the visible mist or aerosol of water droplets formed as water vapor condensation, condenses. Water increases in volume by 1,700 times at standard temperature and pressure; this change in volume can be converted into work (physics), mechanical work by steam engines such as reciprocating engine, reciprocating piston type engines and steam turbines, which are a sub-group of steam engines. Piston type steam engines played a central role in the Industrial Revolution and modern steam turbines are used to generate more than 80% of the world's electricity. If liquid water comes in contact with a very hot surface or depressurizes quic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going from hand production methods to machines, new chemical manufacturing and iron production processes, the increasing use of steam power and water power, the development of machine tools and the rise of the mechanized factory system. Output greatly increased, and a result was an unprecedented rise in population and in the rate of population growth. Textiles were the dominant industry of the Industrial Revolution in terms of employment, value of output and capital invested. The textile industry was also the first to use modern production methods. The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain, and many of the technological and architectural innovations were of British origin. By the mid-18th century, Britain was the world's leadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
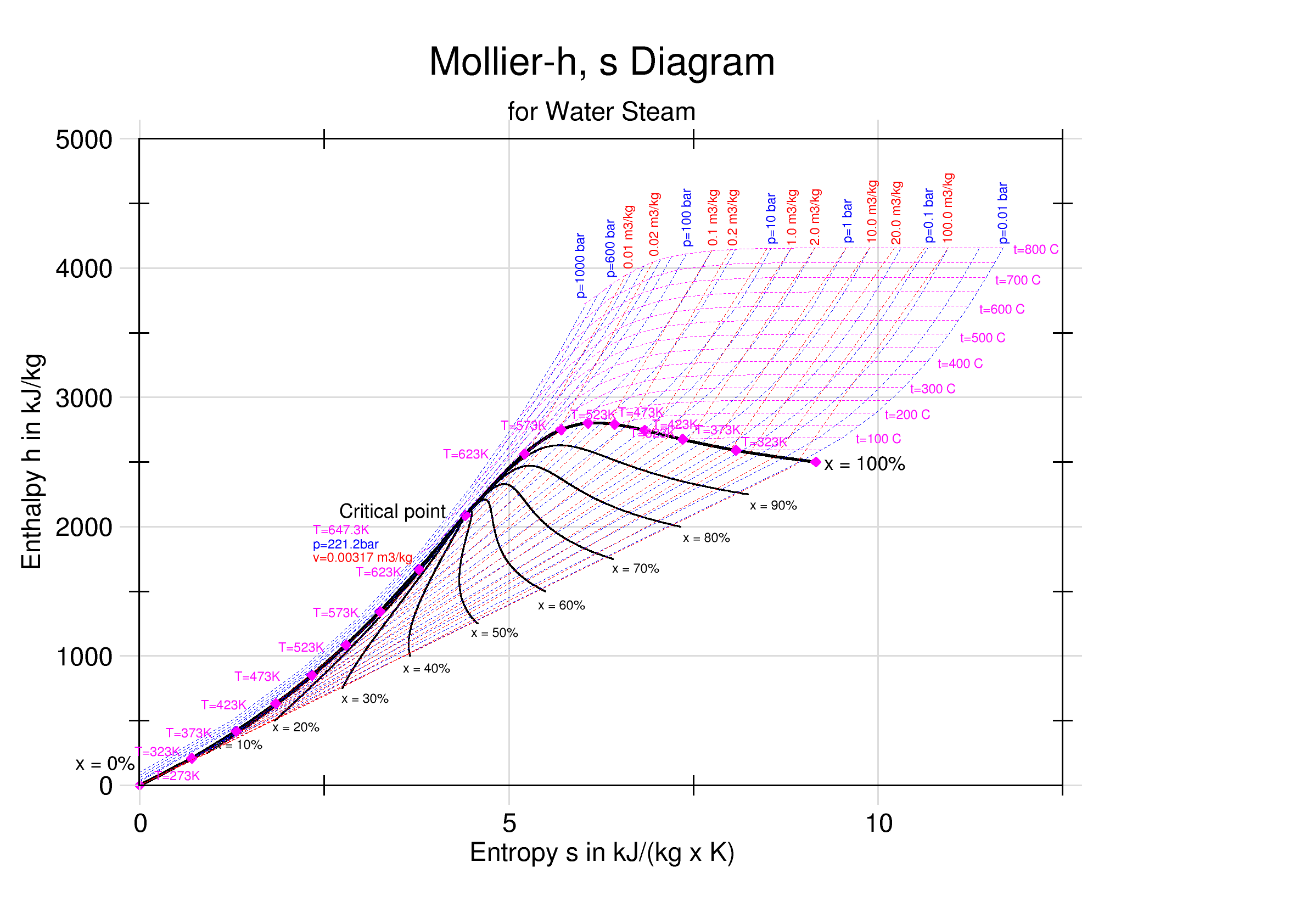
Mollier Enthalpy Entropy Chart For Steam - US Units
Mollier may refer to: * Richard Mollier Richard Mollier (; 30 November 1863, Triest – 13 March 1935, Dresden) was a German professor of Applied Physics and Mechanics in Göttingen and Dresden, a pioneer of experimental research in thermodynamics, particularly for water, steam, and moi ..., German professor of Applied Physics and Mechanics ; * Louis-Marie Mollier, French-American pioneer priest of north-central Kansas ; * Jean-Yves Mollier, French Contemporary History teacher. {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enthalpy–entropy Chart
An enthalpy–entropy chart, also known as the ''H''–''S'' chart or Mollier diagram, plots the total heat against entropy, describing the enthalpy of a thermodynamic system. A typical chart covers a pressure range of 0.01–1000 bar, and temperatures up to 800 degrees Celsius. It shows enthalpy H in terms of internal energy U, pressure p and volume V using the relationship H = U + pV \,\! (or, in terms of specific enthalpy, specific entropy and specific volume, h = u + pv \! ). History The diagram was created in 1904, when Richard Mollier plotted the total heat against entropy . At the 1923 Thermodynamics Conference held in Los Angeles it was decided to name, in his honor, as a "Mollier diagram" any thermodynamic diagram using the enthalpy as one of its axes. Details On the diagram, lines of constant pressure, constant temperature and volume are plotted, so in a two-phase region, the lines of constant pressure and temperature coincide. Thus, coordinates on the diagram repr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Diagram
A phase diagram in physical chemistry, engineering, mineralogy, and materials science is a type of chart used to show conditions (pressure, temperature, volume, etc.) at which thermodynamically distinct phases (such as solid, liquid or gaseous states) occur and coexist at equilibrium. Overview Common components of a phase diagram are ''lines of equilibrium'' or ''phase boundaries'', which refer to lines that mark conditions under which multiple phases can coexist at equilibrium. Phase transitions occur along lines of equilibrium. Metastable phases are not shown in phase diagrams as, despite their common occurrence, they are not equilibrium phases. Triple points are points on phase diagrams where lines of equilibrium intersect. Triple points mark conditions at which three different phases can coexist. For example, the water phase diagram has a triple point corresponding to the single temperature and pressure at which solid, liquid, and gaseous water can coexist in a stabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
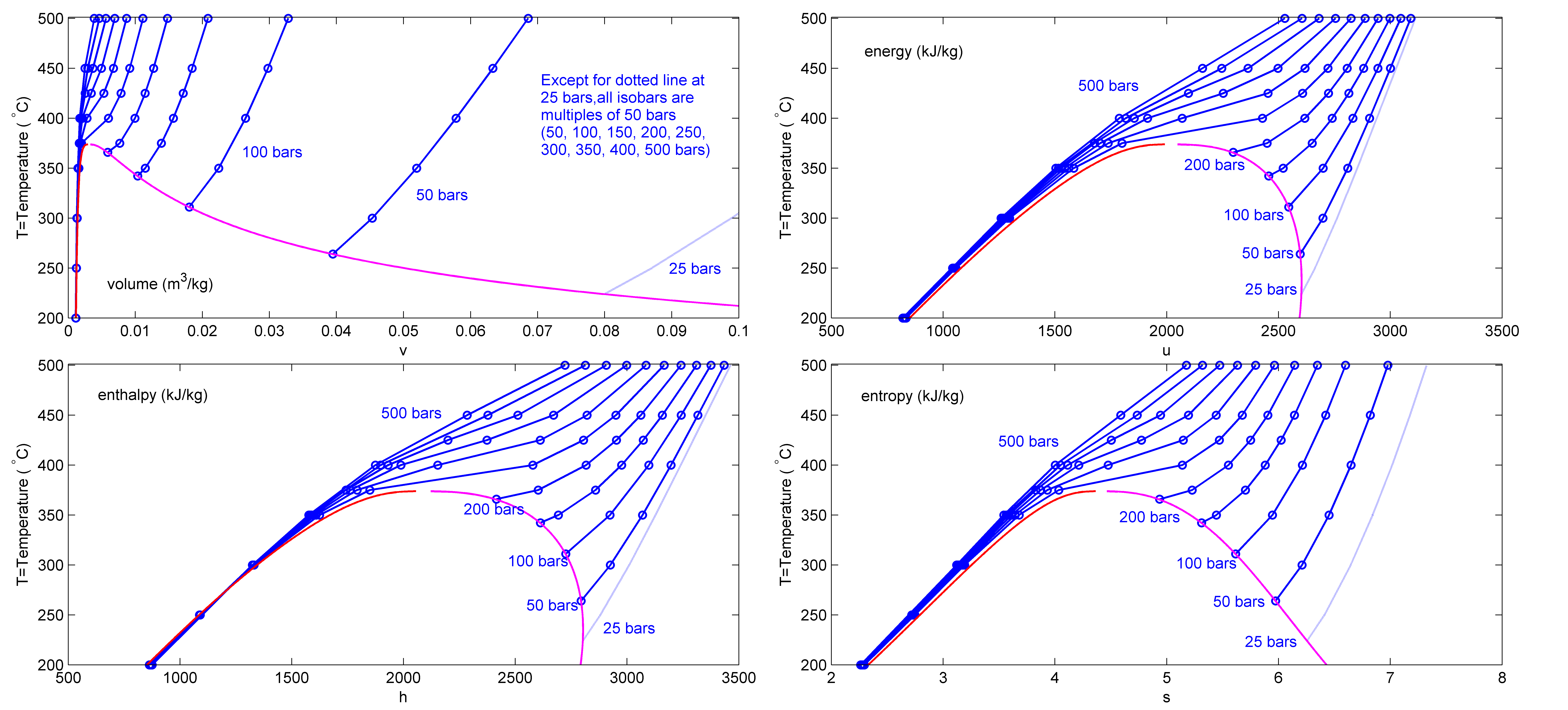
Steam Table
This page provides supplementary data to the article properties of water. Further comprehensive authoritative data can be found at thNIST Webbookpage on thermophysical properties of fluids. Structure and properties Thermodynamic properties Liquid physical properties Water/steam equilibrium properties Vapor pressure formula for steam in equilibrium with liquid water: : \log_ P = A - \frac, where ''P'' is equilibrium vapor pressure in k Pa, and ''T'' is temperature in kelvins. For ''T'' = 273 K to 333 K: ''A'' = 7.2326; ''B'' = 1750.286; ''C'' = 38.1. For ''T'' = 333 K to 423 K: ''A'' = 7.0917; ''B'' = 1668.21; ''C'' = 45.1. Data in the table above is given for water–steam equilibria at various temperatures over the entire temperature range at which liquid water can exist. Pressure of the equilibrium is given in the second column in k Pa. The third column is the heat content of each gram of the liquid phase relative to water at 0 °C. The fourth column is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirax-Sarco Engineering
Spirax-Sarco Engineering plc is a British manufacturer of steam management systems and peristaltic pumps and associated fluid path technologies. It is headquartered in Cheltenham, England. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. History The Company was founded by Herman Sanders in 1888 and after a Mr Rehders joined the business, established as ''Sanders, Rehders & Co.'' ('Sarco') in London importing thermostatic steam traps from Germany. It started to manufacture steam traps in United Kingdom under the ''Spirax'' brand name in 1932 and was first listed on the London Stock Exchange in 1959. In 1960 a range of self-acting pressure controls are introduced for the first time: then in 1963 it bought ''Drayton Controls'', a control valve and instrumentation business. The company diversified into pump manufacturing in 1990 when it bought '' Watson-Marlow''. It acquired the ''Jucker Industrial Division'', an Italian controls business, in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boiling Point
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor. The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding environmental pressure. A liquid in a partial vacuum has a lower boiling point than when that liquid is at atmospheric pressure. A liquid at low pressure has a lower boiling point than when that liquid is at atmospheric pressure. Because of this, water boils at under standard pressure at sea level, but at at altitude. For a given pressure, different liquids will boiling, boil at different temperatures. The normal boiling point (also called the atmospheric boiling point or the atmospheric pressure boiling point) of a liquid is the special case in which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the defined atmospheric pressure at sea level, one Atmosphere (unit), atmosphere. At that temperature, the vapor pressure of the liquid becomes suffici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superheated Steam
Superheated steam is steam at a temperature higher than its vaporization point at the absolute pressure where the temperature is measured. Superheated steam can therefore cool (lose internal energy) by some amount, resulting in a lowering of its temperature without changing state (i.e., condensing) from a gas, to a mixture of saturated vapor and liquid. If unsaturated steam (a mixture which contains both water vapor and liquid water droplets) is heated at constant pressure, its temperature will also remain constant as the vapor quality (think dryness, or percent saturated vapor) increases towards 100%, and becomes dry (i.e., no saturated liquid) saturated steam. Continued heat input will then "super" heat the dry saturated steam. This will occur if saturated steam contacts a surface with a higher temperature. Superheated steam and liquid water cannot coexist under thermodynamic equilibrium, as any additional heat simply evaporates more water and the steam will become saturated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vapor–liquid Equilibrium
In thermodynamics and chemical engineering, the vapor–liquid equilibrium (VLE) describes the distribution of a chemical species between the vapor phase and a liquid phase. The concentration of a vapor in contact with its liquid, especially at equilibrium, is often expressed in terms of vapor pressure, which will be a partial pressure (a part of the total gas pressure) if any other gas(es) are present with the vapor. The equilibrium vapor pressure of a liquid is in general strongly dependent on temperature. At vapor–liquid equilibrium, a liquid with individual components in certain concentrations will have an equilibrium vapor in which the concentrations or partial pressures of the vapor components have certain values depending on all of the liquid component concentrations and the temperature. The converse is also true: if a vapor with components at certain concentrations or partial pressures is in vapor–liquid equilibrium with its liquid, then the component concentration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |