|
Stationary Fronts
A stationary front (or quasi-stationary front) is a weather front or transition zone between two air masses when both air mass is advancing into the other at speeds exceeding 5 knots (about 6 miles per hour or about 9 kilometers per hour) at the ground surface. On weather maps, it's illustrated as a solid line of alternating blue spikes pointing to the warmer air mass and red domes facing the colder air mass. Development A stationary front may form when a cold or warm front slows down or grows over time from underlying surface temperature differences, like a coastal front. Winds on the cold air and warm air sides often flow nearly parallel to the stationary front, often in opposite directions along either side of the stationary front. A stationary front usually remains in the same area for hours to days and may undulate as atmospheric waves move eastward along the front. Stationary fronts may also change into a cold or warm front and may form one or more extratropical or mid-latitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stationary Front Symbol
In addition to its common meaning, stationary may have the following specialized scientific meanings: Mathematics * Stationary point * Stationary process * Stationary state Meteorology * A stationary front is a weather front that is not moving Physics * A time-invariant system quantity, such as a constant position or temperature * A steady state physical process, such as a vibration at constant amplitude and frequency or a steady fluid flow * A stationary wave is a standing wave In physics, a standing wave, also known as a stationary wave, is a wave that oscillates in time but whose peak amplitude profile does not move in space. The peak amplitude of the wave oscillations at any point in space is constant with respect ... * Stationary spacetime in general relativity Other uses * "Stationary", a song from ''Copacetic'' (Knuckle Puck album) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Front
A weather front is a boundary separating air masses for which several characteristics differ, such as air density, wind, temperature, and humidity. Disturbed and unstable weather due to these differences often arises along the boundary. For instance, cold fronts can bring bands of thunderstorms and cumulonimbus precipitation or be preceded by squall lines, while warm fronts are usually preceded by stratiform precipitation and fog. In summer, subtler humidity gradients are known as dry lines can trigger severe weather. Some fronts produce no precipitation and little cloudiness, although there is invariably always a wind shift. Cold fronts generally move from west to east, whereas warm fronts move poleward, although any direction is possible. Occluded fronts are a hybrid merge of the two, and stationary fronts are stalled in their motion. Cold fronts and cold occlusions move faster than warm fronts and warm occlusions because the dense air behind them can lift as we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Mass
In meteorology, an air mass is a volume of air defined by its temperature and humidity. Air masses cover many hundreds or thousands of square miles, and adapt to the characteristics of the surface below them. They are classified according to latitude and their continental or maritime source regions. Colder air masses are termed polar or arctic, while warmer air masses are deemed tropical. Continental and superior air masses are dry, while maritime and monsoon air masses are moist. Weather fronts separate air masses with different density (temperature or moisture) characteristics. Once an air mass moves away from its source region, underlying vegetation and water bodies can quickly modify its character. Classification schemes tackle an air mass' characteristics, as well as modification. Classification and notation The Bergeron classification is the most widely accepted form of air mass classification, though others have produced more refined versions of this scheme over diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Front
A cold front is the leading edge of a cooler mass of air at ground level that replaces a warmer mass of air and lies within a pronounced surface trough of low pressure. It often forms behind an extratropical cyclone (to the west in the Northern Hemisphere, to the east in the Southern), at the leading edge of its cold air advection pattern—known as the cyclone's dry "conveyor belt" flow. Temperature differences across the boundary can exceed from one side to the other. When enough moisture is present, rain can occur along the boundary. If there is significant instability along the boundary, a narrow line of thunderstorms can form along the frontal zone. If instability is weak, a broad shield of rain can move in behind the front, and evaporative cooling of the rain can increase the temperature difference across the front. Cold fronts are stronger in the fall and spring transition seasons and are weakest during the summer. Development of cold fronts A cold front occurs when a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warm Front
A warm front is a density discontinuity located at the leading edge of a homogeneous warm air mass, and is typically located on the equator-facing edge of an isotherm gradient. Warm fronts lie within broader troughs of low pressure than cold fronts, and move more slowly than the cold fronts which usually follow because cold air is denser and less easy to remove from the Earth's surface. This also forces temperature differences across warm fronts to be broader in scale. Clouds ahead of the warm front are mostly stratiform, and rainfall defiantly increases as the front approaches. Fog can also occur preceding a warm frontal passage. Clearing and warming is usually rapid after frontal passage. If the warm air mass is unstable, thunderstorms may be embedded among the stratiform clouds ahead of the front, and after frontal passage thundershowers may continue. On weather maps, the surface location of a warm front is marked with a red line of semicircles pointing in the directio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ageostrophy
Ageostrophy or (ageostrophic flow) is the difference between the ''actual'' wind or current and the geostrophic wind or geostrophic current. Since geostrophy is an exact balance between the Coriolis force and the pressure gradient force, ageostrophic flow reflects an imbalance, and thus is often implicated in disturbances, vertical motions (important for weather), and rapid changes with time. Ageostrophic flow reflects the existence of all the other terms in the momentum equation neglected in that idealization, including friction and material acceleration Dv/Dt, which includes the centrifugal force in curved flow. See also * geostrophic *geostrophic wind In atmospheric science, geostrophic flow () is the theoretical wind that would result from an exact balance between the Coriolis force and the pressure gradient force. This condition is called '' geostrophic equilibrium'' or ''geostrophic balanc ... References External linksMeteo 422 – Lecture 17 – The Omega Equati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontogenesis
Frontogenesis is a meteorological process of tightening of horizontal temperature gradients to produce fronts. In the end, two types of fronts form: cold fronts and warm fronts. A cold front is a narrow line where temperature decreases rapidly. A warm front is a narrow line of warmer temperatures and essentially where much of the precipitation occurs. Frontogenesis occurs as a result of a developing baroclinic wave. According to Hoskins & Bretherton (1972, p. 11), there are eight mechanisms that influence temperature gradients: horizontal deformation, horizontal shearing, vertical deformation, differential vertical motion, latent heat release, surface friction, turbulence and mixing, and radiation. Semigeostrophic frontogenesis theory focuses on the role of horizontal deformation and shear. Kinematics Horizontal deformation in mid-latitude cyclones concentrates temperature gradients—cold air from the poles and warm air from the equator. Horizontal shear has two effects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may compose the droplets and crystals. On Earth, clouds are formed as a result of saturation of the air when it is cooled to its dew point, or when it gains sufficient moisture (usually in the form of water vapor) from an adjacent source to raise the dew point to the ambient temperature. They are seen in the Earth's homosphere, which includes the troposphere, stratosphere, and mesosphere. Nephology is the science of clouds, which is undertaken in the cloud physics branch of meteorology. There are two methods of naming clouds in their respective layers of the homosphere, Latin and common name. Genus types in the troposphere, the atmospheric layer closest to Earth's surface, have Latin names because of the universal adoption of L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, Rain and snow mixed, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor (reaching 100% relative humidity), so that the water condenses and "precipitates" or falls. Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation but colloids, because the water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate. Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are called shower (precipitation), showers. Moisture that is lifted or otherwise forced to rise over a layer of sub-freezi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
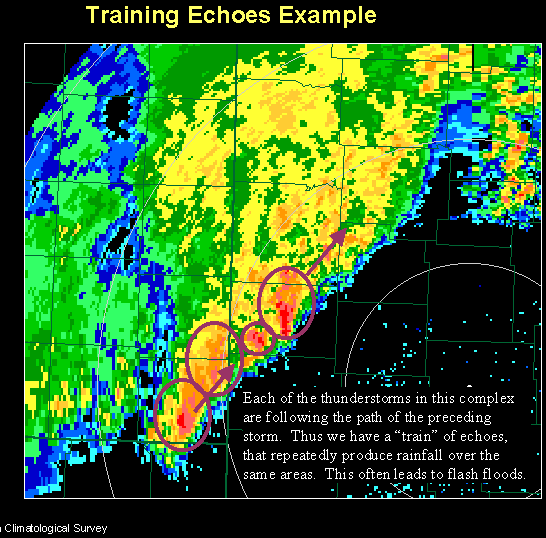
Storm Train
In meteorology, training denotes repeated areas of rain, typically associated with thunderstorms, that move over the same region in a relatively short period of time. Training thunderstorms are capable of producing excessive rainfall totals, often causing flash flooding. The name ''training'' is derived from how a train and its cars travel along a track (moving along a single path), without the track moving. Formation Showers and thunderstorms along thunderstorm trains usually develop in one area of stationary instability, and are advanced along a single path by prevailing winds. Additional showers and storms can also develop when the gust front from a storm collides with warmer air outside of the storm. The same process repeats in the new storms, until overall conditions in the surrounding atmosphere become too stable for support of thunderstorm activity. Showers and storms can also develop along stationary fronts, and winds move them down the front. The showers that often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shear Line (meteorology)
Surface weather analysis is a special type of weather map that provides a view of weather elements over a geographical area at a specified time based on information from ground-based weather stations. Weather maps are created by plotting or tracing the values of relevant quantities such as sea level pressure, temperature, and cloud cover onto a geographical map to help find synoptic scale features such as weather fronts. The first weather maps in the 19th century were drawn well after the fact to help devise a theory on storm systems.Eric R. MillerAmerican Pioneers in Meteorology.Retrieved on 2007-04-18. After the advent of the telegraph, simultaneous surface weather observations became possible for the first time, and beginning in the late 1840s, the Smithsonian Institution became the first organization to draw real-time surface analyses. Use of surface analyses began first in the United States, spreading worldwide during the 1870s. Use of the Norwegian cyclone model for fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Category
Category, plural categories, may refer to: Philosophy and general uses *Categorization, categories in cognitive science, information science and generally * Category of being * ''Categories'' (Aristotle) * Category (Kant) * Categories (Peirce) * Category (Vaisheshika) * Stoic categories * Category mistake Mathematics * Category (mathematics), a structure consisting of objects and arrows * Category (topology), in the context of Baire spaces * Lusternik–Schnirelmann category, sometimes called ''LS-category'' or simply ''category'' * Categorical data, in statistics Linguistics *Lexical category, a part of speech such as ''noun'', ''preposition'', etc. * Syntactic category, a similar concept which can also include phrasal categories * Grammatical category, a grammatical feature such as ''tense'', ''gender'', etc. Other * Category (chess tournament) * Objective-C categories, a computer programming concept * Pregnancy category * Prisoner security categories in the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |