|
Stanisław Piasecki
Stanisław Piasecki (15 December 1900 – 12 June 1941) was a Polish right-wing activist, politician and journalist of partially Jewish descent. Piasecki was born on 15 December 1900 in Lwów, Austrian Galicia. He was the son of scouting activist Eugeniusz Piasecki and Gizela Siberfeld, a daughter from a wealthy Jewish family, who converted to Catholic faith during the wedding and took the name Maria PiaseckaPrawą stroną literatury polskiej: szkice i portrety Maciej Urbanowski page 43 Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Jagiellońskiego 2007 He was related to the athlete Jadwiga Wajs. In his late teens, Piasecki fought in the Battle of Lemberg (1918), and the Polish-Ukrainian War. He also fought in the Polish-Soviet War of 1920–21 as a volunteer. In the 1920s, he studied architecture at University of Jan Kazimierz in Lwow, and law at Adam Mickiewicz University in Poznań. He also was a member of the right-wing student organization Academic Union All-Polish Youth. In 1935, Piasecki fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanisław Piasecki
Stanisław Piasecki (15 December 1900 – 12 June 1941) was a Polish right-wing activist, politician and journalist of partially Jewish descent. Piasecki was born on 15 December 1900 in Lwów, Austrian Galicia. He was the son of scouting activist Eugeniusz Piasecki and Gizela Siberfeld, a daughter from a wealthy Jewish family, who converted to Catholic faith during the wedding and took the name Maria PiaseckaPrawą stroną literatury polskiej: szkice i portrety Maciej Urbanowski page 43 Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Jagiellońskiego 2007 He was related to the athlete Jadwiga Wajs. In his late teens, Piasecki fought in the Battle of Lemberg (1918), and the Polish-Ukrainian War. He also fought in the Polish-Soviet War of 1920–21 as a volunteer. In the 1920s, he studied architecture at University of Jan Kazimierz in Lwow, and law at Adam Mickiewicz University in Poznań. He also was a member of the right-wing student organization Academic Union All-Polish Youth. In 1935, Piasecki fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
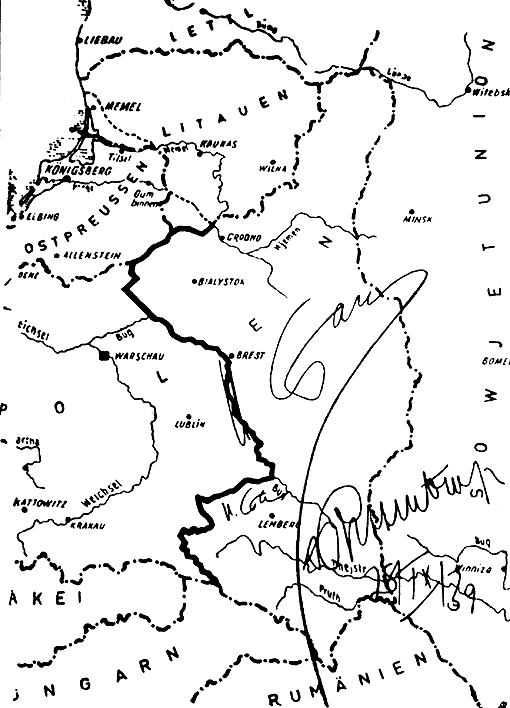
Invasion Of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week after the signing of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact between Germany and the Soviet Union, and one day after the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union had approved the pact. The Soviets invaded Poland on 17 September. The campaign ended on 6 October with Germany and the Soviet Union dividing and annexing the whole of Poland under the terms of the German–Soviet Frontier Treaty. The invasion is also known in Poland as the September campaign ( pl, kampania wrześniowa) or 1939 defensive war ( pl, wojna obronna 1939 roku, links=no) and known in Germany as the Poland campaign (german: Überfall auf Polen, Polenfeldzug). German forces invaded Poland from the north, south, and west the morning after the Gleiwitz incident. Slovak military forces ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paradisus Judaeorum
"''Paradisus Judaeorum''" is a Latin phrase which became one of four members of a 19th-century Polish-language proverb that described the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1569–1795) as "heaven for the nobility, purgatory for townspeople, hell for peasants, paradise for Jews." The proverb's earliest attestation is an anonymous 1606 Latin pasquinade that begins, "''Regnum Polonorum est''" ("The Kingdom of Poland is"). Stanisław Kot surmised that its author may have been a Catholic cleric who criticized what he regarded as defects of the realm; the pasquinade excoriates virtually every group and class of society.hen_the_Zebrzydowski_rebellion_against_the_King_beganwas_scattered_about_during_a_wedding_celebration_that_was_ill-viewed_in_society.") Of_the_two_texts_attributed_to_the_same_anonymous_author,_the_part_that_became_the_proverb_appeared_in_the_"''Regnum_Polonorum_est"''_("The_Kingdom_of_Poland_Is")._Parts_of_the_text_were_quoted_in_Bishop_Stanisław_Zaremba_(bishop_of_Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Government
The General Government (german: Generalgouvernement, pl, Generalne Gubernatorstwo, uk, Генеральна губернія), also referred to as the General Governorate for the Occupied Polish Region (german: Generalgouvernement für die besetzten polnischen Gebiete), was a German zone of occupation established after the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany, Slovakia and the Soviet Union in 1939 at the onset of World War II. The newly occupied Second Polish Republic was split into three zones: the General Government in its centre, Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany in the west, and Polish areas annexed by the Soviet Union in the east. The territory was expanded substantially in 1941, after the German Invasion of the Soviet Union, to include the new District of Galicia. The area of the ''Generalgouvernement'' roughly corresponded with the Austrian part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth after the Third Partition of Poland in 1795. The basis for the formation of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Democracy (Poland)
National Democracy ( pl, Narodowa Demokracja, also known from its abbreviation ND as ''Endecja''; ) was a Polish political movement active from the second half of the 19th century under the foreign partitions of the country until the end of the Second Polish Republic. It ceased to exist after the Nazi–Soviet invasion of Poland of 1939. In its long history, National Democracy went through several stages of development. Created with the intention of promoting the fight for Poland's sovereignty against the repressive imperial regimes, the movement acquired its right-wing nationalist character following the return to independence. A founder and principal ideologue was Roman Dmowski. Other ideological fathers of the movement included Zygmunt Balicki and Jan Ludwik Popławski. The National Democracy's main stronghold was Greater Poland (western Poland), where much of the movement's early impetus derived from efforts to counter Imperial Germany's policy of Germanizing its Polish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myślenice
Myślenice is a town in southern Poland, situated in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship (since 1999), previously in Kraków Voivodeship (1975–1998). Population: 20,261 (2007). The town is divided into six districts. One of them, Zarabie, is a popular local tourist destination. It is located behind the Raba river (Zarabie meaning "Beyond the (River) Raba"), and it has Chełm mountain, with a view tower, a landscape park and ski lifts. Myślenice is located on the so-called Zakopianka Road, which is a popular name of the European route E77 road, connecting Kraków with Zakopane (the E77 itself separates itself from the Zakopianka at Rabka). Myślenice does not have a train station. History First mentions of Myślenice come from 1253 - 1258. At that time, it was a defensive settlement, with a castle and fortifications, designed to protect Kraków from the south. In 1342, Myślenice received its Magdeburg rights town charter, and it started to develop into a local commercial center. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konstanty Ildefons Gałczyński
Konstanty Ildefons Gałczyński (23 January 1905 – 6 December 1953), alias ''Karakuliambro'', was a Polish poet. He is well known for the "paradramatic" absurd humorous sketches of the ''Green Goose Theatre''. Biography Born to a lower-middle-class family in Warsaw, Gałczyński was evacuated with his parents at the outbreak of World War I, and from 1914 to 1918 he lived in Moscow, where he attended a Polish school. Returning to Poland in 1918, he studied classics and English language at the University of Warsaw, submitting a dissertation on a non-existent nineteenth-century English poet, Morris Gordon Cheats. His literary debut came in 1923 and was a member of the Kwadryga group of poets, and he was linked to satirical and political publications. In 1930 he married Natalia Avalov. From 1931-33, he held the post of cultural attaché in Berlin. From 1934-36 he was in Vilnius. He settled there at 2 Młynowa Street. There, in 1936, the couple's daughter Kira was born. Throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmiry
Palmiry () is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Czosnów, within Nowy Dwór County, Masovian Voivodeship, in east-central Poland. It is located at the edge of the Kampinos Forest, approximately south-east of Czosnów, south-east of Nowy Dwór Mazowiecki, and north-west of Warsaw. In 2000 the village had an approximate population of 220. Mass executions during German occupation of Poland During World War II, between 1939 and 1943, the village and the surrounding forest were one of the sites of the Nazi German mass executions of Jews, Polish intelligentsia, politicians and athletes, killed during the German AB-Aktion in Poland. Most of the victims were first arrested and tortured in the Pawiak prison in Warsaw Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ..., t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pawiak
Pawiak () was a prison built in 1835 in Warsaw, Congress Poland. During the January 1863 Uprising, it served as a transfer camp for Poles sentenced by Imperial Russia to deportation to Siberia. During the World War II German occupation of Poland, it was used by the Germans, and in 1944 it was destroyed in the Warsaw Uprising. History Pawiak Prison took its name from that of the street on which it stood, ''ulica Pawia'' (Polish for "Peacock Street"). Pawiak Prison was built in 1829–35 to the design of Enrico Marconi and Fryderyk Florian Skarbek, prison reformer and godfather to composer Frédéric Chopin. During the 19th century, it was under tsarist control as Warsaw was part of the Russian Empire. During that time, it was the main prison of central Poland, where political prisoners and criminals alike were incarcerated. During the January 1863 Uprising, the prison served as a transfer camp for Poles sentenced by Imperial Russia to deportation to Siberia. After Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gestapo
The (), abbreviated Gestapo (; ), was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe. The force was created by Hermann Göring in 1933 by combining the various political police agencies of Prussia into one organisation. On 20 April 1934, oversight of the Gestapo passed to the head of the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS), Heinrich Himmler, who was also appointed Chief of German Police by Hitler in 1936. Instead of being exclusively a Prussian state agency, the Gestapo became a national one as a sub-office of the (SiPo; Security Police). From 27 September 1939, it was administered by the Reich Security Main Office (RSHA). It became known as (Dept) 4 of the RSHA and was considered a sister organisation to the (SD; Security Service). During World War II, the Gestapo played a key role in the Holocaust. After the war ended, the Gestapo was declared a criminal organisation by the International Military Tribunal (IMT) at the Nuremberg trials. History After Adol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Witold Lutosławski
Witold Roman Lutosławski (; 25 January 1913 – 7 February 1994) was a Polish composer and conductor. Among the major composers of 20th-century classical music, he is "generally regarded as the most significant Polish composer since Szymanowski, and possibly the greatest Polish composer since Chopin". His compositions—of which he was a notable conductor—include representatives of most traditional genres, aside from opera: symphonies, concertos, orchestral song cycles, other orchestral works, and chamber works. Among his best known works are his four symphonies, the Variations on a Theme by Paganini (1941), the Concerto for Orchestra (1954), and his cello concerto (1970). During his youth, Lutosławski studied piano and composition in Warsaw. His early works were influenced by Polish folk music and demonstrated a wide range of rich atmospheric textures. His folk-inspired music includes the Concerto for Orchestra (1954)—which first brought him international renown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tadeusz Gajcy
Tadeusz Stefan Gajcy (; 8 February 1922, Warsaw - 16 August 1944, Warsaw) pseudonym. ''Karol Topornicki”, „Roman Oścień”, „Topór”, „Orczyk“'' , was a Polish poet, playwright, editor-in-chief of the Sztuka i Naród (Art and Nation) periodical, member of the Konfederacja Narodu (Confederation of the Nation), soldier of the Armia Krajowa (Polish Home Army). He was born on 8 February 1922 on Dzika Street in Warsaw. His ancestors on his father's side came to Poland from Hungary, which is why several forms of the poet's polonized family name exist in documents (Gajc, Gajca, Gaycy, Gajczy). Tadeusz's parents were Stefan Gajcy and Irena Gajcy, née Zmarzlik. Gajcy's father was a telegraphist during the Polish-Bolshevik war and after the war he worked as a locksmith in the Railway Repair Plant in Warsaw's Praga district. His mother was a midwife in a hospital and had roots in the landed gentry. In her free time, she carried out social and charitable activities, which won ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)