|
St Philip And St James' Church, Clifton
St Philip and St James' Church is a parish church in Clifton, a suburb of inner northern York, in England. Until the mid-19th century, Clifton fell mostly within the parish of St Olave's Church, and also a detached part of the parish of St Michael le Belfrey. The heirs of Thomas de Grey, 2nd Earl de Grey donated a site by Clifton Green for the construction of a church. It was designed by George Fowler Jones, and was completed in 1867, at a cost of £3,800. It was given its own parish in 1871. The church celebrated its centenary in 1967 by commissioning Kenneth Leighton to write a hymn, "O God, enfold me in the sun". Between 1984 and 1989, the church was reordered by Ronald Sims, who replaced the pews with chairs, and converted the chancel and transepts into meeting rooms. The building was grade II listed in 1997. Nikolaus Pevsner was critical of the design, describing a "ponderous west tower", but praised the "excellent fittings in a plainer Pace style". The church is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
York
York is a cathedral city in North Yorkshire, England, with Roman Britain, Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers River Ouse, Yorkshire, Ouse and River Foss, Foss. It has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a York Minster, minster, York Castle, castle and York city walls, city walls, all of which are Listed building, Grade I listed. It is the largest settlement and the administrative centre of the wider City of York district. It is located north-east of Leeds, south of Newcastle upon Tyne and north of London. York's built-up area had a recorded population of 141,685 at the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census. The city was founded under the name of Eboracum in AD 71. It then became the capital of Britannia Inferior, a province of the Roman Empire, and was later the capital of the kingdoms of Deira, Northumbria and Jórvík, Scandinavian York. In the England in the Middle Ages, Middle Ages it became the Province of York, northern England ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grade II Listed
In the United Kingdom, a listed building is a structure of particular architectural or historic interest deserving of special protection. Such buildings are placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Historic Environment Division of the Department for Communities in Northern Ireland. The classification schemes differ between England and Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland (see sections below). The term has also been used in the Republic of Ireland, where buildings are protected under the Planning and Development Act 2000, although the statutory term in Ireland is " protected structure". A listed building may not be demolished, extended, or altered without permission from the local planning authority, which typically consults the relevant central government agency. In England and Wales, a national amenity society must be notified of any work to be done on a listed building ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grade II Listed Churches In York
Grade most commonly refers to: * Grading in education, a measurement of a student's performance by educational assessment (e.g. A, pass, etc.) * A designation for students, classes and curricula indicating the number of the year a student has reached in a given educational stage (e.g. first grade, second grade, K–12, etc.) * Grade (slope), the steepness of a slope * Graded voting Grade or grading may also refer to: Music * Grade (music), a formally assessed level of profiency in a musical instrument * Grade (band), punk rock band * Grades (producer), British electronic dance music producer and DJ Science and technology Biology and medicine * Grading (tumors), a measure of the aggressiveness of a tumor in medicine * The Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach * Evolutionary grade, a paraphyletic group of organisms Geology * Graded bedding, a description of the variation in grain size through a bed in a sedimentary rock * Metamorphic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Churches Completed In 1867
Church may refer to: Religion * Church (building), a place/building for Christian religious activities and praying * Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination * Church service, a formalized period of Christian communal worship * Christian denomination, a Christian organization with distinct doctrine and practice * Christian Church, either the collective body of all Christian believers, or early Christianity Places United Kingdom * Church, a former electoral ward of Kensington and Chelsea London Borough Council that existed from 1964 to 2002 * Church (Liverpool ward), a Liverpool City Council ward * Church (Reading ward), a Reading Borough Council ward * Church (Sefton ward), a Metropolitan Borough of Sefton ward * Church, Lancashire, England United States * Church, Iowa, an unincorporated community * Church Lake, a lake in Minnesota * Church, Michigan, ghost town Arts, entertainment, and media * '' Church magazine'', a pastoral theology magazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Ward Knowles
John Ward Knowles (1838–1931) was a prominent British York-based stained-glass manufacturer, and commentator on local art and music. Family Knowles may have been related to the civil engineer George Knowles (c. 1776-1856june23: will 1856aug13ref PROB 11/2237/206), who designed Scarborough's spa promenade and South Cliff Gardens. His brother was William Knowles (1846nov3-1908sep7). His son John Alder Knowles (1881-1961) continued the craft traditions but also moved with the times. He spent some time studying glass manufacturing methods in the USA before the First World War. Enthused by the work of Tiffany, he attempted an English version of the famous lamps, but charming though his prototypes were, they lacked the delicacy of the originals and failed to catch on. Career After training in art, Knowles dabbled in photography. In 1869 John Ward Knowles took the premises at No.41, (The Star Inn) previously the house of Mr Robinson, Hosier. According to his notes he moved there in 186 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clayton And Bell
Clayton and Bell was one of the most prolific and proficient British workshops of stained-glass windows during the latter half of the 19th century and early 20th century. The partners were John Richard Clayton (1827–1913) and Alfred Bell (1832–1895). The company was founded in 1855 and continued until 1993. Their windows are found throughout the United Kingdom, in the United States, Canada, Australia and New Zealand. Clayton and Bell's commercial success was due to the high demand for stained-glass windows at the time, their use of the best-quality glass available, the excellence of their designs and their employment of efficient factory methods of production. They collaborated with many of the most prominent Gothic Revival architects and were commissioned, for example, by John Loughborough Pearson to provide the windows for the newly constructed Truro Cathedral. Background During the Middle Ages, Medieval period, from the Norman Conquest of England in 1066 until the 1530 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
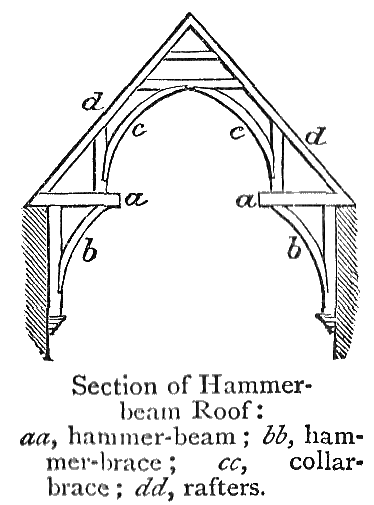
Hammerbeam Roof
A hammerbeam roof is a decorative, open timber roof truss typical of English Gothic architecture and has been called "the most spectacular endeavour of the English Medieval carpenter". They are traditionally timber framed, using short beams projecting from the wall on which the rafters land, essentially a tie beam which has the middle cut out. These short beams are called hammer-beams and give this truss its name. A hammerbeam roof can have a single, double or false hammerbeam truss. Design A hammer-beam is a form of timber roof truss, allowing a hammerbeam roof to span greater than the length of any individual piece of timber. In place of a normal tie beam spanning the entire width of the roof, short beams – the hammer beams – are supported by curved braces from the wall, and hammer posts or arch-braces are built on top to support the rafters and typically a collar beam. The hammerbeam truss exerts considerable thrust on the walls or posts that support it. Hamme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trefoil
A trefoil () is a graphic form composed of the outline of three overlapping rings, used in architecture, Pagan and Christian symbolism, among other areas. The term is also applied to other symbols with a threefold shape. A similar shape with four rings is called a quatrefoil. Architecture Ornamentation 'Trefoil' is a term in Gothic architecture given to the ornamental foliation or cusping introduced in the heads of window-lights, tracery, and panellings, in which the centre takes the form of a three-lobed leaf (formed from three partially overlapping circles). One of the earliest examples is in the plate tracery at Winchester Cathedral (1222–1235). The fourfold version of an architectural trefoil is a quatrefoil. A simple trefoil shape in itself can be symbolic of the Trinity, while a trefoil combined with an equilateral triangle was also a moderately common symbol of the Christian Trinity during the late Middle Ages in some parts of Europe, similar to a quatrefoil#Barbed qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancet Window
A lancet window is a tall, narrow window with a sharp pointed arch at its top. This arch may or may not be a steep lancet arch (in which the compass centres for drawing the arch fall outside the opening). It acquired the "lancet" name from its resemblance to a lance. Instances of this architectural element are typical of Gothic church edifices of the earliest period. Lancet windows may occur singly, or paired under a single moulding, or grouped in an odd number with the tallest window at the centre. The lancet window first appeared in the early French Gothic period (c. 1140–1200), and later in the Early English period of Gothic architecture (1200–1275). So common was the lancet window feature that this era is sometimes known as the "Lancet Period". The term ''lancet window'' is properly applied to single-light windows of austere form, without tracery. Paired windows were sometimes surmounted by a simple opening such as a quatrefoil cut in plate tracery. This form gave way t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestry
A vestry was a committee for the local secular and ecclesiastical government of a parish in England, Wales and some English colony, English colonies. At their height, the vestries were the only form of local government in many places and spent nearly one-fifth of the budget of the British government. They were stripped of their secular functions in 1894 (1900 in London) and were abolished in 1921. The term ''vestry'' remains in use outside of England and Wales to refer to the elected governing body and legal representative of a parish church, for example in the Episcopal Church (United States), American and Scottish Episcopal Churches. Etymology The word vestry comes from Norman language, Anglo-Norman vesterie, from Old French ''vestiaire'', ultimately from Latin language, Latin ''vestiarium'' ‘wardrobe’. In a church building a Sacristy, vestry (also known as a sacristy) is a secure room for the storage or religious valuables and for changing into vestments. The vestry m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finial
A finial () or hip-knob is an element marking the top or end of some object, often formed to be a decorative feature. In architecture, it is a small decorative device, employed to emphasize the Apex (geometry), apex of a dome, spire, tower, roof, or gable or any of various distinctive ornaments at the top, end, or corner of a building or structure. A finial is typically carved in stone. Where there are several such elements they may be called pinnacles. The very top of a finial can be a floral or foliated element called a bouquet. Smaller finials in materials such as metal or wood are used as a decorative ornament on the tops or ends of poles or rods such as tent-poles or curtain rods or any object such as a piece of furniture. These are frequently seen on top of bed posts or clocks. Decorative finials are also commonly used to fasten lampshades, and as an ornamental element at the end of the handles of souvenir spoons. The charm at the end of a pull chain (such as for a ceiling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |