|
Sporothrix Schenckii
''Sporothrix schenckii'', a fungus that can be found worldwide in the environment, is named for medical student Benjamin Schenck, who in 1896 was the first to isolate it from a human specimen. The species is present in soil as well as in and on living and decomposing plant material such as peat moss. It can infect humans as well as animals and is the causative agent of sporotrichosis, commonly known as "rose handler's disease." The most common route of infection is the introduction of spores to the body through a cut or puncture wound in the skin. Infection commonly occurs in otherwise healthy individuals but is rarely life-threatening and can be treated with antifungals. In the environment it is found growing as filamentous hyphae. In host tissue it is found as a yeast. The transition between the hyphal and yeast forms is temperature dependent making ''S. schenckii'' a thermally dimorphic fungus. Morphology ''Sporothrix schenckii'' can be found in one of two morphologies, hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Contrast Microscopy
__NOTOC__ Phase-contrast microscopy (PCM) is an optical microscopy technique that converts phase shifts in light passing through a transparent specimen to brightness changes in the image. Phase shifts themselves are invisible, but become visible when shown as brightness variations. When light waves travel through a medium other than a vacuum, interaction with the medium causes the wave amplitude and phase to change in a manner dependent on properties of the medium. Changes in amplitude (brightness) arise from the scattering and absorption of light, which is often wavelength-dependent and may give rise to colors. Photographic equipment and the human eye are only sensitive to amplitude variations. Without special arrangements, phase changes are therefore invisible. Yet, phase changes often convey important information. Phase-contrast microscopy is particularly important in biology. It reveals many cellular structures that are invisible with a bright-field microscope, as exemplif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermis (skin)
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. The epidermis is composed of multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer (stratum basale) composed of columnar cells arranged perpendicularly. The layers of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. The human epidermis is a familiar example of epithelium, particularly a stratified squamous epithelium. The word epidermis is derived through Latin , itself and . Something related to or part of the epidermis is termed epidermal. Structure Cellular components The epidermis primarily consists of keratinocytes ( proliferating basal and differentiated suprabasal), which comprise 90% of its cells, but also contains melanocytes, Langerhans c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
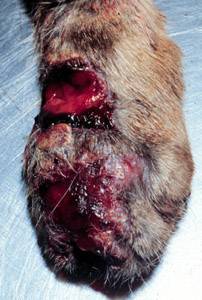
Feline Sporotrichosis 3
Feline may refer to: Zoology * Loosely, Felidae, a member of the cat family, which includes the subfamilies Pantherinae and Felinae (conventionally designated a felid) ** Following the taxonomic convention, Felinae, the subfamily of Felidae that includes domestic cats and smaller wild cats *** Cat, the domesticated feline Music * Feline (band), a late-1990s London-based English rock group * ''Feline'' (The Stranglers album), 1983 * ''Feline'' (1998 album), the self-titled album by Feline, expanded release of ''Save Your Face'' * ''Feline'' (Ella Eyre album) (2015), the debut studio album by Ella Eyre * Feline (song), a song on Delta Goodrem's 2016 album ''Wings of the Wild'' * Feline (song) ''Wings of the Wild'' is the fifth studio album by Australian singer-songwriter Delta Goodrem. It was released on 1 July 2016, through Sony Music Australia. A follow-up to her last studio album, '' Child of the Universe'' (2012), it was her first ..., a song by Juice World Feat. Polo G. Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affect the patient's immune system. Examples of these extrinsic factors include HIV infection and environmental factors, such as nutrition. Immunocompromisation may also be due to genetic diseases/flaws such as SCID. In clinical settings, immunosuppression by some drugs, such as steroids, can either be an adverse effect or the intended purpose of the treatment. Examples of such use is in organ transplant surgery as an anti- rejection measure and in patients with an overactive immune system, as in autoimmune diseases. Some people are born with intrinsic defects in their immune system, or primary immunodeficiency. A person who has an immunodeficiency of any kind is said to be immunocompromised. An immunocompromised individual may particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forestry
Forestry is the science and craft of creating, managing, planting, using, conserving and repairing forests, woodlands, and associated resources for human and environmental benefits. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands. The science of forestry has elements that belong to the biological, physical, social, political and managerial sciences. Forest management play essential role of creation and modification of habitats and affect ecosystem services provisioning. Modern forestry generally embraces a broad range of concerns, in what is known as multiple-use management, including: the provision of timber, fuel wood, wildlife habitat, natural water quality management, recreation, landscape and community protection, employment, aesthetically appealing landscapes, biodiversity management, watershed management, erosion control, and preserving forests as " sinks" for atmospheric carbon dioxide. Forest ecosystems have come to be seen as the most important componen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landscape Contracting
Landscape contracting is: "a profession that involves the art and technology of landscape and garden project planning, construction and landscape management, and maintenance and gardening; for garden aesthetics, human enjoyment and safety, and ecosystem-plant community sustainability." Profession Landscape contracting is a licensed profession in many jurisdictions in the United States, with requirements varying, but including a combination of formal education, work experience and/or apprenticeship of a certain time length, technical testing, posting a bond, and periodic renewal submittals. Landscape Contracting Associations offer ongoing education, specialty skills certifications, and recognition of outstanding professional accomplishments. Education The Bachelor of Science in Landscape Contracting and Management degree was first offered by Mississippi State University in the Department of Landscape Architecture, and has recently begun being offered as a four-year academic major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gardening
Gardening is the practice of growing and cultivating plants as part of horticulture. In gardens, ornamental plants are often grown for their flowers, foliage, or overall appearance; useful plants, such as root vegetables, leaf vegetables, fruits, and herbs, are grown for consumption, for use as dyes, or for medicinal or cosmetic use. Gardening ranges in scale from fruit orchards, to long boulevard plantings with one or more different types of shrubs, trees, and herbaceous plants, to residential back gardens including lawns and foundation plantings, all the way to container gardens grown inside or outside. Gardening may be very specialized, with only one type of plant grown, or involve a variety of plants in mixed plantings. It involves an active participation in the growing of plants, and tends to be labor-intensive, which differentiates it from farming or forestry. History Ancient times Forest gardening, a forest-based food production system, is the world's oldest form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetics
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek language, Greek wikt:φυλή, φυλή/wikt:φῦλον, φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, Protein, protein Amino acid, amino acid sequences, or Morphology (biology), morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Analysis
In bioinformatics, sequence analysis is the process of subjecting a DNA, RNA or peptide sequence to any of a wide range of analytical methods to understand its features, function, structure, or evolution. Methodologies used include sequence alignment, searches against biological databases, and others. Since the development of methods of high-throughput production of gene and protein sequences, the rate of addition of new sequences to the databases increased very rapidly. Such a collection of sequences does not, by itself, increase the scientist's understanding of the biology of organisms. However, comparing these new sequences to those with known functions is a key way of understanding the biology of an organism from which the new sequence comes. Thus, sequence analysis can be used to assign function to genes and proteins by the study of the similarities between the compared sequences. Nowadays, there are many tools and techniques that provide the sequence comparisons (sequence al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg , image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg , other_symbol = Great Seal of the State , other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal , national_motto = "Firm and Happy for the Union" , national_anthem = "National Anthem of Peru" , march = "March of Flags" , image_map = PER orthographic.svg , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Lima , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Peruvian Spanish, Spanish , languages_type = Co-official languages , languages = , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2017 , demonym = Peruvians, Peruvian , government_type = Unitary state, Unitary Semi-presidential system, semi-presidential republic , leader_title1 = President of Peru, President ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macroscopic Scale
The macroscopic scale is the length scale on which objects or phenomena are large enough to be visible with the naked eye, without magnifying optical instruments. It is the opposite of microscopic. Overview When applied to physical phenomena and bodies, the macroscopic scale describes things as a person can directly perceive them, without the aid of magnifying devices. This is in contrast to observations (microscopy) or theories ( microphysics, statistical physics) of objects of geometric lengths smaller than perhaps some hundreds of micrometers. A macroscopic view of a ball is just that: a ball. A microscopic view could reveal a thick round skin seemingly composed entirely of puckered cracks and fissures (as viewed through a microscope) or, further down in scale, a collection of molecules in a roughly spherical shape (as viewed through an electron microscope). An example of a physical theory that takes a deliberately macroscopic viewpoint is thermodynamics. An example of a topi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |