|
Spoke Card
A spoke is one of some number of rods radiating from the center of a wheel (the hub where the axle connects), connecting the hub with the round traction surface. The term originally referred to portions of a log that had been riven (split lengthwise) into four or six sections. The radial members of a wagon wheel were made by carving a spoke (from a log) into their finished shape. A spokeshave is a tool originally developed for this purpose. Eventually, the term spoke was more commonly applied to the finished product of the wheelwright's work, than to the materials they used. History The spoked wheel was invented to allow the construction of lighter and swifter vehicles. Earliest physical evidence for spoked wheels were found in Sintashta culture, dating to 2000 BC. Soon after this, horse cultures of the Caucasus region used horse-drawn spoked-wheel war chariots for the greater part of three centuries. They moved deep into the Greek peninsula where they joined with the exist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheel
A wheel is a circular component that is intended to rotate on an axle Bearing (mechanical), bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the Simple machine, six simple machines. Wheels, in conjunction with axles, allow heavy objects to be moved easily facilitating movement or transportation while supporting a load, or performing labor in machines. Wheels are also used for other purposes, such as a ship's wheel, steering wheel, potter's wheel, and flywheel. Common examples are found in transport applications. A wheel reduces friction by facilitating motion by rolling together with the use of Axle, axles. In order for wheels to rotate, a Moment (physics), moment needs to be applied to the wheel about its axis, either by way of gravity or by the application of another external force or torque. Using the wheel, Sumer, Sumerians invented a device that spins clay as a potter shapes it into the desired object. Terminology The English word '':wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates and is the capital of the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, with its recorded history spanning over 3,400 years and its earliest human presence beginning somewhere between the 11th and 7th millennia BC. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state. It was a centre for the arts, learning and philosophy, and the home of Plato's Academy and Aristotle's Lyceum. It is widely referred to as the cradle of Western civilization and the birthplace of democracy, largely because of its cultural and political influence on the European continent—particularly Ancient Rome. In modern times, Athens is a large cosmopolitan metropolis and central to economic, financial, industrial, maritime, political and cultural life in Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wire Wheels
Wire wheels, wire-spoked wheels, tension-spoked wheels, or "suspension" wheels are wheels whose rims connect to their hubs by wire spokes. Although these wires are generally stiffer than a typical wire rope, they function mechanically the same as tensioned flexible wires, keeping the rim true while supporting applied loads. The term ''suspension wheel'' should not be confused with vehicle suspension. Wire wheels are used on most bicycles and are still used on many motorcycles. They were invented by aeronautical engineer George Cayley in 1808. Although Cayley first proposed wire wheels, he did not apply for a patent. The first patent for wire wheels was issued to Theodore Jones of London, England on October 11, 1826. Eugène Meyer of Paris, France was the first person to receive, in 1869, a patent for wire wheels on bicycles. Bicycle wheels were not strong enough for cars until the development of tangentially spoked wheels. They rapidly became well established in the bicyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicycle
A bicycle, also called a pedal cycle, bike or cycle, is a human-powered or motor-powered assisted, pedal-driven, single-track vehicle, having two wheels attached to a frame, one behind the other. A is called a cyclist, or bicyclist. Bicycles were introduced in the 19th century in Europe. By the early 21st century, more than 1 billion were in existence. These numbers far exceed the number of cars, both in total and ranked by the number of individual models produced. They are the principal means of transportation in many regions. They also provide a popular form of recreation, and have been adapted for use as children's toys, general fitness, military and police applications, courier services, bicycle racing, and bicycle stunts. The basic shape and configuration of a typical upright or "safety bicycle", has changed little since the first chain-driven model was developed around 1885. However, many details have been improved, especially since the advent of modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radius
In classical geometry, a radius ( : radii) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The name comes from the latin ''radius'', meaning ray but also the spoke of a chariot wheel. as a function of axial position ../nowiki>" Spherical coordinates In a spherical coordinate system, the radius describes the distance of a point from a fixed origin. Its position if further defined by the polar angle measured between the radial direction and a fixed zenith direction, and the azimuth angle, the angle between the orthogonal projection of the radial direction on a reference plane that passes through the origin and is orthogonal to the zenith, and a fixed reference direction in that plane. See also *Bend radius *Filling radius in Riemannian geometry *Radius of convergence * Radius of convexity *Radius of curvature *Radius of gyration ''Radius of gyration'' or gyradius of a body about the axis of r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
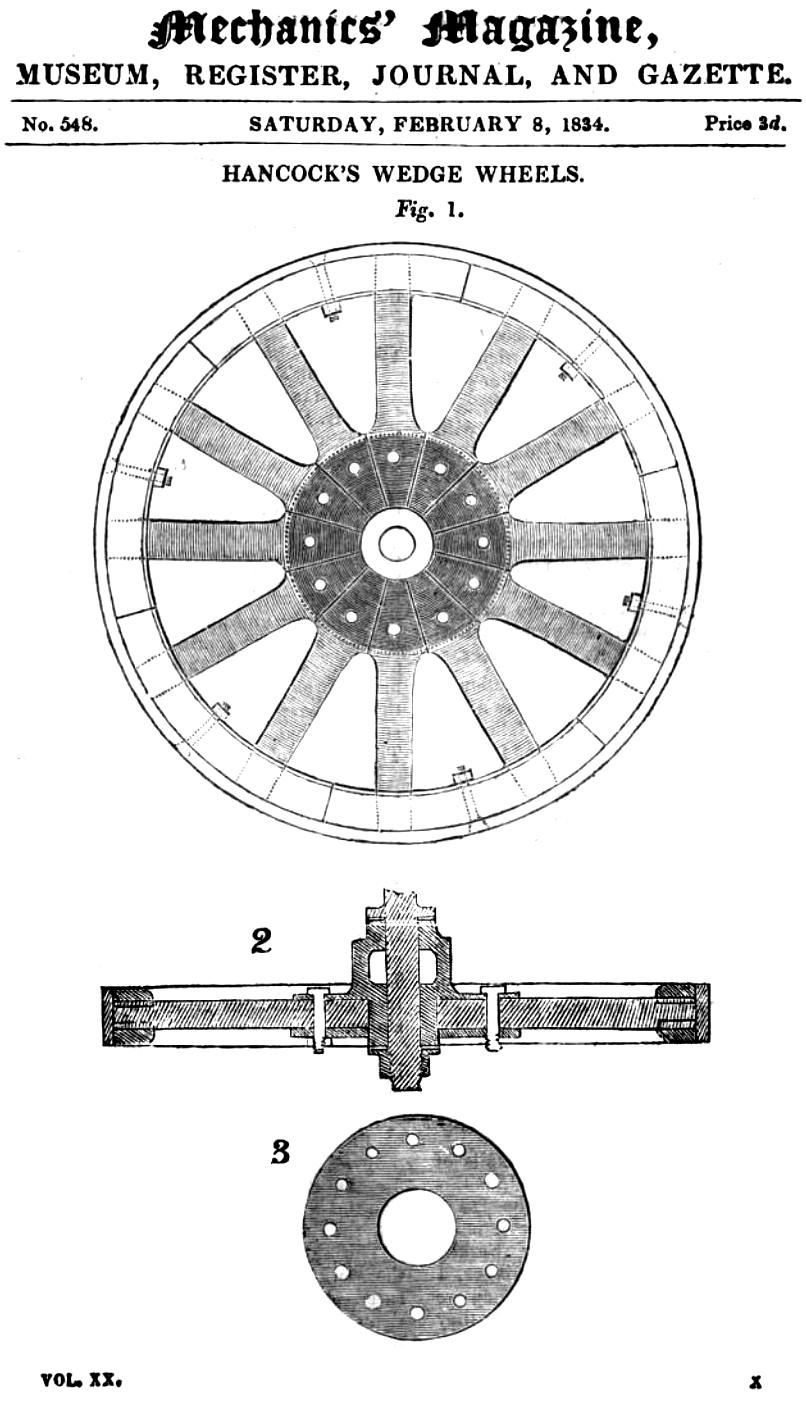
Artillery Wheel
The artillery wheel was a nineteenth-century and early-twentieth-century style of wagon, gun carriage, and automobile wheel. Rather than having its spokes mortised into a wooden nave (hub), it has them fitted together in a keystone fashion with miter joints, bolted into a two-piece metal nave. Its tyre is shrunk onto the rim in the usual way but it may also be bolted on for security. The design evolved over the nineteenth and early twentieth century, and was ultimately imitated in drawn steel for auto wheels which sometimes show little immediate resemblance to most of their design ancestry. Wood artillery wheels Wheels with wood spokes fitted together in a keystone fashion with miter joints, bolted into a two-piece metal nave, were called "wedge wheels" by Walter Hancock who described them in 1834, as he used them on his steam-powered road vehicles. In response to Hancock's description, John Robison said he had wheels of the same description built in 1811 for artillery carri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wagon
A wagon or waggon is a heavy four-wheeled vehicle pulled by draught animals or on occasion by humans, used for transporting goods, commodities, agricultural materials, supplies and sometimes people. Wagons are immediately distinguished from carts (which have two wheels) and from lighter four-wheeled vehicles primarily for carrying people, such as carriages. Animals such as horses, mules, or oxen usually pull wagons. One animal or several, often in pairs or teams may pull wagons. However, there are examples of human-propelled wagons, such as mining corfs. A wagon was formerly called a wain and one who builds or repairs wagons is a wainwright. More specifically, a wain is a type of horse- or oxen-drawn, load-carrying vehicle, used for agricultural purposes rather than transporting people. A wagon or cart, usually four-wheeled; for example, a haywain, normally has four wheels, but the term has now acquired slightly poetical connotations, so is not always used with technical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carriage
A carriage is a private four-wheeled vehicle for people and is most commonly horse-drawn. Second-hand private carriages were common public transport, the equivalent of modern cars used as taxis. Carriage suspensions are by leather strapping and, on those made in recent centuries, steel springs. Two-wheeled carriages are informal and usually owner-driven. Coaches are a special category within carriages. They are carriages with four corner posts and a fixed roof. Two-wheeled war chariots and transport vehicles such as four-wheeled wagons and two-wheeled carts were forerunners of carriages. In the twenty-first century, horse-drawn carriages are occasionally used for public parades by royalty and for traditional formal ceremonies. Simplified modern versions are made for tourist transport in warm countries and for those cities where tourists expect open horse-drawn carriages to be provided. Simple metal sporting versions are still made for the sport known as competitive driving. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million years from a small multi-toed creature, ''Eohippus'', into the large, single-toed animal of today. Humans began domesticating horses around 4000 BCE, and their domestication is believed to have been widespread by 3000 BCE. Horses in the subspecies ''caballus'' are domesticated, although some domesticated populations live in the wild as feral horses. These feral populations are not true wild horses, as this term is used to describe horses that have never been domesticated. There is an extensive, specialized vocabulary used to describe equine-related concepts, covering everything from anatomy to life stages, size, colors, markings, breeds, locomotion, and behavior. Horses are adapted to run, allowing them to quickly escape predators, and po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Compression
In mechanics, compression is the application of balanced inward ("pushing") forces to different points on a material or structure, that is, forces with no net sum or torque directed so as to reduce its size in one or more directions.Ferdinand Pierre Beer, Elwood Russell Johnston, John T. DeWolf (1992), "Mechanics of Materials". (Book) McGraw-Hill Professional, It is contrasted with tension or traction, the application of balanced outward ("pulling") forces; and with shearing forces, directed so as to displace layers of the material parallel to each other. The compressive strength of materials and structures is an important engineering consideration. In uniaxial compression, the forces are directed along one direction only, so that they act towards decreasing the object's length along that direction. The compressive forces may also be applied in multiple directions; for example inwards along the edges of a plate or all over the side surface of a cylinder, so as to reduce its a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tension (mechanics)
In physics, tension is described as the pulling force transmitted axially by the means of a string, a rope, chain, or similar object, or by each end of a rod, truss member, or similar three-dimensional object; tension might also be described as the action-reaction pair of forces acting at each end of said elements. Tension could be the opposite of compression. At the atomic level, when atoms or molecules are pulled apart from each other and gain potential energy with a restoring force still existing, the restoring force might create what is also called tension. Each end of a string or rod under such tension could pull on the object it is attached to, in order to restore the string/rod to its relaxed length. Tension (as a transmitted force, as an action-reaction pair of forces, or as a restoring force) is measured in newtons in the International System of Units (or pounds-force in Imperial units). The ends of a string or other object transmitting tension will exert forces on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
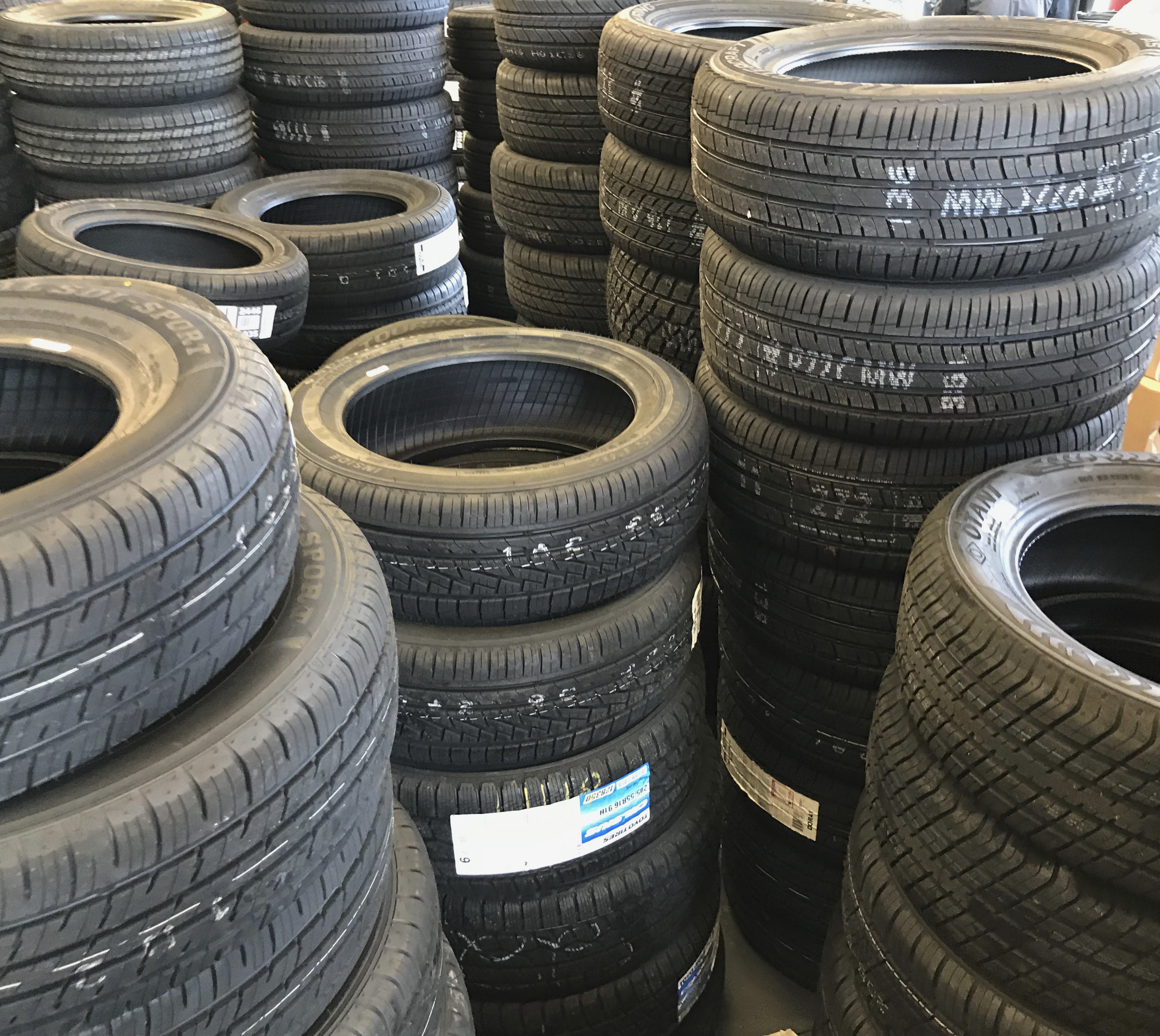
Tire
A tire (American English) or tyre (British English) is a ring-shaped component that surrounds a Rim (wheel), wheel's rim to transfer a vehicle's load from the axle through the wheel to the ground and to provide Traction (engineering), traction on the surface over which the wheel travels. Most tires, such as those for automobiles and bicycles, are pneumatically inflated structures, which also provide a flexible cushion that absorbs shock as the tire rolls over rough features on the surface. Tires provide a footprint, called a contact patch, that is designed to match the weight of the vehicle with the bearing strength of the surface that it rolls over by providing a bearing pressure that will not deform the surface excessively. The materials of modern pneumatic tires are synthetic rubber, natural rubber, fabric, and wire, along with carbon black and other chemical compounds. They consist of a tire tread, tread and a body. The tread provides Traction (engineering), traction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |