|
Speck (cipher)
Speck is a family of lightweight block ciphers publicly released by the National Security Agency (NSA) in June 2013. Speck has been optimized for performance in software implementations, while its sister algorithm, Simon, has been optimized for hardware implementations. Speck is an add–rotate–xor (ARX) cipher. The NSA began working on the Simon and Speck ciphers in 2011. The agency anticipated some agencies in the US federal government would need a cipher that would operate well on a diverse collection of Internet of Things devices while maintaining an acceptable level of security. Cipher description Speck supports a variety of block and key sizes. A block is always two words, but the words may be 16, 24, 32, 48 or 64 bits in size. The corresponding key is 2, 3 or 4 words. The round function consists of two rotations, adding the right word to the left word, xoring the key into the left word, then xoring the left word into the right word. The number of rounds depends o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speck Block Cipher 0 Indexing
Speck can refer to a number of European cured pork products, typically salted and air-cured and often lightly smoked but not cooked. In Germany, speck is pickled pork fat with or without some meat in it. Throughout much of the rest of Europe and parts of the English-speaking culinary world, speck often refers to South Tyrolean speck, a type of smoked prosciutto. The term "speck" became part of popular parlance only in the eighteenth century and replaced the older term "bachen", a cognate of "bacon". Regional varieties There are a number of regional varieties of speck, including: * Bacon, e.g. ''Frühstücksspeck'' ("breakfast speck") in Germany * Gailtaler speck from Austria, with ''PGI'' status, which has been made since the 15th century in the Gail Valley ("Gailtal") in Carinthia [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AES (cipher)
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), also known by its original name Rijndael (), is a specification for the encryption of electronic data established by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2001. AES is a variant of the Rijndael block cipher developed by two Belgian cryptographers, Joan Daemen and Vincent Rijmen, who submitted a proposal to NIST during the AES selection process. Rijndael is a family of ciphers with different key and block sizes. For AES, NIST selected three members of the Rijndael family, each with a block size of 128 bits, but three different key lengths: 128, 192 and 256 bits. AES has been adopted by the U.S. government. It supersedes the Data Encryption Standard (DES), which was published in 1977. The algorithm described by AES is a symmetric-key algorithm, meaning the same key is used for both encrypting and decrypting the data. In the United States, AES was announced by the NIST as U.S. FIPS PUB 197 (FIPS 197) on November ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
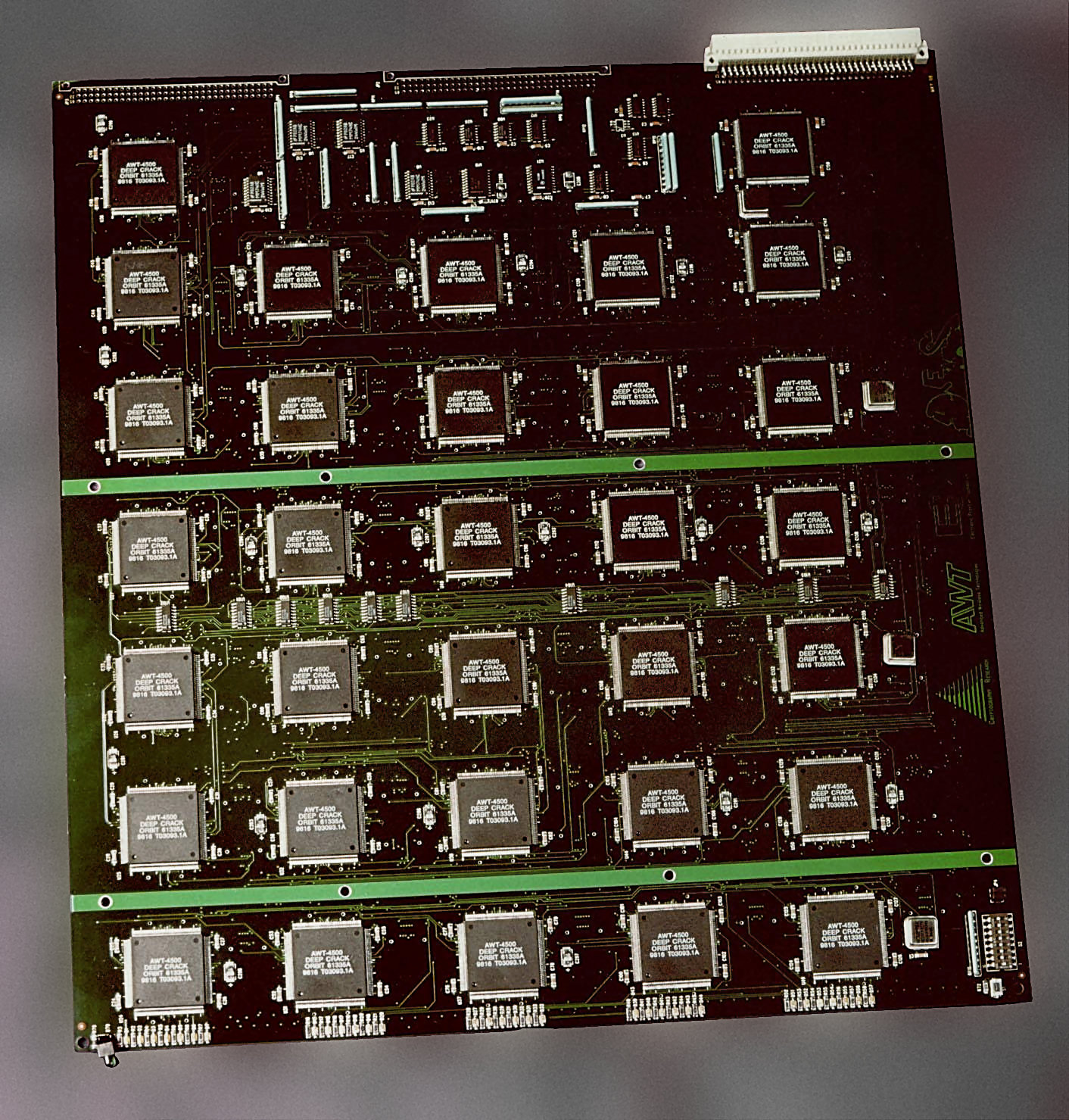
Brute-force Attacks
In cryptography, a brute-force attack consists of an attacker submitting many passwords or passphrases with the hope of eventually guessing correctly. The attacker systematically checks all possible passwords and passphrases until the correct one is found. Alternatively, the attacker can attempt to guess the key which is typically created from the password using a key derivation function. This is known as an exhaustive key search. A brute-force attack is a cryptanalytic attack that can, in theory, be used to attempt to decrypt any encrypted data (except for data encrypted in an information-theoretically secure manner). Such an attack might be used when it is not possible to take advantage of other weaknesses in an encryption system (if any exist) that would make the task easier. When password-guessing, this method is very fast when used to check all short passwords, but for longer passwords other methods such as the dictionary attack are used because a brute-force search ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Cryptanalysis
Differential cryptanalysis is a general form of cryptanalysis applicable primarily to block ciphers, but also to stream ciphers and cryptographic hash functions. In the broadest sense, it is the study of how differences in information input can affect the resultant difference at the output. In the case of a block cipher, it refers to a set of techniques for tracing differences through the network of transformation, discovering where the cipher exhibits non-random behavior, and exploiting such properties to recover the secret key (cryptography key). History The discovery of differential cryptanalysis is generally attributed to Eli Biham and Adi Shamir in the late 1980s, who published a number of attacks against various block ciphers and hash functions, including a theoretical weakness in the Data Encryption Standard (DES). It was noted by Biham and Shamir that DES was surprisingly resistant to differential cryptanalysis but small modifications to the algorithm would make it much mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hash Function
A hash function is any function that can be used to map data of arbitrary size to fixed-size values. The values returned by a hash function are called ''hash values'', ''hash codes'', ''digests'', or simply ''hashes''. The values are usually used to index a fixed-size table called a ''hash table''. Use of a hash function to index a hash table is called ''hashing'' or ''scatter storage addressing''. Hash functions and their associated hash tables are used in data storage and retrieval applications to access data in a small and nearly constant time per retrieval. They require an amount of storage space only fractionally greater than the total space required for the data or records themselves. Hashing is a computationally and storage space-efficient form of data access that avoids the non-constant access time of ordered and unordered lists and structured trees, and the often exponential storage requirements of direct access of state spaces of large or variable-length keys. Use of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Known-key Distinguishing Attack
In cryptography, a known-key distinguishing attack is an attack model against symmetric ciphers, whereby an attacker who knows the key can find a structural property in cipher, where the transformation from plaintext to ciphertext is not random. There is no common formal definition for what such a transformation may be. The chosen-key distinguishing attack is strongly related, where the attacker can choose a key to introduce such transformations. These attacks do not directly compromise the confidentiality of ciphers, because in a classical scenario, the key is unknown to the attacker. Known-/chosen-key distinguishing attacks apply in the "open key model" instead. They are known to be applicable in some situations where block ciphers are converted to hash functions, leading to practical collision attacks against the hash. Known-key distinguishing attacks were first introduced in 2007 by Lars Knudsen and Vincent Rijmen in a paper that proposed such an attack against 7 out of 10 round ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Related-key Attack
In cryptography, a related-key attack is any form of cryptanalysis where the attacker can observe the operation of a cipher under several different keys whose values are initially unknown, but where some mathematical relationship connecting the keys is known to the attacker. For example, the attacker might know that the last 80 bits of the keys are always the same, even though they don't know, at first, what the bits are. This appears, at first glance, to be an unrealistic model; it would certainly be unlikely that an attacker could persuade a human cryptographer to encrypt plaintexts under numerous secret keys related in some way. KASUMI KASUMI is an eight round, 64-bit block cipher with a 128-bit key. It is based upon MISTY1, and was designed to form the basis of the 3G confidentiality and integrity algorithms. Mark Blunden and Adrian Escott described differential related key attacks on five and six rounds of KASUMI. Differential attacks were introduced by Biham and Shamir. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chosen-ciphertext Attack
A chosen-ciphertext attack (CCA) is an attack model for cryptanalysis where the cryptanalyst can gather information by obtaining the decryptions of chosen ciphertexts. From these pieces of information the adversary can attempt to recover the hidden secret key used for decryption. For formal definitions of security against chosen-ciphertext attacks, see for example: Michael Luby and Mihir Bellare et al. Introduction A number of otherwise secure schemes can be defeated under chosen-ciphertext attack. For example, the El Gamal cryptosystem is semantic security, semantically secure under chosen-plaintext attack, but this semantic security can be trivially defeated under a chosen-ciphertext attack. Early versions of RSA (algorithm), RSA padding used in the Secure Sockets Layer, SSL protocol were vulnerable to a sophisticated adaptive chosen-ciphertext attack which revealed SSL session keys. Chosen-ciphertext attacks have implications for some self-synchronizing stream ciphers as wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chosen-plaintext Attack
A chosen-plaintext attack (CPA) is an attack model for cryptanalysis which presumes that the attacker can obtain the ciphertexts for arbitrary plaintexts.Ross Anderson, ''Security Engineering: A Guide to Building Dependable Distributed Systems''. The first edition (2001): http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/~rja14/book.html The goal of the attack is to gain information that reduces the security of the encryption scheme. Modern ciphers aim to provide semantic security, also known as ''ciphertext indistinguishability under chosen-plaintext attack'', and they are therefore, by design, generally immune to chosen-plaintext attacks if correctly implemented. Introduction In a chosen-plaintext attack the adversary can (possibly adaptively) ask for the ciphertexts of arbitrary plaintext messages. This is formalized by allowing the adversary to interact with an encryption oracle, viewed as a black box. The attacker’s goal is to reveal all or a part of the secret encryption key. It may seem infeasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adiantum (cipher)
Adiantum is a cipher construction for disk encryption, which uses the ChaCha and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) ciphers, and Poly1305 cryptographic message authentication code (MAC). It was designed in 2018 by Paul Crowley and Eric Biggers at Google specifically for low-powered mobile devices running Android Go. It has been included in the Linux kernel since version 5.0. HPolyC is an earlier variant of Adiantum, which uses a different construction for the Poly1305 hash function. Adiantum is implemented in Android 10 as an alternative cipher for device encryption, particularly on low-end devices lacking hardware-accelerated support for AES. The company stated that Adiantum ran five times faster than AES-256-XTS on ARM Cortex-A7 The ARM Cortex-A7 MPCore is a 32-bit microprocessor core licensed by ARM Holdings implementing the ARMv7-A architecture announced in 2011. Overview It has two target applications; firstly as a smaller, simpler, and more power-efficient succes ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AES Instruction Set
An Advanced Encryption Standard instruction set is now integrated into many processors. The purpose of the instruction set is to improve the speed and security of applications performing encryption and decryption using Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). They are often implemented as instructions implementing a single round of AES along with a special version for the last round which has a slightly different method. The side channel attack surface of AES is reduced when implemented in an instruction set, compared to when AES is implemented in software only. x86 architecture processors AES-NI (or the Intel Advanced Encryption Standard New Instructions; AES-NI) was the first major implementation. AES-NI is an extension to the x86 instruction set architecture for microprocessors from Intel and AMD proposed by Intel in March 2008. Instructions Intel The following Intel processors support the AES-NI instruction set: * Westmere based processors, specifically: ** Westmere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Android (operating System)
Android is a mobile operating system based on a modified version of the Linux kernel and other open-source software, designed primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Android is developed by a consortium of developers known as the Open Handset Alliance and commercially sponsored by Google. It was unveiled in November 2007, with the first commercial Android device, the HTC Dream, being launched in September 2008. Most versions of Android are proprietary. The core components are taken from the Android Open Source Project (AOSP), which is free and open-source software (FOSS) primarily licensed under the Apache License. When Android is installed on devices, the ability to modify the otherwise free and open-source software is usually restricted, either by not providing the corresponding source code or by preventing reinstallation through technical measures, thus rendering the installed version proprietary. Most Android devices ship with additional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_Round_Function.png)