|
Southern Range
On the island of Trinidad, the Southern Range is a discontinuous chain of low hills along the southern coast, reaching their highest altitude in the high Trinity Hills of the southeast. According to legend, the sight of the three neighboring hilltops of the then unnamed Trinity Hills, led to Christopher Columbus, on his third voyage to the New World, to name the island, "La Trinidad" (as a form of devotion to his notion of god as the Holy Trinity). The broad lowland area on the west between the Southern Range and the Central Range is the Naparima Plain; the lowland area on the east is the Nariva Plain. The Oropuche River flows through the Naparima Plain and drains into the Oropuche Lagoon, a swampy area, on the Gulf of Paria coast, whereas the 31-mile long Ortoire River flows through the Nariva Plain and drains into the Nariva Swamp on the Atlantic Ocean coast. The Southern region of the island has sandy and less fertile soil. The Southern Range, particularly its Western and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinidad And Tobago Shaded Relief PCL Texas Annotated
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmost island in the West Indies. With an area of , it is also the fifth largest in the West Indies. Name The original name for the island in the Arawaks' language was which meant "Land of the Hummingbird". Christopher Columbus renamed it ('The Island of the Trinity'), fulfilling a vow he had made before setting out on his third voyage. This has since been shortened to ''Trinidad''. History Caribs and Arawaks lived in Trinidad long before Christopher Columbus encountered the islands on his third voyage on 31 July 1498. The island remained Spanish until 1797, but it was largely settled by French colonists from the French Caribbean, especially Martinique.Besson, Gerard (2000-08-27). "Land of Beginnings – A historical digest", ''Newsday N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ortoire River
The Ortoire River is a river in Trinidad and Tobago. It forms the boundary between Nariva County and Mayaro County in east Trinidad. At over in length, it is one of Trinidad's longest rivers and is navigable by very small crafts for at least a third of its length from its mouth at the Atlantic coast near Point Radix and the village of Ortoire. It is green in color and it once had an iron bridge with wooden planks but it has been replaced by an all paved concrete bridge; also it was made higher to reduce flooding. The river is famous for a bioluminescent Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by living organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some b ... blueish glow that is occasionally emitted by living organisms in the water. References Rivers of Trinidad and Tobago Trinidad (island) {{Trinidad-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Ranges Of Trinidad And Tobago
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
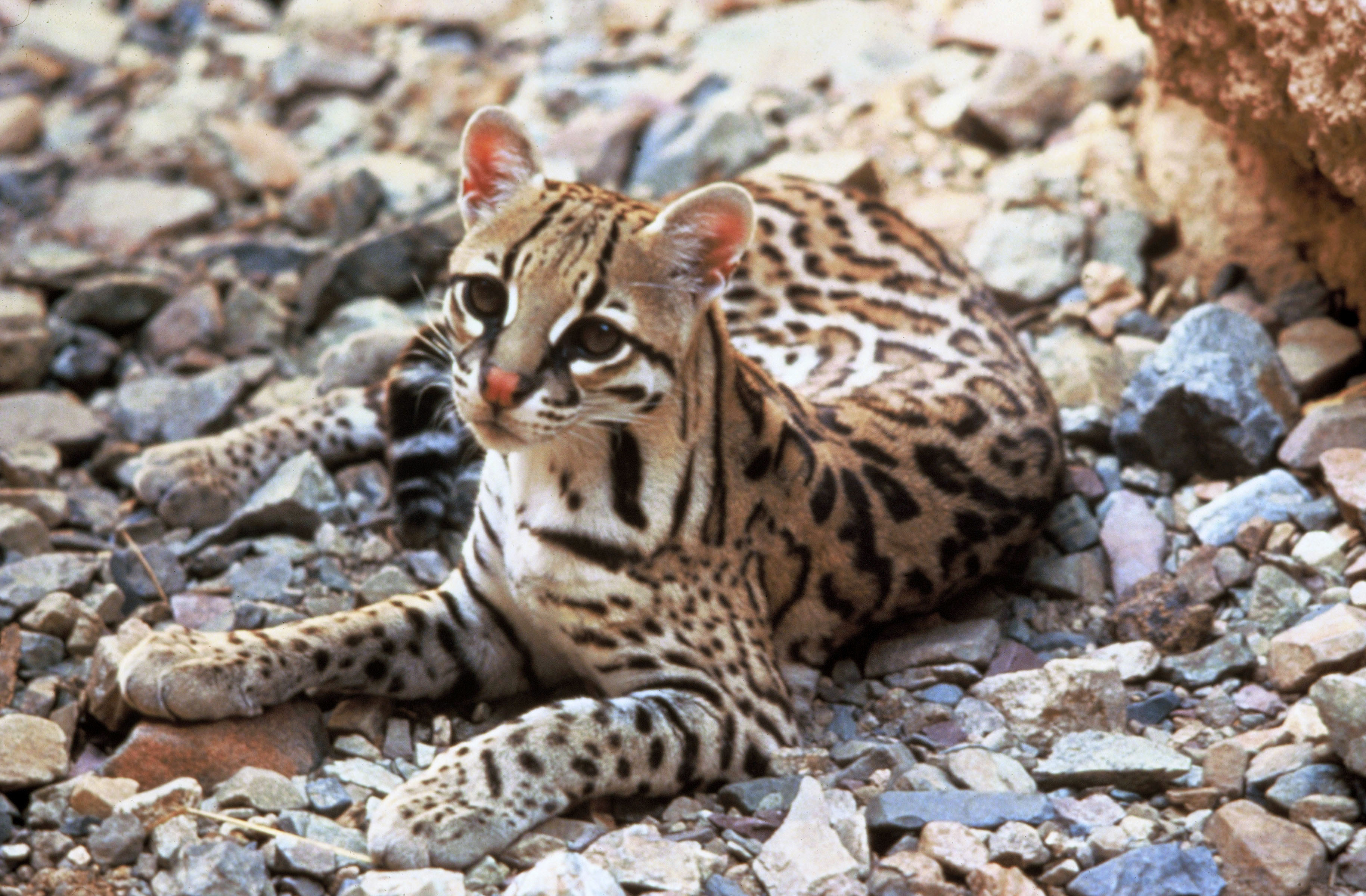
Ocelot
The ocelot (''Leopardus pardalis'') is a medium-sized spotted wild cat that reaches at the shoulders and weighs between on average. It was first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1758. Two subspecies are recognized. It is native to the southwestern United States, Mexico, Central and South America, and to the Caribbean islands of Trinidad and Margarita. It prefers areas close to water sources with dense vegetation cover and high prey availability. Typically active during twilight and at night, the ocelot tends to be solitary and territorial. It is efficient at climbing, leaping and swimming. It preys on small terrestrial mammals, such as armadillos, opossums, and lagomorphs. Both sexes become sexually mature at around two years of age and can breed throughout the year; peak mating season varies geographically. After a gestation period of two to three months the female gives birth to a litter of one to three kittens. They stay with their mother for up to two years, after whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Brocket Deer
The red brocket (''Mazama americana'') is a species of brocket deer from forests in South America, ranging from northern Argentina to Colombia and the Guianas. It also occurs on the Caribbean island of Trinidad (it also occurred on the island of Tobago until very recent historical times, but has been extirpated there). Taxonomy It formerly included the Central American red brocket (''M. temama'') and sometimes the Yucatan brown brocket (''M. pandora'') as subspecies. Considerable taxonomic confusion still exists for the populations remaining in the red brocket. Pending a solution to this, it has been evaluated as data deficient by the IUCN, though as presently defined, it is the most widespread species of brocket. It is sympatric with the smaller Amazonian brown brocket over much of its range (the latter tends to have significantly lower population densities). The karyotype A karyotype is the general appearance of the complete set of metaphase chromosomes in the cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White-fronted Capuchin
White-fronted capuchin can refer to any of a number of species of gracile capuchin monkey which used to be considered as the single species ''Cebus albifrons''. White-fronted capuchins are found in seven different countries in South America: Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, and Trinidad and Tobago. White-fronted capuchins are medium-sized monkeys with a light brown back and a creamy white underside. Like other capuchin monkeys, they are omnivorous, feeding primarily on fruits, invertebrates, other plant parts and sometimes small vertebrates. They are predated upon primarily by raptors and probably small cats, especially the margay, though snakes have been known to attack them. They are polygamous primates and live in fairly large groups of 15 to 35 individuals. Reproductive females give birth to a single young at biennial intervals. They maintain home ranges of and have complex vocal repertoires. They are among the few primates to have been observed craft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howler Monkeys
Howler monkeys (genus ''Alouatta'', monotypic in subfamily Alouattinae) are the most widespread primate genus in the Neotropics and are among the largest of the platyrrhines along with the muriquis (''Brachyteles''), the spider monkeys (''Ateles'') and woolly monkeys (''Lagotrix''). These monkeys are native to South and Central American forests. They are famous for their loud howls, which can travel more than a mile through dense rain forest. Fifteen species are recognized. Previously classified in the family Cebidae, they are now placed in the family Atelidae. They are primarily folivores but also significant frugivores, acting as seed dispersal agents through their digestive system and their locomotion. Threats include human predation, habitat destruction, and capture for pets or zoo animals. Classification * ''A. palliata'' group ** Coiba Island howler, ''Alouatta coibensis'' *** '' Alouatta coibensis coibensis'' *** Azuero howler, ''Alouatta coibensis trabeata'' ** M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nariva Swamp
The Nariva Swamp is the largest freshwater wetland in Trinidad and Tobago and has been designated a ''Wetland of International Importance'' under the Ramsar Convention. The swamp is located on the east coast of Trinidad, immediately inland from the Manzanilla Bay through Biche and covers over 60 square kilometres (23 mi2). The Nariva Swamp is extremely biodiverse. It is home to 45 mammal species, 39 reptile species, 33 fish species, 204 bird species, 19 frog species, 213 insect species and 15 mollusc species. All this contained in just 60 square kilometers. Description The area provides important habitat for waterfowl and is key habitat for the West Indian manatee (''Trichechus manatus'')., caimans, anacondas, boa constrictors, red howler monkeys, white-fronted capuchin monkeys, numerous species of parrots, including both the blue-and-gold macaw and red-bellied macaws, as well as many wetland and savanna birds. Four major wetland vegetation typesAs defined by Beard (1946). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
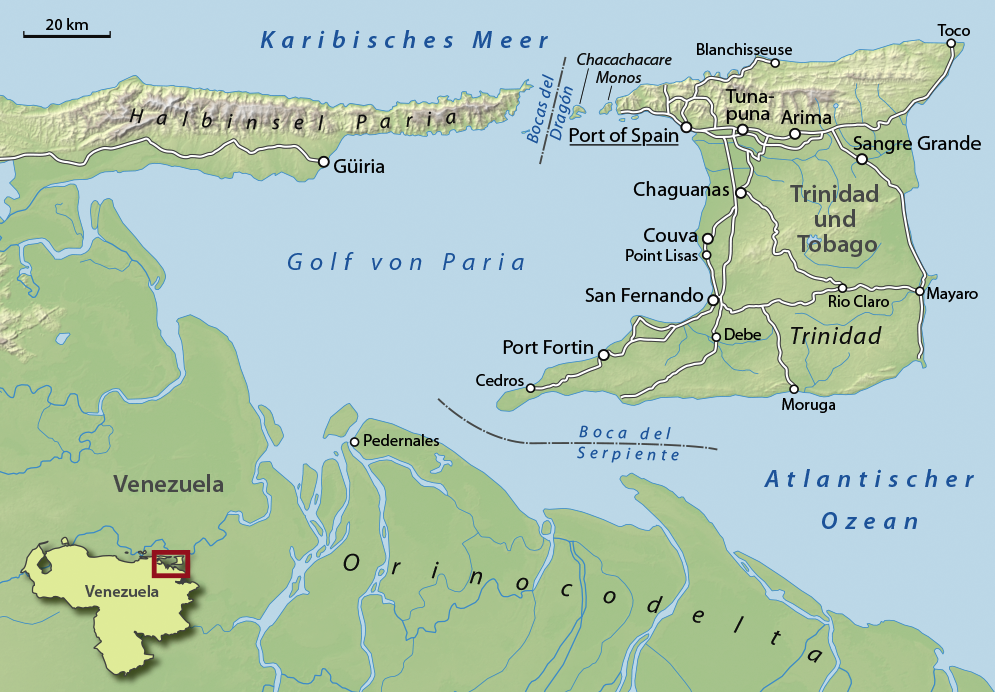
Gulf Of Paria
The Gulf of Paria ( ; es, Golfo de Paria) is a shallow (180 m at its deepest) semi-enclosed inland sea located between the island of Trinidad (Republic of Trinidad and Tobago) and the east coast of Venezuela. It separates the two countries by as little as 15 km at its narrowest and 120 km at its widest points. The tides within the Gulf are semi-diurnal in nature with a range of approximately 1m. The Gulf of Paria is considered to be one of the best natural harbors on the Atlantic coast of the Americas. The jurisdiction of the Gulf of Paria is split between Trinidad and Tobago and Venezuela with Trinidad and Tobago having control over approximately (37.7%) and Venezuela the remainder (62.3%). It was originally named the Gulf of the Whale ( es, Golfo de la Ballena) by Christopher Columbus, but the 19th-century whaling industry eliminated whales from the area and populations have never recovered. Cartographic sources of the late 18th century repeatedly refer to it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmost island in the West Indies. With an area of , it is also the fifth largest in the West Indies. Name The original name for the island in the Arawaks' language was which meant "Land of the Hummingbird". Christopher Columbus renamed it ('The Island of the Trinity'), fulfilling a vow he had made before setting out on his third voyage. This has since been shortened to ''Trinidad''. History Caribs and Arawaks lived in Trinidad long before Christopher Columbus encountered the islands on his third voyage on 31 July 1498. The island remained Spanish until 1797, but it was largely settled by French colonists from the French Caribbean, especially Martinique.Besson, Gerard (2000-08-27). "Land of Beginnings – A historical digest", ''Newsday Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oropuche River
Oropouche or Oropuche can refer to: *Cumaca Cave * Oropouche (constituency), a constituency in the parliament of Trinidad and Tobago *Oropouche fever *Oropouche River *Oropouche West (constituency) Oropouche or Oropuche can refer to: *Cumaca Cave *Oropouche (constituency), a constituency in the parliament of Trinidad and Tobago *Oropouche fever *Oropouche River * Oropouche West (constituency), a constituency in the parliament of Trinidad and T ..., a constituency in the parliament of Trinidad and Tobago * South Oropouche, a community in Trinidad and Tobago {{dab, geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nariva Plain
On the island of Trinidad, the Nariva Plain is a lowland area on the east between the Central Range and the Southern Range; the lowland area on the west is the Naparima Plain. To the north of the Central Range is the Caroni Plain On the island of Trinidad in the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, the Caroni Plain is a lowland area between the Northern Range and the Central Range. The lowland areas to the south of the Central Range are the Naparima Plain on the west and the .... The lowland areas are either flat or consist of gently rolling hills. The eastern half of the island is not as thickly settled as the western. The 35-mile long Ortoire River flows eastward through the Nariva Plain and drains in the Nariva Swamp (see map and picture below) on the Atlantic Ocean coast. Notes References * {{coord, 10.34, -61.13, type:landmark_region:TT_dim:20000, display=title Plains of Trinidad and Tobago Trinidad (island) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_com_filhote.jpg)