|
Southern Congolian Forest–savanna Mosaic
The southern Congolian forest–savanna mosaic is an ecoregion that covers a large area of the southern Democratic Republic of the Congo and northeastern Angola. Its rich blend of habitats provides key insights into the biogeography of central Africa with the extensive climatic variation that it has been experiencing for the last 10 million years. The human population is not high. Geography The Southern Congolian forest–savanna mosaic is a transitional region between the equatorial Congolian forests region to the north and the woodlands and savannas of the Zambezian region to the south. The Central Congolian lowland forests lie to the north, west of the Congo River, and the Northeastern Congolian lowland forests are east of the Congo. In the highlands to the east are the Albertine Rift montane forests. The Central Zambezian miombo woodlands lie to the southeast, and the Angolan miombo woodlands to the southwest. To the west across the Kwango River is the Western Congolian forest� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masi-Manimba
Masi-Manimba is a town in Kwilu Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo, the headquarters of the Masi-Manimba Territory. As of 2012 the population was estimated to be 31,802. The town lies on the Lukula River, a tributary of the Kwilu River. It is on the road between Kenge to the west and Kikwit to the east. Masi-Manimba is served by Masi-Manimba Airport (MSM), with a runway length of and an altitude of . The area was led by Anne Mbusu who was the administrator appointed by former President Joseph Kabila Kabang. She was one of the women entrusted with such a role in the DRC. The town elects seven national deputies and the majority recently were from the Unified Lumumbist Party Unified Lumumbist Party (french: Parti Lumumbiste Unifié or ''PALU'') is a political party in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The party's name comes from Patrice Lumumba, the first prime minister of Congo after its independence in 1960 fr .... References Populated places in Kwilu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
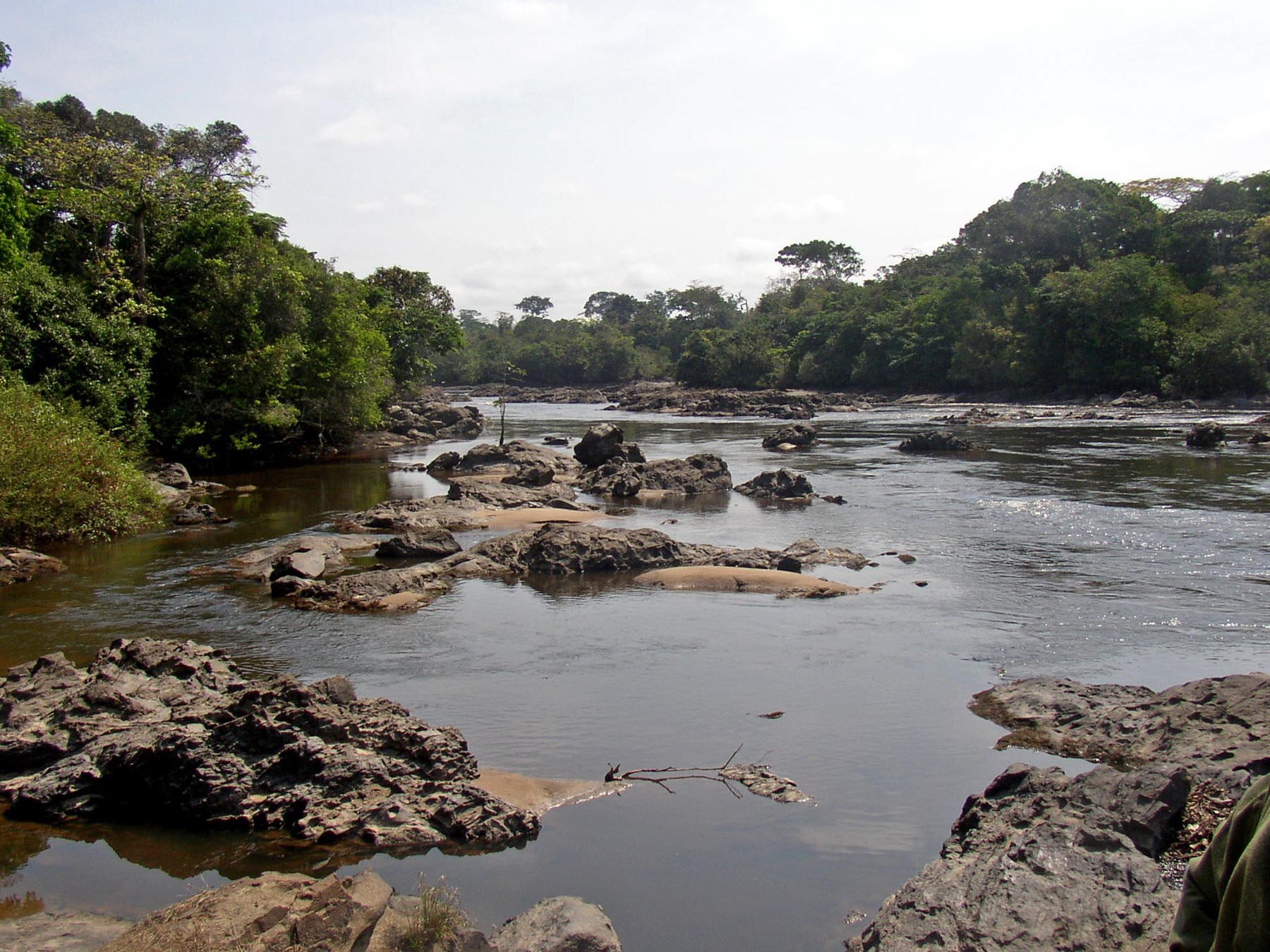
Rain Forest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainforest, but other types have been described. Estimates vary from 40% to 75% of all biotic species being indigenous to the rainforests. There may be many millions of species of plants, insects and microorganisms still undiscovered in tropical rainforests. Tropical rainforests have been called the "jewels of the Earth" and the " world's largest pharmacy", because over one quarter of natural medicines have been discovered there. Rainforests as well as endemic rainforest species are rapidly disappearing due to deforestation, the resulting habitat loss and pollution of the atmosphere. Definition Rainforest are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, high humidity, the presence of moisture-dependent vegetation, a moist layer of leaf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
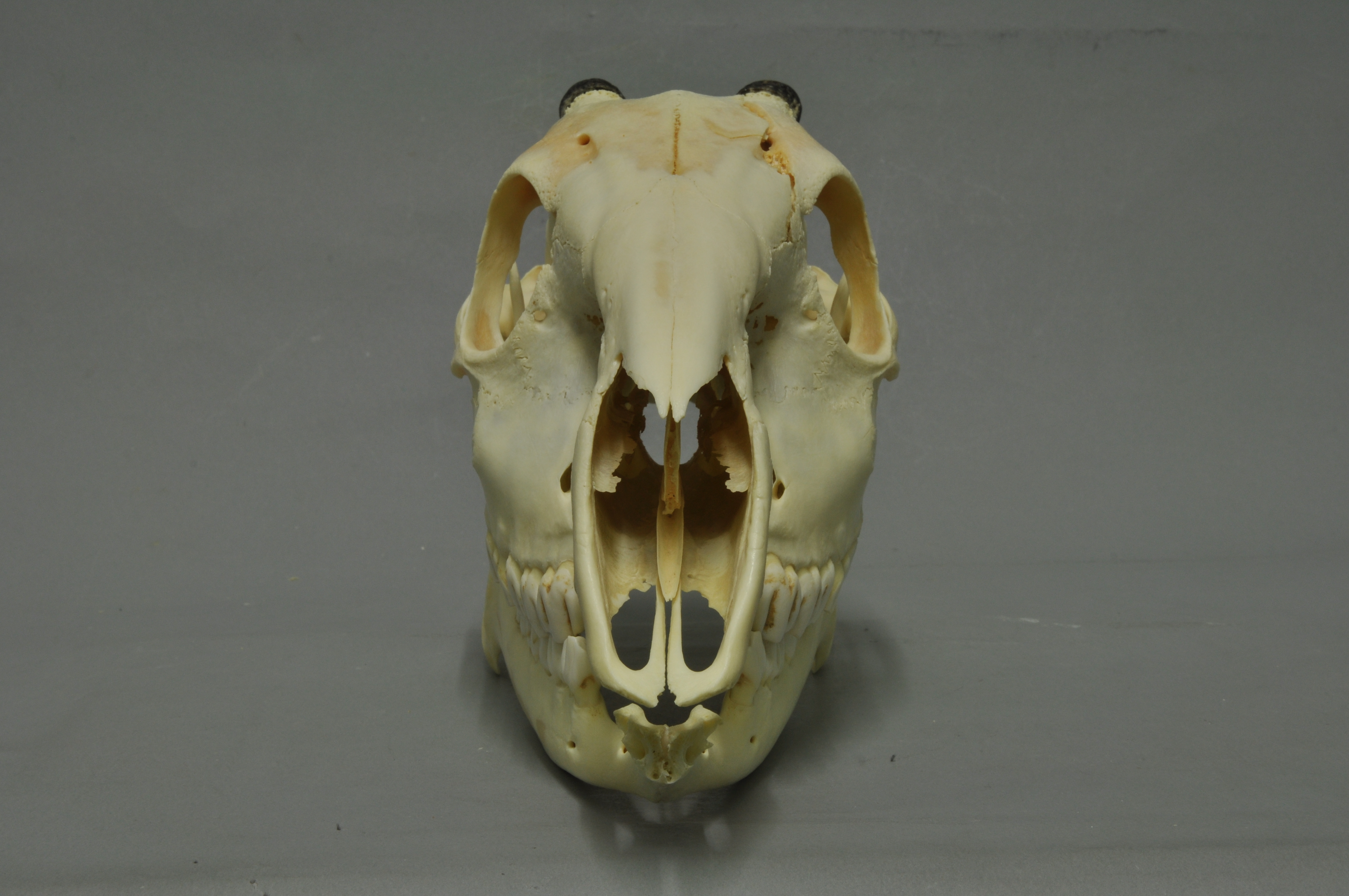
Hippopotamus
The hippopotamus ( ; : hippopotamuses or hippopotami; ''Hippopotamus amphibius''), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two extant species in the family Hippopotamidae, the other being the pygmy hippopotamus (''Choeropsis liberiensis'' or ''Hexaprotodon liberiensis''). Its name comes from the ancient Greek for "river horse" (). Aside from elephants and rhinos, the hippopotamus is the largest land mammal. It is also the largest extant land artiodactyl. Despite their physical resemblance to pigs and other terrestrial even-toed ungulates, the closest living relatives of the hippopotamids are cetaceans (whales, dolphins, porpoises, etc.), from which they diverged about 55 million years ago. Hippos are recognisable for their barrel-shaped torsos, wide-opening mouths with large canine tusks, nearly hairless bodies, pillar-like legs, and large size: adults average ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Reedbuck
The southern reedbuck, rietbok or common reedbuck (''Redunca arundinum'') is a diurnal antelope typically found in southern Africa. It was first described by Pieter Boddaert, a Dutch physician and naturalist, in 1785. It is placed in the genus '' Redunca'' and family Bovidae. This antelope has an average mass of and a body length of about . Taxonomy and etymology It was first described by Pieter Boddaert, a Dutch physician and naturalist, in 1785. It is placed in the genus '' Redunca'' and family Bovidae. It gets its name from two Latin words: ''reduncas'' (meaning bent backwards and curved, while the horns are bent forwards) and ''arundo'' (harundo) (meaning a reed; hence ''arundinum'', pertaining to reeds). Description The southern reedbuck is larger than the other species in ''Redunca'', namely '' R. redunca'' (Bohor reedbuck) and '' R. fulvorufula'' (mountain reedbuck). It stands at the shoulder. Females weigh , while the males weigh . It has distinctive dark lines r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterbuck
The waterbuck (''Kobus ellipsiprymnus'') is a large antelope found widely in sub-Saharan Africa. It is placed in the genus '' Kobus'' of the family Bovidae. It was first described by Irish naturalist William Ogilby in 1833. Its 13 subspecies are grouped under two varieties: the common or ellipsiprymnus waterbuck and the defassa waterbuck. The head-and-body length is typically between and the typical height is between . In this sexually dimorphic antelope, males are taller and heavier than females. Males reach roughly at the shoulder, while females reach . Males typically weigh and females . Their coat colour varies from brown to grey. The long, spiral horns, present only on males, curve backward, then forward, and are long. Waterbucks are rather sedentary in nature. As gregarious animals, they may form herds consisting of six to 30 individuals. These groups are either nursery herds with females and their offspring or bachelor herds. Males start showing territorial behaviou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Bush Elephant
The African bush elephant (''Loxodonta africana'') is one of two extant African elephant species and one of three extant elephant species. It is the largest living terrestrial animal, with bulls reaching a shoulder height of up to and a body mass of up to . It is distributed across 37 African countries and inhabits forests, grasslands and woodlands, wetlands and agricultural land. Since 2021, it has been listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List. It is threatened foremost by habitat destruction, and in parts of its range also by poaching for meat and ivory. It is a social mammal, travelling in herds composed of cows and their offspring. Adult bulls usually live alone or in small bachelor groups. It is a herbivore, feeding on grasses, creepers, herbs, leaves, and bark. The menstrual cycle lasts three to four months, and females are pregnant for 22 months, the longest gestation period of any mammal. Taxonomy ''Elephas africanus'' was the scientific name proposed by Johann Fri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow-backed Duiker
The yellow-backed duiker (''Cephalophus silvicultor'') is a forest dwelling antelope in the order Artiodactyla from the family Bovidae. Yellow-backed duikers are the most widely distributed of all duikers. They are found mainly in Central and Western Africa, ranging from Senegal to Western Uganda with possibly a few in Gambia. Their range also extends southward into Rwanda, Burundi, Zaire, and most of Zambia. Taxonomy and etymology The scientific name of the yellow-backed duiker is ''Cephalophus silvicultor''. It is the type species of ''Cephalophus'', and placed in the subfamily Cephalophinae and family Bovidae. The species was first described by English botanist Adam Afzelius in the journal ''Nova Acta Regiæ Societatis Scientiarum Upsaliensis'' in 1815. The generic name has possibly originated from the combination of the New Latin word ''cephal'', meaning head, and the Greek word ''lophos'', meaning crest. The specific name ''silvicultor'' is composed by two Latin words: ''s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Duiker
The blue duiker (''Philantomba monticola'') is a small antelope found in central, southern and eastern Africa. It is the smallest duiker. The species was first described by Swedish naturalist Carl Peter Thunberg in 1789. 12 subspecies are identified. The blue duiker reaches at the shoulder and weighs . Sexually dimorphic, the females are slightly larger than the males. The dark tail measures slightly above . It has short, spiky horns, around long and hidden in hair tufts. The subspecies show a great degree of variation in their colouration. The blue duiker bears a significant resemblance to Maxwell's duiker. Activity is diurnal (limited to daytime). Secretive and cautious, the blue duiker confines itself to the forest fringes. Territorial, individuals of opposite sexes form pairs and occupy territories, nearly large and marked by preorbital gland secretions. The blue duiker feeds on fallen fruits, foliage, flowers and pieces of bark, provided mainly by the forest canopies i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bongo (antelope)
The bongo (''Tragelaphus eurycerus'') is a herbivorous, mostly nocturnal forest ungulate. Bongos are characterised by a striking reddish-brown coat, black and white markings, white-yellow stripes and long slightly spiralled horns. They are the only tragelaphid in which both sexes have horns. They have a complex social interaction and are found in African dense forest mosaics. Native to Africa, they are the third-largest antelope in the world. The western or lowland bongo, ''T. e. eurycerus'', faces an ongoing population decline, and the IUCN Antelope Specialist Group considers it to be Near Threatened on the conservation status scale. The eastern or mountain bongo, ''T. e. isaaci'', of Kenya, has a coat even more vibrant than that of ''T. e. eurycerus''. The mountain bongo is only found in the wild in a few mountain regions of central Kenya. This bongo is classified by the IUCN Antelope Specialist Group as Critically Endangered, with fewer individuals in the wild than in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guineo-Congolian Region
The Guineo-Congolian region is a biogeographical region in Africa straddling the Equator and stretching from the Atlantic Ocean through the Congo Basin to the Congo / Nile divide in Rwanda and Burundi. Formerly, this region was largely covered in rain forest, on both well-drained sites and in swamp forests, but little undisturbed primary forest now remains, having been replaced in many areas by savanna and secondary-growth forest. Description The Guineo-Congolian region is a tropical, lowland rain forest area, typified by the forests of the Congo Basin. The terrain is generally under and the annual rainfall is typically in the range . The forest is tall with a dense canopy, or more above the ground, with emergent trees up to tall, and with several layers. The constituent trees are mostly evergreen or semi-evergreen, with a scattering of deciduous species. In the wetter areas, the trees may be clad with numerous epiphytes, but these are less common in drier areas. Large trees ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
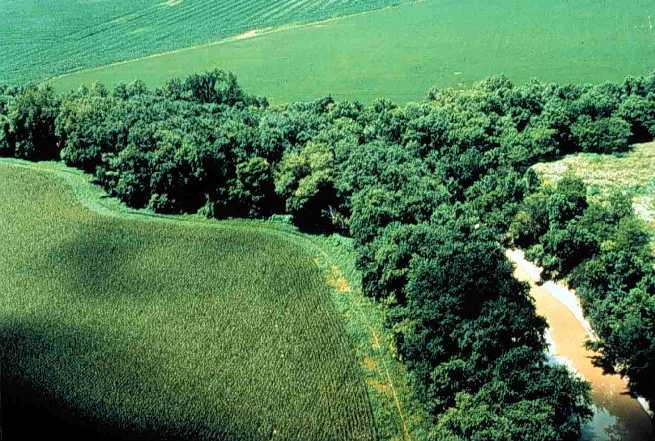
Riparian
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks are called riparian vegetation, characterized by hydrophilic plants. Riparian zones are important in ecology, environmental resource management, and civil engineering because of their role in soil conservation, their habitat biodiversity, and the influence they have on fauna and aquatic ecosystems, including grasslands, woodlands, wetlands, or even non-vegetative areas. In some regions, the terms riparian woodland, riparian forest, riparian buffer zone, riparian corridor, and riparian strip are used to characterize a riparian zone. The word ''riparian'' is derived from Latin '' ripa'', meaning " river bank". Characteristics Riparian zones may be natural or engineered for soil stabilization or restoration. These zones are important natural b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


%2C_Kruger_National_Park.jpg)

_03.jpg)