|
Yellow-backed Duiker
The yellow-backed duiker (''Cephalophus silvicultor'') is a forest dwelling antelope in the order Artiodactyla from the family Bovidae. Yellow-backed duikers are the most widely distributed of all duikers. They are found mainly in Central and Western Africa, ranging from Senegal to Western Uganda with possibly a few in Gambia. Their range also extends southward into Rwanda, Burundi, Zaire, and most of Zambia. Taxonomy and etymology The scientific name of the yellow-backed duiker is ''Cephalophus silvicultor''. It is the type species of '' Cephalophus'', and placed in the subfamily Cephalophinae and family Bovidae. The species was first described by English botanist Adam Afzelius in the journal ''Nova Acta Regiæ Societatis Scientiarum Upsaliensis'' in 1815. The generic name has possibly originated from the combination of the New Latin word ''cephal'', meaning head, and the Greek word ''lophos'', meaning crest. The specific name ''silvicultor'' is composed by two Latin words: ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disney's Animal Kingdom
Disney's Animal Kingdom Theme Park is a zoological theme park at the Walt Disney World Resort in Bay Lake, Florida, near Orlando. Owned and operated by The Walt Disney Company through its Parks, Experiences and Products division, it is the largest theme park in the world, covering . The park opened on Earth Day, April 22, 1998, and was the fourth theme park built at the resort. The park is dedicated and themed around natural environment and animal conservation, a philosophy once pioneered by Walt Disney. Disney's Animal Kingdom distinguishes itself from the rest of Walt Disney World's theme parks by featuring traditional attractions as well as hundreds of species of live animals. Special designs and provisions were incorporated throughout the park to protect the animals' welfare. The park is located on the western edge of the resort and is isolated from the other theme parks and properties to minimize external disruptions to the animals; as a result, the park's former nigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generic Name (biology)
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus '' Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should clearly dem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
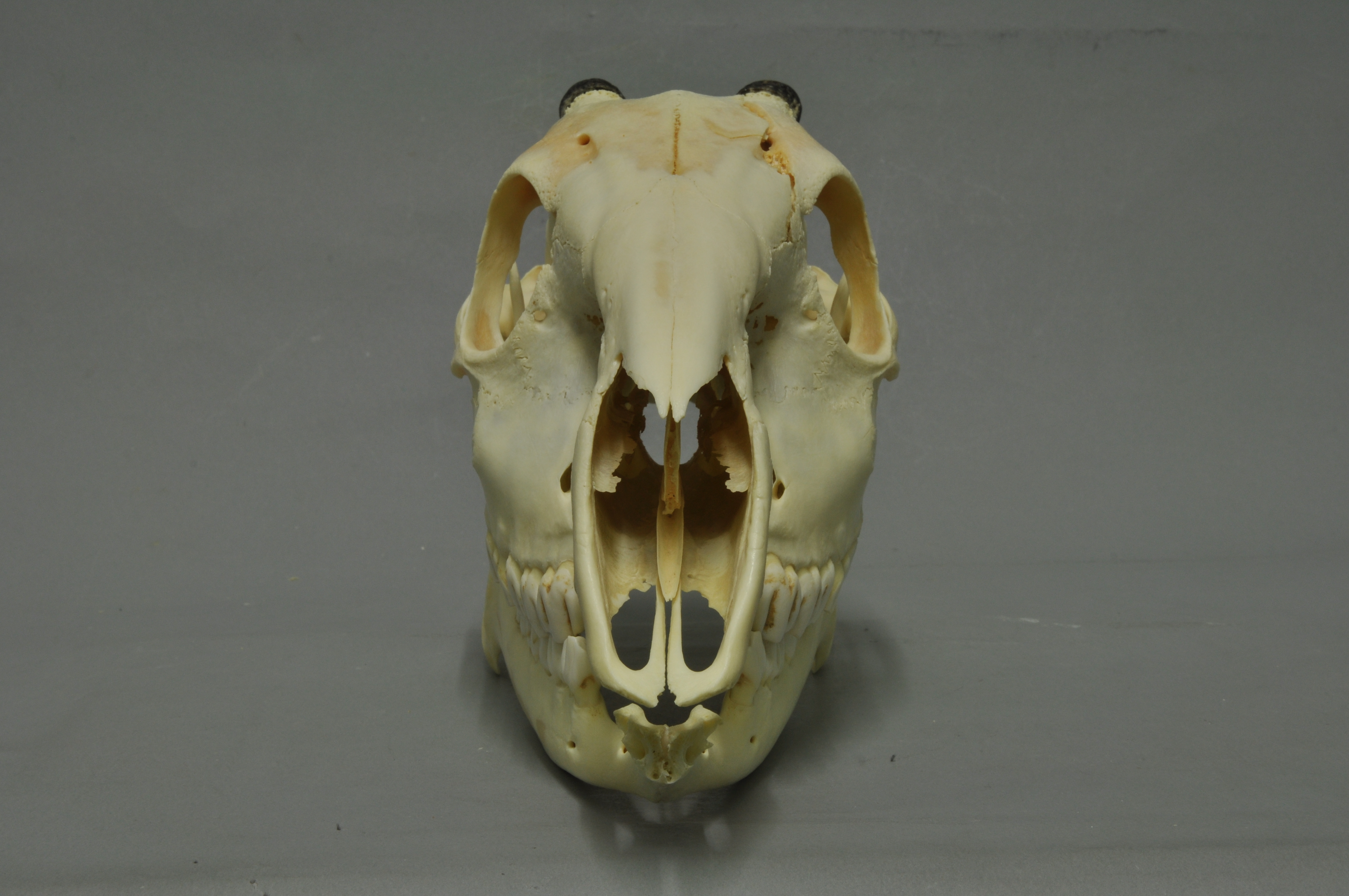
Cephalophus Silvicultor 01 MWNH 751
''Cephalophus'' is a mammal genus which contains at least fifteen species of duiker, a type of small antelope. Species Following Groves (2005), the species within ''Cephalophus'' include: * Aders's duiker ''Cephalophus adersi'' * Brooke's duiker ''Cephalophus brookei'' * Peters' duiker ''Cephalophus callipygus'' * Bay duiker ''Cephalophus dorsalis'' * Jentink's duiker ''Cephalophus jentinki'' * White-bellied duiker ''Cephalophus leucogaster'' * Red duiker ''Cephalophus natalensis'' * Black duiker ''Cephalophus niger'' * Black-fronted duiker ''Cephalophus nigrifrons'' * Ogilby's duiker ''Cephalophus ogilbyi'' * Ruwenzori duiker ''Cephalophus rubidus'' * Red-flanked duiker ''Cephalophus rufilatus'' * Yellow-backed duiker ''Cephalophus silvicultor'' * Abbott's duiker ''Cephalophus spadix'' * Weyns's duiker Weyns's duiker (''Cephalophus weynsi'') is a tiny antelope found in the Democratic Republic of Congo, Uganda and western Kenya. It is sometimes spelled "Weyn's", "Weyns", or " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José Vicente Barbosa Du Bocage
José Vicente Barbosa du Bocage (2 May 1823 – 3 November 1907) was a Portuguese zoologist and politician. He was the curator of Zoology at the Museu Nacional de Lisboa in Lisbon. He published numerous works on mammals, birds, and fishes. In the 1880s he became the Minister of the Navy and later the Minister for Foreign Affairs for Portugal. The zoology collection at the Lisbon Museum is called the Bocage Museum in his honor. Du Bocage was born in Funchal, Madeira. He studied at the University of Coimbra from 1839 to 1846. He became lecturer of the chair of Zoology at the Polytechnic School, Lisbon (later the Science Faculty of the University of Lisbon) in 1851, where he taught for more than 30 years. In 1858, he became also the scientific director and curator of Zoology of the Natural History Museum of the Polytechnic School. which was established as a support for the chair. His work at the Museum consisted in acquiring, describing and coordinating collections, many of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most animals and some plants. Differences may include secondary sex characteristics, size, weight, colour, markings, or behavioural or cognitive traits. These differences may be subtle or exaggerated and may be subjected to sexual selection and natural selection. The opposite of dimorphism is ''monomorphism'', which is when both biological sexes are phenotypically indistinguishable from each other. Overview Ornamentation and coloration Common and easily identified types of dimorphism consist of ornamentation and coloration, though not always apparent. A difference in coloration of sexes within a given species is called sexual dichromatism, which is commonly seen in many species of birds and reptiles. Sexual selection leads to the exaggerat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jentink's Duiker
Jentink's duiker (''Cephalophus jentinki''), also known as ''gidi-gidi'' in Krio and ''kaikulowulei'' in Mende, is a forest-dwelling duiker found in the southern parts of Liberia, southwestern Côte d'Ivoire, and scattered enclaves in Sierra Leone. It is named in honor of Fredericus Anna Jentink. Jentink's duikers stand around tall at the shoulder and weigh about , making them the largest species of the duikers. They are gray from the shoulders back and dark black from the shoulders forward. A white band goes over the shoulders, between the two colours and joining the white undersides. Jentink's duikers have long, thin horns, which curl back a little at the ends, and reach between . Jentink's duikers live mainly in very thick rainforest, where they eat fruit, flowers, and leaves which have fallen from the canopy, as well as stems of seedlings, roots, and, to the annoyance of local farmers, palm nuts, mangos, and cocoa pods. They are nocturnal and shelter during the day in de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Duiker
The bay duiker (''Cephalophus dorsalis''), also known as the black-striped duiker and the black-backed duiker, is a forest-dwelling duiker native to western and southern Africa. It was first described by British zoologist John Edward Gray in 1846. Two subspecies are identified. The bay duiker is reddish-brown and has a moderate size. Both sexes reach at the shoulder. The sexes do not vary considerably in their weights, either; the typical weight range for this duiker is . Both sexes have a pair of spiky horns, measuring . A notable feature of this duiker is the well-pronounced solid stripe of black extending from the back of the head to the tail. The bay duiker is a nocturnal animal. It tends to remain solitary, but pairs can also be observed. The leopard is the main predator of this duiker. It mainly prefers fruits, but may also feed on animal matter such as bird eggs. Females may conceive by the age of 18 months. Breeding occurs throughout the year. Gestation lasts about 24 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbott's Duiker
The Abbott's duiker (''Cephalophus spadix''), also known as ''minde'' in Swahili, is a large, forest-dwelling duiker (small antelope) found only in a few scattered enclaves in Tanzania. It may be a subspecies of the yellow-backed duiker. It is very rare, and the first photograph of an Abbott's duiker in the wild was taken as recently as 2003. Characteristics Abbott's duikers stand around tall at the shoulder and weigh about . This duiker has a glossy, dark brown coat which is lighter on the underside. The face is paler and gray in color, with a large red tuft on the forehead; the horns are thin and short (). The secretive behavior of Abbott's duiker, along with its largely nocturnal habits and preference for dense vegetation, means little is known about the ecology and behavior of this species. It has been observed feeding on leaves in the forest understory, and on vegetation in forest clearings, and may feed on fruits, flowers and moss. An Abbott's duiker has also been seen wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Grubb (zoologist)
Peter Grubb (1942 - 23 December 2006) was an English zoologist. He often collaborated with Colin Groves and described several new mammal taxa including ''Felis margarita harrisoni'' (a subspecies of the sand cat), the Bornean yellow muntjac, the Nigerian white-throated guenon, ''Cephalophus nigrifrons hypoxanthus'', the white-legged duiker, '' Cephalophus silvicultor curticeps'', ''Cephalophus weynsi lestradei'', the Kashmir musk deer, and the Niger Delta red colobus. Grubb was born in Dumfries in Scotland, but moved to Ealing West London when he was a small child. His father William Grubb was a research chemist at the Imperial Chemical Industries and later worked as a science teacher in London. His mother Anne Sirutis was a school teacher from Lithuania. His younger sister Katrina is an artist. After his BSc graduation in Zoology at the University College London Grubb was research assistant in the Wellcome Institute of the Zoological Society of London. In the 1960s he went ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colin Groves
Colin Peter Groves (24 June 1942 – 30 November 2017) was a British-Australian biologist and anthropologist. Groves was Professor of Biological Anthropology at the Australian National University in Canberra, Australia. Education Born in England, Groves completed a Bachelor of Science at University College London in 1963, and a Doctor of Philosophy at the Royal Free Hospital School of Medicine in 1966. From 1966 to 1973, he was a Postdoctoral Researcher and Teaching Fellow at the University of California, Berkeley, Queen Elizabeth College and the University of Cambridge. Career Groves emigrated to Australia in 1973 and joined the Australian National University, where he was promoted to full Professor in 2000 and remained Emeritus Professor until his death. Along with the Czech biologist Professor Vratislav Mazák, Groves was the describer of ''Homo ergaster''. Groves also wrote ''Primate Taxonomy'' published by the Smithsonian Institution Press in 2001, and Ungulate Taxonom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Language
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_Cephalophus_dorsalis.png)
