|
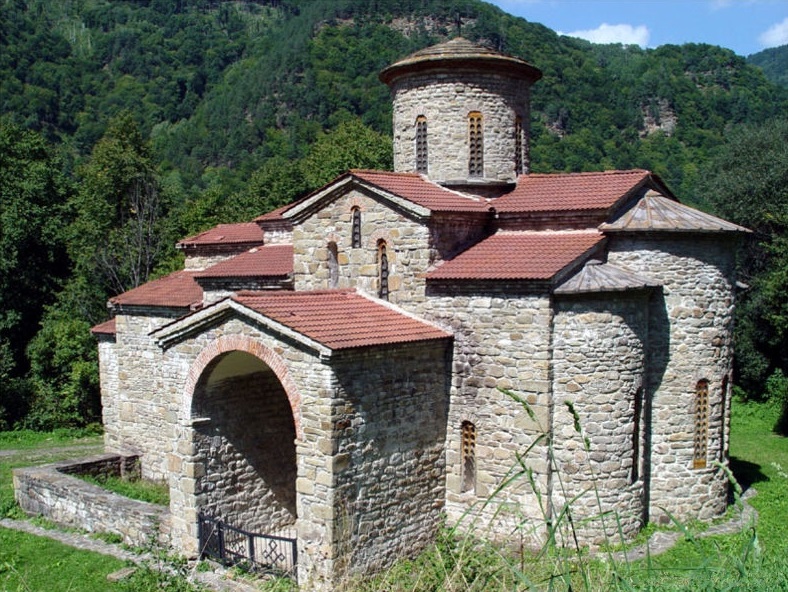
South Zelenchuksky Church
The South Zelenchuksky Church is a former Alanian church located in modern-day Arkhyz, Russia, dating to the late 10th century or early 11th century. The church's modest size suggests that it was privately owned, potentially by a member of the nobility. History The South Zelenchuksky Church dates back to the late 10th or early 11th century, and is one of three cross-in-square churches known to have been built in the Alanian Diocese, the other two being the North Zelenchuksky Church and the Shoana Church. Unlike the other two churches, the South Zelenchuksky Church is a simple cross-domed church without beams. The church was renovated at the end of the 19th century, during which a cornice was added under the dome, the walls were plastered, the frescoes were painted over, the slab flooring was replaced with wooden flooring, and the drum was covered in a wooden facade. Additionally, because the church's original doorway was plastered over, a new doorway was built into the church' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alanian
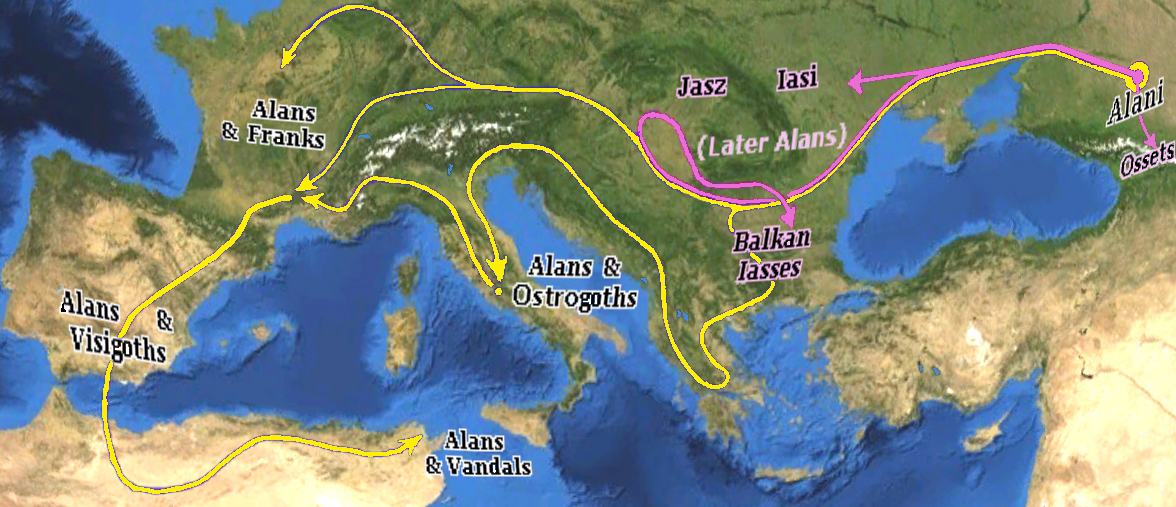
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Alans with the Central Asian Yancai of Chinese sources and with the Aorsi of Roman sources. Having migrated westwards and becoming dominant among the Sarmatians on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Alans are mentioned by Roman sources in the . At that time they had settled the region north of the Black Sea and frequently raided the Parthian Empire and the Caucasian provinces of the Roman Empire. From the Goths broke their power on the Pontic Steppe. Upon the Hunnic defeat of the Goths on the Pontic Steppe around , many of the Alans migrated westwards along with various Germanic tribes. They crossed the Rhine in 406CE along with the Vandals and Suebi, settling in Orléans and Valence. Around 409 CE they joined the Vandals and Suebi in cross ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arkhyz
Arkhyz (also Nizhny Arkhyz russian: Архыз; krc, Ырхыз, ''Irxız''; "mudflows") is a village in the valley of the Bolshoy Zelenchuk River, in the Republic of Karachay–Cherkessia, Greater Caucasus, Russia, about 70 km inland from the Black Sea shore. The modern village was founded in 1923 near the confluence of the Arkhyz and Pshish rivers. It is located in a mountainous region in the vicinity of the eponymous aul sitting at an altitude of 1,450 meters. The elevation of the surrounding mountains is more than 3,000 meters above the sea. The population is Zelenchuksky Churches The Zelenchuksky Churches are an archaeological preserve extending for around the ruins of Nizhnearkhyzskoe gorodishche, tentatively identified as the medieval capital of Alania, a Christian state destroyed by the hordes of Möngke Khan in the 13th century. No Byzantine document mentions the name of this city, whereas al-Mas'udi refers to it as Ma'as, or Maghas. The most remarkable feat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and shares Borders of Russia, land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than List of countries and territories by land borders, any other country but China. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, world's ninth-most populous country and List of European countries by population, Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city is Moscow, the List of European cities by population within city limits, largest city entirely within E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Architecture
Byzantine architecture is the architecture of the Byzantine Empire, or Eastern Roman Empire. The Byzantine era is usually dated from 330 AD, when Constantine the Great moved the Roman capital to Byzantium, which became Constantinople, until the fall of the Byzantine Empire in 1453. However, there was initially no hard line between the Byzantine and Roman empires, and early Byzantine architecture is stylistically and structurally indistinguishable from earlier Roman architecture. This terminology was introduced by modern historians to designate the medieval Roman Empire as it evolved as a distinct artistic and cultural entity centered on the new capital of Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) rather than the city of Rome and its environs. Its architecture dramatically influenced the later medieval architecture throughout Europe and the Near East, and became the primary progenitor of the Renaissance and Ottoman architectural traditions that followed its collapse. Characteristic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Alans with the Central Asian Yancai of Chinese sources and with the Aorsi of Roman sources. Having migrated westwards and becoming dominant among the Sarmatians on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Alans are mentioned by Roman sources in the . At that time they had settled the region north of the Black Sea and frequently raided the Parthian Empire and the Caucasian provinces of the Roman Empire. From the Goths broke their power on the Pontic Steppe. Upon the Hunnic defeat of the Goths on the Pontic Steppe around , many of the Alans migrated westwards along with various Germanic tribes. They crossed the Rhine in 406CE along with the Vandals and Suebi, settling in Orléans and Valence. Around 409 CE they joined the Vandals and Suebi in cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Century
The 10th century was the period from 901 ( CMI) through 1000 ( M) in accordance with the Julian calendar, and the last century of the 1st millennium. In China the Song dynasty was established. The Muslim World experienced a cultural zenith, especially in al-Andalus under the Caliphate of Córdoba and in the Samanid Empire under Ismail Samani. Additionally, there was a cultural flourishing for the Byzantine Empire and the First Bulgarian Empire. The Medievalist and historian of technology Lynn White said that "to the modern eye, it is very nearly the darkest of the Dark Ages ... if it was dark, it was the darkness of the womb". Similarly, Helen Waddell wrote that the 10th century was that which "in the textbooks disputes with the seventh the bad eminence, the nadir of the human intellect". Caesar Baronius famously described it as the Iron Century, because it was ‘iron in its harshness and in its sterility of goodness', while Lorenzo Valla gave it the similar name "Age of L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
11th Century
The 11th century is the period from 1001 ( MI) through 1100 ( MC) in accordance with the Julian calendar, and the 1st century of the 2nd millennium. In the history of Europe, this period is considered the early part of the High Middle Ages. There was, after a brief ascendancy, a sudden decline of Byzantine power and a rise of Norman domination over much of Europe, along with the prominent role in Europe of notably influential popes. Christendom experienced a formal schism in this century which had been developing over previous centuries between the Latin West and Byzantine East, causing a split in its two largest denominations to this day: Roman Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy. In Song dynasty China and the classical Islamic world, this century marked the high point for both classical Chinese civilization, science and technology, and classical Islamic science, philosophy, technology and literature. Rival political factions at the Song dynasty court created strife amongst th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-in-square
A cross-in-square or crossed-dome floor plan, plan was the dominant architectural form of middle- and late-period Byzantine Empire, Byzantine church architecture, churches. It featured a square centre with an internal structure shaped like a cross, topped by a dome. The first cross-in-square churches were probably built in the late 8th century, and the form has remained in use throughout the Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox world unto the present day. In the West, Donato Bramante's first design (1506) for St. Peter's Basilica was a centrally planned cross-in-square under a dome and four subsidiary domes. In German, such a church is a , or ‘cross-dome church’. In French, it is an , ‘church with an inscribed figure, inscribed cross’. Architecture Architectural form A cross-in-square church is centered around a quadratic cella, naos (the ‘square’) which is divided by four columns or piers into nine bay (architecture), bays (divisions of space). The inner five divisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornice
In architecture, a cornice (from the Italian ''cornice'' meaning "ledge") is generally any horizontal decorative moulding that crowns a building or furniture element—for example, the cornice over a door or window, around the top edge of a pedestal, or along the top of an interior wall. A simple cornice may be formed just with a crown, as in crown moulding atop an interior wall or above kitchen cabinets or a bookcase. A projecting cornice on a building has the function of throwing rainwater free of its walls. In residential building practice, this function is handled by projecting gable ends, roof eaves and gutters. However, house eaves may also be called "cornices" if they are finished with decorative moulding. In this sense, while most cornices are also eaves (overhanging the sides of the building), not all eaves are usually considered cornices. Eaves are primarily functional and not necessarily decorative, while cornices have a decorative aspect. A building's projecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fresco
Fresco (plural ''frescos'' or ''frescoes'') is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plaster, the painting becomes an integral part of the wall. The word ''fresco'' ( it, affresco) is derived from the Italian adjective ''fresco'' meaning "fresh", and may thus be contrasted with fresco-secco or secco mural painting techniques, which are applied to dried plaster, to supplement painting in fresco. The fresco technique has been employed since antiquity and is closely associated with Italian Renaissance painting. The word ''fresco'' is commonly and inaccurately used in English to refer to any wall painting regardless of the plaster technology or binding medium. This, in part, contributes to a misconception that the most geographically and temporally common wall painting technology was the painting into wet lime plaster. Even in appar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grout
Grout is a dense fluid which hardens to fill gaps or used as reinforcement in existing structures. Grout is generally a mixture of water, cement and sand, and is employed in pressure grouting, embedding rebar in masonry walls, connecting sections of pre-cast concrete, filling voids, and sealing joints such as those between tiles. Common uses for grout in the household include filling in tiles of shower floors and kitchen tiles. It is often color tinted when it has to be kept visible and sometimes includes fine gravel when being used to fill large spaces (such as the cores of concrete blocks). Unlike other structural pastes such as plaster or joint compound, correctly mixed and applied grout forms a water resistant seal. Although both grout and its close relative mortar are applied as a thick emulsion and harden over time, grout is distinguished by its low viscosity and lack of lime (added to mortar for pliability); grout is thin so it flows readily into gaps, while mortar is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zelenchuk Churches
The Zelenchuksky Churches or, Lower-Arkhyz Churches are located in an archaeological preserve extending for four kilometers around the ruins of Nizhnearkhyzskoe gorodishche near Arkhyz, Karachay–Cherkessia, Russian Federation. The site is tentatively identified as the medieval capital of Alania, a Christian state destroyed by the hordes of Möngke Khan in the 13th century. History No Byzantine document mentions the name of this city, whereas al-Mas'udi refers to it as Ma'as, or Maghas. The most remarkable feature of the site is a cluster of three early medieval churches, whose construction is associated with the missionary activities of Patriarch Nicholas Mystikos in the Northern Caucasus. These structures bear much resemblance to the Shoana Church and Senty Church, situated in the neighbouring valleys. In the 19th century the churches were affiliated with the monastery of St. Alexander Nevsky. A monastic community was revived there after the fall of the Soviet Union. The No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



.jpg)

