|
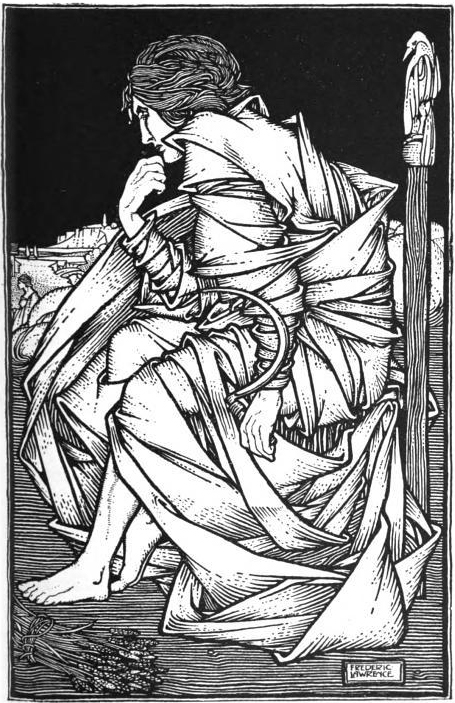
Skírnismál
''Skírnismál'' (Old Norse: 'The Lay of Skírnir', but in the Codex Regius known as ''Fǫr Skírnis'' ‘Skírnir’s journey’) is one of the poems of the ''Poetic Edda''. It is preserved in the 13th-century manuscripts Codex Regius and AM 748 I 4to but may have been originally composed in the early 10th century. Many scholars believe that the poem was acted out, perhaps in a sort of '' hiéros gamos''. Synopsis The prose prologue to the poem says that the god Freyr, the son of Njörðr, sits in Odin's throne, Hliðskjálf and looked over all the worlds. On looking to Jötunheimr, the land of the giants, Freyr sees a beautiful girl, Gerðr, and is immediately seized by desire. Fearing that the object of his heart's desire is unattainable, gloom settles upon him. The poem itself starts with the wife of Njörðr, Skaði, bidding Skírnir to ask Freyr why he is so sad. Freyr's response is sullen, yet he does confess his feelings and asks Skírnir to undertake a journey to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Names Of Freyr
The Germanic god Freyr is referred to by many names in Old Norse poetry and Old Norse literature, literature. Multiple of these are attested only once in the extant record and are found principally in Skáldskaparmál. Some names have been further proposed by scholars to have referred to the god in the Medieval period, including one from Old English literature. Names Proposed names Scholars have proposed names that may have been used historically to refer to Freyr. In contrast to the first table, these names rely to varying extents on speculation and are not unequivocal. See also *List of names of Odin *List of names of Thor *Names of God in Old English poetry References Bibliography Primary * * * * * * * ≈ * * * * * * * * * * * Secondary * * * * * * * * * * {{Norse paganism topics Germanic paganism and mythology lists, Freyr, names of Freyr, * Epithets of Germanic deities, Freyr Masculine names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freyr
Freyr (Old Norse: 'Lord'), sometimes anglicized as Frey, is a widely attested Æsir, god in Norse mythology, associated with kingship, fertility, peace, prosperity, fair weather, and good harvest. Freyr, sometimes referred to as Yngvi-Freyr, was especially associated with Sweden and seen as an ancestor of the Yngling, Swedish royal house. According to Adam of Bremen, Freyr was associated with peace and pleasure, and was represented with a phallus, phallic statue in the Temple at Uppsala. According to Snorri Sturluson, Freyr was "the most renowned of the æsir", and was venerated for good harvest and peace. In the mythological stories in the Icelandic books the ''Poetic Edda'' and the ''Prose Edda'', Freyr is presented as one of the Vanir, the son of the god Njörðr and Sister-wife of Njörðr, his sister-wife, as well as the twin brother of the goddess Freyja. The gods gave him Álfheimr, the realm of the Álfar, Elves, as a teething present. He rides the shining Norse dwarves, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerðr
In Norse mythology, Gerðr (Old Norse: ; "fenced-in"Orchard (1997:54).) is a jötunn, Æsir, goddess, and the wife of the god Freyr. Gerðr is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources; the ''Prose Edda'' and ''Heimskringla'', written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson; and in the poetry of skalds. ''Gerðr'' is sometimes modernly anglicized as Gerd or Gerth. In both the ''Poetic Edda'' and the ''Prose Edda'', Freyr sees Gerðr from a distance, becomes deeply lovesick at the sight of her shimmering beauty, and has his servant Skírnir go to Jötunheimr (where Gerðr and her father Gymir (father of Gerðr), Gymir reside) to gain her love. In the ''Poetic Edda'' Gerðr initially refuses, yet after a series of threats by Skírnir she is forced to yield. In the ''Prose Edda'', no mention of threats is made. In both sources, Gerðr agrees to meet Freyr at a fixed time at the location of Barri and, after Skírnir returns with Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skírnir
In Norse mythology, Skírnir (Old Norse" ; "bright one") is the god Freyr's messenger and vassal. He appears in both the Poetic and Prose Eddas. Attestations ''Poetic Edda'' In the Eddic poem '' Skírnismál'', Skírnir is sent as a messenger to Jötunheimr to conduct lovesick Freyr's wooing of the giantess Gerðr on condition of being given Freyr's powerful sword as a reward. Skírnir begins by offering Gerðr 11 golden apples (or apples of eternal life, in a common emendation), which Gerðr rejects, adding that she and Freyr will never be together as long as they live. He next offers Gerðr a ring that produces eight more gold rings every ninth night. Gerðr responds that she is not interested in the ring for she shares her father Gymir's property, and he has no lack of gold. Skírnir then turns to a series of threats. He first threatens to cut Gerðr's head from her neck and then threatens her father's life. He next tells Gerðr that she will sit on an eagle's mou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jötunheimr
The terms Jötunheimr (in Old Norse orthography: Jǫtunheimr ; often Old Norse orthography#Anglicized spelling, anglicised as Jotunheim) or Jötunheimar refer to either a land or multiple lands respectively in Nordic mythology inhabited by the jötnar (relatives of the gods, in English sometimes inaccurately called "giants"). are typically, but not exclusively, presented in Eddic sources as prosperous lands located to the north and are commonly separated from the lands inhabited by gods and humans by barriers that cannot be traversed by usual means. Etymology is a compound word formed from and , meaning a 'home' or 'world'. When attested in Eddic sources, the word is typically found in its plural form, ('-lands'). Attestations Poetic Edda are mentioned in three poems of the Poetic Edda. In the beginning of Völuspá, the coming of three women out of marks the end of the Golden Age#Germanic, Age of Gold for the gods. Towards the end of the poem, in the section describing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gambantein
''Gambanteinn'' is an Old Norse term referring to a magic staff or wand. It is attested in two poems in the Poetic Edda: ''Hárbarðsljóð'' and ''Skírnismál''. Etymology The word is a compound of the prefix with the noun ''teinn''. The latter essentially means "rod, twig" and thereof, but the prefix is dubious. In Old Norse, it is used as an indicator of magnitude, or potentially magical potency or divine power. Compounds include: ''gambanreiði'' ("great wrath") and ''gambansumbl'' ("great banquet"). It could potentially be a calque from , which is attested twice in Old English, the first instance, in the phrase ''gomban gyldan'' ("to pay tribute"), at the start of Beowulf, the second instance, in the same phrase ''gombon gieldan'', found in the Old English Biblical poem Genesis A. Further theories exist on its poetic and root meaning. ''Hárbarðsljóð'' In ''Hárbarðsljóð'' stanza 20, Hárbarðr says: A giant hard was Hlébard, methinks: His ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eddic Poetry
The ''Poetic Edda'' is the modern name for an untitled collection of Old Norse anonymous narrative poems in alliterative verse. It is distinct from the closely related ''Prose Edda'', although both works are seminal to the study of Old Norse poetry. Several versions of the ''Poetic Edda'' exist; especially notable is the medieval Icelandic manuscript '' Codex Regius'', which contains 31 poems. Composition The ''Eddic poems'' are composed in alliterative verse. Most are in ''fornyrðislag'' ("old story metre"), while '' málaháttr'' ("speech form") is a common variation. The rest, about a quarter, are composed in '' ljóðaháttr'' ("song form"). The language of the poems is usually clear and relatively unadorned. Kennings are often employed, though they do not arise as frequently, nor are they as complex, as those found in typical skaldic poetry. Authorship Like most early poetry, the Eddic poems were minstrel poems, passed orally from singer to singer and from poet to po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hliðskjálf
In Norse mythology, the Hliðskjálf (literally meaning the high seat with an expansive view) allowed Odin to see into all realms as well as listen to them. Although not explicit in any surviving source, there may be a connection between Hliðskjálf and the art of seiðr, a type of magic said to be practiced by Odin that was often performed from a high, raised platform called a seiðhjallr. The works of Rudolf Simek suggest that Hliðskjálf could be the model that actual seiðhjallr platforms attempted to emulate. ''Poetic Edda'' In ''Grímnismál'', Odin and Frigg are both sitting in Hliðskjálf when they see their foster sons Agnarr and Geirröðr, one living in a cave with a giantess and the other a king. Frigg then made the accusation to her husband that Geirröðr was miserly and inhospitable toward guests, so after wagering with one another over the veracity of the statement, Odin set out to visit Geirröðr in order to settle the matter. In ''Skírnismál'', Freyr snea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bergen Rune-charm
The Bergen rune charm is a runic inscription on a piece of wood found among the medieval rune-staves of Bergen. It is noted for its similarities to the Eddaic poem ''Skírnismál'' (particularly stanza 36); Klaus von See, Beatrice la Farge, Eve Picard, Ilona Priebe and Katja Schulz, ''Kommentar zu den Liedern der Edda'' (Heidelberg: Winter, 1997–), II 136-37. as a rare example of a poetic rune-stave inscription; and of runes being used in love magic. The inscription has number 257 in the Bryggen inscriptions numbering and N B257 ''(Norway Bryggen no. 257)'' in the Rundata database, and P 6 in McKinnell, Simek and Düwel's collection. It is thought to date from the fourteenth century. Description The stave is four-sided, with text on each side, but one end is missing, leaving the text of each side incomplete. It is dated to ca. 1335, making it roughly contemporary to the Ribe healing-stick (ca. 1300). Inscription The Scandinavian Runic-text Database (Rundata) gives the follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymir (father Of Gerðr)
Gymir (Old Norse: ) is a jötunn in Norse mythology. He is the spouse of Aurboða, and the father of the beautiful jötunn Gerðr, who married the god Freyr. ''Gymir'' may be the same figure as Ægir, a personification of the sea or ocean, or a separate figure who shares the same name. Name The meaning of the Old Norse name ''Gymir'' is unclear. Proposed translations include 'the earthly' (from Old Norse ''gumi''), 'the wintry one' (from ''gemla''), or 'the protector', the 'engulfer' (from ''geyma''). In ''Lokasenna'' (Loki's Flyting) and ''Skáldskaparmál'' (The Language of Poetry), Gymir is given by Snorri Sturluson as an alternative name for the divine personification of the sea Ægir. Rudolf Simek argues that it may be an erroneous interpretation of kennings in which different giant-names are used interchangeably. Attestations ''Poetic Edda'' In both ''Skírnismál'' (The Lay of Skírnir) and ''Gylfaginning'' (The Beguiling of Gylfi), Gymir is portrayed as the spouse of Au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poetic Edda
The ''Poetic Edda'' is the modern name for an untitled collection of Old Norse anonymous narrative poems in alliterative verse. It is distinct from the closely related ''Prose Edda'', although both works are seminal to the study of Old Norse poetry. Several versions of the ''Poetic Edda'' exist; especially notable is the medieval Icelandic manuscript '' Codex Regius'', which contains 31 poems. Composition The ''Eddic poems'' are composed in alliterative verse. Most are in ''fornyrðislag'' ("old story metre"), while '' málaháttr'' ("speech form") is a common variation. The rest, about a quarter, are composed in '' ljóðaháttr'' ("song form"). The language of the poems is usually clear and relatively unadorned. Kennings are often employed, though they do not arise as frequently, nor are they as complex, as those found in typical skaldic poetry. Authorship Like most early poetry, the Eddic poems were minstrel poems, passed orally from singer to singer and from poet to po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AM 748 I 4to
AM 748 I 4to is an Icelandic vellum manuscript fragment containing several Eddaic poems. It dates to the beginning of the 14th century. AM 748 I is split into two parts. AM 748 I a 4to is kept in the Arnamagnæan Institute in Copenhagen. AM 748 I b 4to is kept at the Árni Magnússon Institute for Icelandic Studies in Reykjavík. The six sheets which have been preserved of AM 748 I a 4to contain the following poems, all mythological. *''Grímnismál'' (complete) *''Hymiskviða'' (complete) *'' Baldrs draumar'' (complete) *''Skírnismál'' (partial) *'' Hárbarðsljóð'' (partial) *''Vafþrúðnismál'' (partial) *'' Völundarkviða'' (only the beginning of the prose prologue) AM 748 I a 4to is the only mediaeval manuscript to preserve '' Baldrs draumar''. The other poems are also preserved in Codex Regius. References AM 748 I 4toFacsimile A facsimile (from Latin ''fac simile'', "to make alike") is a copy or reproduction of an old book, manuscript, map, art print, or ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |