|
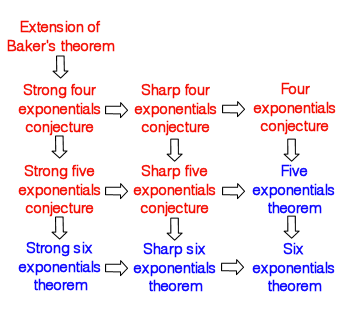
Six Exponentials Theorem
In mathematics, specifically transcendental number theory, the six exponentials theorem is a result that, given the right conditions on the exponents, guarantees the transcendence of at least one of a set of exponentials. Statement If ''x''1, ''x''2, ..., ''x''''d'' are ''d'' complex numbers that are linearly independent over the rational numbers, and ''y''1, ''y''2, ..., ''y''''l'' are ''l'' complex numbers that are also linearly independent over the rational numbers, and if ''dl'' > ''d'' + ''l'', then at least one of the following ''dl'' numbers is transcendental: :\exp(x_i y_j),\quad (1 \leq i \leq d,\ 1 \leq j \leq l). The most interesting case is when ''d'' = 3 and ''l'' = 2, in which case there are six exponentials, hence the name of the result. The theorem is weaker than the related but thus far unproved four exponentials conjecture, whereby the strict inequality ''dl'' > ''d'' + ''l'' is replaced with ''dl' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiprime
In mathematics, a semiprime is a natural number that is the product of exactly two prime numbers. The two primes in the product may equal each other, so the semiprimes include the squares of prime numbers. Because there are infinitely many prime numbers, there are also infinitely many semiprimes. Semiprimes are also called biprimes. Examples and variations The semiprimes less than 100 are: Semiprimes that are not square numbers are called discrete, distinct, or squarefree semiprimes: The semiprimes are the case k=2 of the k- almost primes, numbers with exactly k prime factors. However some sources use "semiprime" to refer to a larger set of numbers, the numbers with at most two prime factors (including unit (1), primes, and semiprimes). These are: Formula for number of semiprimes A semiprime counting formula was discovered by E. Noel and G. Panos in 2005. Let \pi_2(n) denote the number of semiprimes less than or equal to n. Then \pi_2(n) = \sum_^ pi(n/p_k) - k + 1 /math> w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transactions Of The American Mathematical Society
The ''Transactions of the American Mathematical Society'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal of mathematics published by the American Mathematical Society. It was established in 1900. As a requirement, all articles must be more than 15 printed pages. See also * ''Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society'' * '' Journal of the American Mathematical Society'' * '' Memoirs of the American Mathematical Society'' * '' Notices of the American Mathematical Society'' * '' Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society'' External links * ''Transactions of the American Mathematical Society''on JSTOR JSTOR (; short for ''Journal Storage'') is a digital library founded in 1995 in New York City. Originally containing digitized back issues of academic journals, it now encompasses books and other primary sources as well as current issues of j ... American Mathematical Society academic journals Mathematics journals Publications established in 1900 {{math-journa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elliptic Curve
In mathematics, an elliptic curve is a smooth, projective, algebraic curve of genus one, on which there is a specified point . An elliptic curve is defined over a field and describes points in , the Cartesian product of with itself. If the field's characteristic is different from 2 and 3, then the curve can be described as a plane algebraic curve which consists of solutions for: :y^2 = x^3 + ax + b for some coefficients and in . The curve is required to be non-singular, which means that the curve has no cusps or self-intersections. (This is equivalent to the condition , that is, being square-free in .) It is always understood that the curve is really sitting in the projective plane, with the point being the unique point at infinity. Many sources define an elliptic curve to be simply a curve given by an equation of this form. (When the coefficient field has characteristic 2 or 3, the above equation is not quite general enough to include all non-singular cub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field (mathematics)
In mathematics, a field is a set on which addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division are defined and behave as the corresponding operations on rational and real numbers do. A field is thus a fundamental algebraic structure which is widely used in algebra, number theory, and many other areas of mathematics. The best known fields are the field of rational numbers, the field of real numbers and the field of complex numbers. Many other fields, such as fields of rational functions, algebraic function fields, algebraic number fields, and ''p''-adic fields are commonly used and studied in mathematics, particularly in number theory and algebraic geometry. Most cryptographic protocols rely on finite fields, i.e., fields with finitely many elements. The relation of two fields is expressed by the notion of a field extension. Galois theory, initiated by Évariste Galois in the 1830s, is devoted to understanding the symmetries of field extensions. Among other result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Variety
In mathematics, an algebraic group is an algebraic variety endowed with a group structure which is compatible with its structure as an algebraic variety. Thus the study of algebraic groups belongs both to algebraic geometry and group theory. Many groups of geometric transformations are algebraic groups; for example, orthogonal groups, general linear groups, projective groups, Euclidean groups, etc. Many matrix groups are also algebraic. Other algebraic groups occur naturally in algebraic geometry, such as elliptic curves and Jacobian varieties. An important class of algebraic groups is given by the affine algebraic groups, those whose underlying algebraic variety is an affine variety; they are exactly the algebraic subgroups of the general linear group, and are therefore also called ''linear algebraic groups''. Another class is formed by the abelian varieties, which are the algebraic groups whose underlying variety is a projective variety. Chevalley's structure theorem sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image (mathematics)
In mathematics, the image of a function is the set of all output values it may produce. More generally, evaluating a given function f at each element of a given subset A of its domain produces a set, called the "image of A under (or through) f". Similarly, the inverse image (or preimage) of a given subset B of the codomain of f, is the set of all elements of the domain that map to the members of B. Image and inverse image may also be defined for general binary relations, not just functions. Definition The word "image" is used in three related ways. In these definitions, f : X \to Y is a function from the set X to the set Y. Image of an element If x is a member of X, then the image of x under f, denoted f(x), is the value of f when applied to x. f(x) is alternatively known as the output of f for argument x. Given y, the function f is said to "" or "" if there exists some x in the function's domain such that f(x) = y. Similarly, given a set S, f is said to "" if t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homomorphism
In algebra, a homomorphism is a structure-preserving map between two algebraic structures of the same type (such as two groups, two rings, or two vector spaces). The word ''homomorphism'' comes from the Ancient Greek language: () meaning "same" and () meaning "form" or "shape". However, the word was apparently introduced to mathematics due to a (mis)translation of German meaning "similar" to meaning "same". The term "homomorphism" appeared as early as 1892, when it was attributed to the German mathematician Felix Klein (1849–1925). Homomorphisms of vector spaces are also called linear maps, and their study is the subject of linear algebra. The concept of homomorphism has been generalized, under the name of morphism, to many other structures that either do not have an underlying set, or are not algebraic. This generalization is the starting point of category theory. A homomorphism may also be an isomorphism, an endomorphism, an automorphism, etc. (see below). Eac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michel Waldschmidt
Michel Waldschmidt (born June 17, 1946 at Nancy, France) is a French mathematician, specializing in number theory, especially transcendental numbers. Biography Waldschmidt was educated at Lycée Henri Poincaré and the University of Nancy until 1968. In 1972 he defended his thesis, titled ''Indépendance algébrique de nombres transcendants'' (Algebraic independence of transcendental numbers) and directed by Jean Fresnel, the University of Bordeaux, where he was research associate of CNRS in 1971–2. He was then a lecturer at Paris-Sud 11 University in 1972–3, then a lecturer at the University of Paris VI (Pierre et Marie Curie), where he is Professor since 1973. Waldschmidt was also a visiting professor at places including the École normale supérieure. He is a member of the . Today, Michel Waldschmidt is an expert in the theory of transcendental numbers and diophantine approximations. He was awarded the Albert Châtelet Prize in 1974, the CNRS Silver Medal in 1978, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Logarithm
In mathematics, a complex logarithm is a generalization of the natural logarithm to nonzero complex numbers. The term refers to one of the following, which are strongly related: * A complex logarithm of a nonzero complex number z, defined to be any complex number w for which e^w = z.Ahlfors, Section 3.4.Sarason, Section IV.9. Such a number w is denoted by \log z. If z is given in polar form as z = re^, where r and \theta are real numbers with r>0, then \ln r + i \theta is one logarithm of z, and all the complex logarithms of z are exactly the numbers of the form \ln r + i\left(\theta + 2\pi k\right) for integers ''k''. These logarithms are equally spaced along a vertical line in the complex plane. * A complex-valued function \log \colon U \to \mathbb, defined on some subset U of the set \mathbb^* of nonzero complex numbers, satisfying e^ = z for all z in U. Such complex logarithm functions are analogous to the real logarithm function \ln \colon \mathbb_ \to \mathbb, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector Space
In mathematics and physics, a vector space (also called a linear space) is a set whose elements, often called '' vectors'', may be added together and multiplied ("scaled") by numbers called '' scalars''. Scalars are often real numbers, but can be complex numbers or, more generally, elements of any field. The operations of vector addition and scalar multiplication must satisfy certain requirements, called ''vector axioms''. The terms real vector space and complex vector space are often used to specify the nature of the scalars: real coordinate space or complex coordinate space. Vector spaces generalize Euclidean vectors, which allow modeling of physical quantities, such as forces and velocity, that have not only a magnitude, but also a direction. The concept of vector spaces is fundamental for linear algebra, together with the concept of matrix, which allows computing in vector spaces. This provides a concise and synthetic way for manipulating and studying systems of li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |