|
Sinauli Chariot ASI
Sinauli is an archaeological site in western Uttar Pradesh, India, at the Ganga-Yamuna Doab. The site gained attention for its Bronze Age solid-disk wheel carts, found in 2018, which were interpreted by some as horse-pulled Chariot, "chariots". The excavations in Sinauli were conducted by Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) in 2005-06 and in mid-2018. The remains found in 2005–2006 season, the "Sanauli cemetery", belong to the Late Bronze Age, and were ascribed by excavation director Sharma to the Harappan civilisation, though a Indus Civilisation, Late Harappan Phase or post-Harappan identification is more likely. Major findings from 2018 trial excavations are dated to c. 2000 - 1800 BCE, and ascribed to the Ochre Coloured Pottery culture (OCP)/Copper Hoard Culture, which was contemporaneous with the Late Harappan culture. They include several wooden coffin burials, copper swords, helmets, and wooden carts, with solid disk wheels and protected by copper sheets. The carts we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonauli
Sonauli is a town, near city of Maharajganj in Maharajganj district in Uttar Pradesh, India. It located on the Indo-Nepal Border and is a well-known and most famous transit point between India and Nepal. Sonauli is around 75 km from district headquarter Mahrajganj, Uttar Pradesh. 90 km from Gorakhpur, which is the nearest major city. The nearest Railway station from Sonauli is Nautanwa Railway Station, which is around 7 km away and is now well connected with Indian Railway Network. Earlier Nautanwa was connected with Gorakhpur through Meter Gauge Railway Track. But with the development of Indian Railway Network, this track is converted into Broad gauge which facilitate fast long railway transit. Sonauli India–Nepal Border Crossing The Sonauli India–Nepal border crossing or Sonauli Integrated Check Post in Uttar Pradesh is the most popular and designated Integrated Check Posts (ICP), with both customs and immigration facilities:http://www.mdoner.gov.in/node/1483 IC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baraut
Baraut is a city and municipal board, near the city of Baghpat in Baghpat district, Uttar Pradesh, India. Geography Baraut is located a29.6°N 77.16°E covering an area of 10.36 square kilometers (4.00 sq mi) and lying between the Ganga and Yamuna river plains. Its average elevation is 231 m (758 feet). Baraut is served by NH-709B and state highways SH-57 and SH-82. Baraut is located 55 kilometers (34 mi) from Delhi (the national capital of India) and 55 kilometers from Meerut, and is within the National Capital Region (NCR). Demographics Population As of 2011 Indian Census, Baraut had a total population of 103,764, of which 55,013 were males and 48,751 were females. Population within the age group of 0 to 6 years was 14,149. The total number of literates in Baraut was 68,690 , which constituted 66.2% of the population with male literacy of 71.8% and female literacy of 59.9%. The effective literacy rate of 7+ population of Baraut was 76.7%, of which male liter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
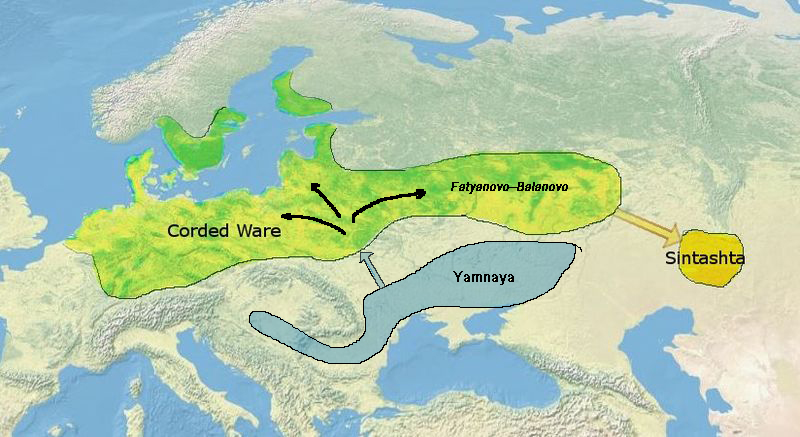
Chariots
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000 BCE. The critical invention that allowed the construction of light, horse-drawn chariots was the spoked wheel. The chariot was a fast, light, open, two-wheeled conveyance drawn by two or more horses that were hitched side by side, and was little more than a floor with a waist-high guard at the front and sides. It was initially used for ancient warfare during the Bronze and Iron Ages, but after its military capabilities had been superseded by light and heavy cavalries, chariots continued to be used for travel and transport, in processions, for games, and in races. Etymology The word "chariot" comes from the Latin term ''carrus'', a loanword from Gaulish. In ancient Rome and some other ancient Mediterranean civilizations, a ''biga'' requ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neeraj Pandey
Neeraj Pandey (born 17 December 1973) is an Indian film director, producer and screenwriter who works in Hindi cinema. Pandey was made his directoral debut in ''A Wednesday!'', which was largely praised by critics and which later became a recipient of many accolades. His second film was ''Special 26'' (2013), which was followed by ''Baby (2015 Hindi film), Baby'' (2015), the latter of which received critical acclaim and became a huge commercial success. He served as a producer in ''Rustom (film), Rustom'' (2016). Pandey returned to directing in 2016 helming the biopic movie ''M.S. Dhoni: The Untold Story'' based on Indian cricketer MS Dhoni, M.S.Dhoni which fared well critically and commercially. Besides being a filmmaker, Pandey is also a writer and has written a novel named ''Ghalib Danger'' in 2013. In 2016, his production house Friday Filmworks entered into a joint venture with Reliance Entertainment and formed Plan C Studios. He has also directed a Web Short 'Ouch' with Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Aryans
Indigenous Aryanism, also known as the Indigenous Aryans theory (IAT) and the Out of India theory (OIT), is the conviction that the Aryans are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent, and that the Indo-European languages radiated out from a homeland in India into their present locations. It is a " religio-nationalistic" view on Indian history, and propagated as an alternative to the established migration model, which considers the Pontic–Caspian steppe to be the area of origin of the Indo-European languages. Reflecting traditional Indian views based on the Puranic chronology, indigenists propose an older date than is generally accepted for the Vedic period, and argue that the Indus Valley civilisation was a Vedic civilization. In this view, "the Indian civilization must be viewed as an unbroken tradition that goes back to the earliest period of the Sindhu-Sarasvati (or Indus) tradition (7000 or 8000 BCE)." Support for the IAT mostly exists among a subset of Indian schola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the ''Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the Kurukshetra War and the fates of the Kaurava and the Pāṇḍava princes and their successors. It also contains philosophical and devotional material, such as a discussion of the four "goals of life" or ''puruṣārtha'' (12.161). Among the principal works and stories in the ''Mahābhārata'' are the '' Bhagavad Gita'', the story of Damayanti, the story of Shakuntala, the story of Pururava and Urvashi, the story of Savitri and Satyavan, the story of Kacha and Devayani, the story of Rishyasringa and an abbreviated version of the ''Rāmāyaṇa'', often considered as works in their own right. Traditionally, the authorship of the ''Mahābhārata'' is attributed to Vyāsa. There have been many attempts to unravel its historical growth and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochre Coloured Pottery
The Ochre Coloured Pottery culture (OCP) is a Bronze Age culture of the Indo-Gangetic Plain "generally dated 2000–1500 BCE," extending from eastern Punjab to northeastern Rajasthan and western Uttar Pradesh. Artefacts of this culture show similarities with both the Late Harappan culture and the Vedic culture. Archaeologist Akinori Uesugi considers it as an archaeological continuity of the previous Harappan Bara style, while according to Parpola, the find of carts in this culture may reflect an Indo-Iranian migration into the India subcontinent, in contact with Late Harappans. The OCP marked the last stage of the North Indian Bronze Age and was succeeded by the Iron Age black and red ware culture and the Painted Grey Ware culture. Geography and dating The 'Ochre Coloured Pottery culture is "generally dated 2000-1500 BCE," Early specimens of the characteristic ceramics found near Jodhpura, Rajasthan, date from the 3rd millennium (this Jodhpura is located in the district of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratha
Ratha ( Proto-Indo-Iranian: ''*Hrátʰas'', Sanskrit: रथ, '; Avestan: ''raθa'') is also known as the Indo-Iranian term for a spoked-wheel chariot or a cart of antiquity. Harappan Civilisation The Indus Valley Civilization sites of Daimabad and Harappa in the Indian subcontinent, there is evidence for the use of terracotta model carts as early as 3500 BC during the Ravi Phase. There is evidence of wheeled vehicles (especially miniature models) in the Indus Valley Civilization, but not of chariots. According to Kenoyer, Indo-Aryan Indigenists have argued for the presence of chariots before its introduction by the Indo-Aryans in the early 2nd millennium BCE. Archaeologist B. B. Lal argues that finds of terracotta wheels painted lines (or low relief lines) and similar seals indicate the existence and use of spoked wheel chariots in Harappan Civilization, as showed in the Bhirrana excavations in 2005–06. Bhagwan Singh has made a similar assertion and S.R. Rao has presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imagination Of Coffin Burial 1 Of Sinauli
Imagination is the production or simulation of novel objects, sensations, and ideas in the mind without any immediate input of the senses. Stefan Szczelkun characterises it as the forming of experiences in one's mind, which can be re-creations of past experiences, such as vivid memories with imagined changes, or completely invented and possibly fantastic scenes. Imagination helps make knowledge applicable in solving problems and is fundamental to integrating experience and the learning process.Norman 2000 pp. 1-2Brian Sutton-Smith 1988, p. 22 Kieran Egan 1992, pp. 50 As an approach to build theory, it is called "disciplined imagination". A basic training for imagination is listening to storytelling (narrative), in which the exactness of the chosen words is the fundamental factor to "evoke worlds". One view of imagination links it with cognition, seeing imagination as a cognitive process used in mental functioning. It is increasingly used - in the form of visual imagery - by clini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth-most populous state, with a population of 60.4 million. It is bordered by Rajasthan to the northeast, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the south, Maharashtra to the southeast, Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea and the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west. Gujarat's capital city is Gandhinagar, while its largest city is Ahmedabad. The Gujaratis are indigenous to the state and their language, Gujarati, is the state's official language. The state encompasses 23 sites of the ancient Indus Valley civilisation (more than any other state). The most important sites are Lothal (the world's first dry dock), Dholavira (the fifth largest site), and Gola Dhoro (where 5 uncommon seals were found). Lothal i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dholavira
Dholavira ( gu, ધોળાવીરા) is an archaeological site at Khadirbet in Bhachau Taluka of Kutch District, in the state of Gujarat in western India, which has taken its name from a modern-day village south of it. This village is from Radhanpur. Also known locally as ''Kotada timba'', the site contains ruins of a city of the ancient Indus Valley civilization. Earthquakes have repeatedly affected Dholavira, including a particularly severe one around 2600 BC. Dholavira's location is on the Tropic of Cancer. It is one of the five largest Harappan sites and the most prominent of archaeological sites in India belonging to the Indus Valley Civilization. It is also considered as having been the grandest of cities of its time. It is located on ''Khadir bet'' island in the Kutch Desert Wildlife Sanctuary in the Great Rann of Kutch. The quadrangular city lay between two seasonal streams, the Mansar in the north and Manhar in the south. The site was thought to be occupied f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punjab, Pakistan
Punjab (; , ) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in central-eastern region of the country, Punjab is the second-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the largest province by population. It shares land borders with the Pakistani provinces of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa to the north-west, Balochistan to the south-west and Sindh to the south, as well as Islamabad Capital Territory to the north-west and Autonomous Territory of AJK to the north. It shares an International border with the Indian states of Rajasthan and Punjab to the east and Indian-administered Kashmir to the north-east. Punjab is the most fertile province of the country as River Indus and its four major tributaries Ravi, Jhelum, Chenab and Sutlej flow through it. The province forms the bulk of the transnational Punjab region, now divided among Pakistan and India. The provincial capital is Lahore — a cultural, modern, historical, economic, and cosmopolitan centre of Pakistan. Other major cities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |