|
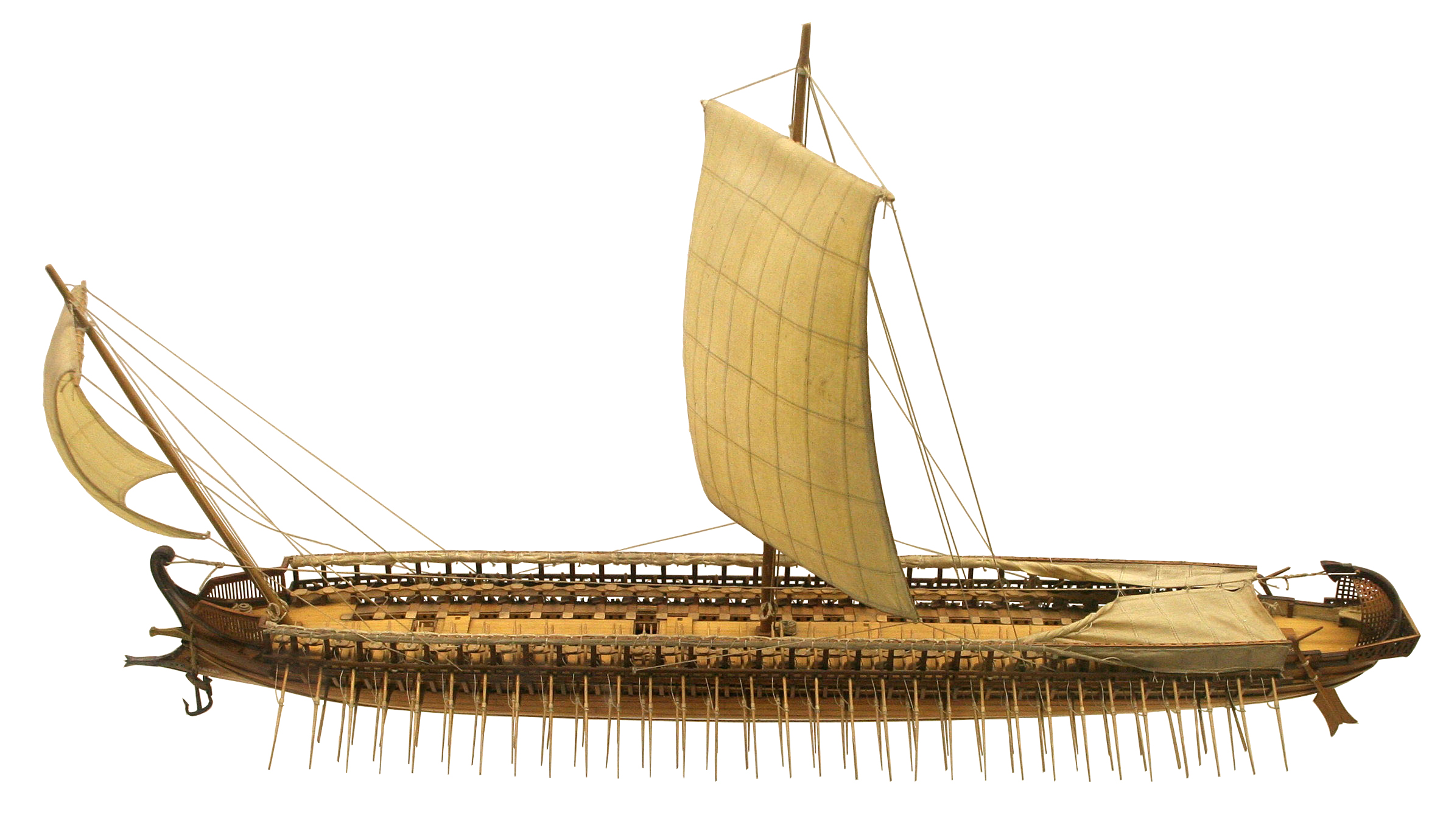
Chariots
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000 BCE. The critical invention that allowed the construction of light, horse-drawn chariots was the spoked wheel. The chariot was a fast, light, open, two-wheeled conveyance drawn by two or more horses that were hitched side by side, and was little more than a floor with a waist-high guard at the front and sides. It was initially used for ancient warfare during the Bronze and Iron Ages, but after its military capabilities had been superseded by light and heavy cavalries, chariots continued to be used for travel and transport, in processions, for games, and in races. Etymology The word "chariot" comes from the Latin term ''carrus'', a loanword from Gaulish. In ancient Rome and some other ancient Mediterranean civilizations, a ''biga'' re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biga (chariot)
The ''biga'' (Latin, plural ''bigae'') is the two-horse chariot as used in ancient Rome for sport, transportation, and ceremonies. Other animals may replace horses in art and occasionally for actual ceremonies. The term ''biga'' is also used by modern scholars for the similar chariots of other Indo-European cultures, particularly the two-horse chariot of the ancient Greeks and Celts. The driver of a ''biga'' is a ''bigarius''. Other Latin words that distinguish chariots by the number of animals yoked as a team are ''quadriga'', a four-horse chariot used for racing and associated with the Roman triumph; ''triga'', or three-horse chariot, probably driven for ceremonies more often than racing (see Trigarium); and ''seiugis'' or ''seiuga'', the six-horse chariot, more rarely raced and requiring a high degree of skill from the driver. The ''biga'' and ''quadriga'' are the most common types. Two-horse chariots are a common icon on Roman coins; see '' bigatus'', a type of denarius so c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spoke
A spoke is one of some number of rods radiating from the center of a wheel (the hub where the axle connects), connecting the hub with the round traction surface. The term originally referred to portions of a log that had been riven (split lengthwise) into four or six sections. The radial members of a wagon wheel were made by carving a spoke (from a log) into their finished shape. A spokeshave is a tool originally developed for this purpose. Eventually, the term spoke was more commonly applied to the finished product of the wheelwright's work, than to the materials they used. History The spoked wheel was invented to allow the construction of lighter and swifter vehicles. Earliest physical evidence for spoked wheels were found in Sintashta culture, dating to 2000 BC. Soon after this, horse cultures of the Caucasus region used horse-drawn spoked-wheel war chariots for the greater part of three centuries. They moved deep into the Greek peninsula where they joined with the exis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sintashta Culture
The Sintashta culture (russian: Синташтинская культура, Sintashtinskaya kul'tura), around 2050–1900 BCE, is the first phase of the Sintashta–Petrovka culture. or Sintashta–Arkaim culture,. and is a late Middle Bronze Age archaeological culture, located to the east of the Southern Urals, within the northern Eurasian steppe on the borders of Eastern Europe and Central Asia. The whole Sintashta–Petrovka complex was dated in a recent publication by Stephan Lindner, based on a series of 19 calibrated radiocarbon dating samples as belonging to c. 2050–1750 BCE. The phase of the Petrovka culture can be dated c. 1900–1750 BCE. The oldest reliable analysis of human remains from Sintashta is radiocarbon dated to a mean of cal BC (2335–2041 calBC), and genetically analyzed as Y-haplogroup R1a-Z93 < R-Z2124. The Sintashta culture was previously dated to the period 2200–1800 BCE. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Warfare
Ancient warfare is war that was conducted from the beginning of recorded history to the end of the ancient period. The difference between prehistoric and ancient warfare is more organization oriented than technology oriented. The development of first city-states, and then empires, allowed warfare to change dramatically. Beginning in Mesopotamia, states produced sufficient agricultural surplus. This allowed full-time ruling elites and military commanders to emerge. While the bulk of military forces were still farmers, the society could portion off each year. Thus, organized armies developed for the first time. These new armies were able to help states grow in size and become increasingly centralized. In Europe and the Near East, the end of antiquity is often equated with the Fall of Rome in 476 AD, the wars of the Eastern Roman Empire on its Southwestern Asian and North African borders, and the beginnings of the Muslim conquests in the 7th century. In China, it can also be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadriga
A () is a car or chariot drawn by four horses abreast and favoured for chariot racing in Classical Antiquity and the Roman Empire until the Late Middle Ages. The word derives from the Latin contraction of , from ': four, and ': yoke. The four-horse abreast arrangement in quadriga is distinct from the more common four-in-hand array of two horses in the front and two horses in the back. Quadriga was raced in the Ancient Olympic Games and other contests. It is represented in profile as the chariot of gods and heroes on Greek vases and in bas-relief. During the festival of the Halieia, the ancient Rhodians would sacrifice a quadriga by throwing it into the sea. The quadriga was adopted in ancient Roman chariot racing. Quadrigas were emblems of triumph; Victory or Fame often are depicted as the triumphant woman driving it. In classical mythology, the quadriga is the chariot of the gods; the god of the sun Helios (often identified with Apollo, the god of light) was depicte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chariot Racing
Chariot racing ( grc-gre, ἁρματοδρομία, harmatodromia, la, ludi circenses) was one of the most popular ancient Greek, Roman, and Byzantine sports. In Greece, chariot racing played an essential role in aristocratic funeral games from a very early time. With the institution of formal races and permanent racetracks, chariot racing was adopted by many Greek states and their religious festivals. Horses and chariots were very costly. Their ownership was a preserve of the wealthiest aristocrats, whose reputations and status benefitted from offering such extravagant, exciting displays. Their successes could be further broadcast and celebrated through commissioned odes and other poetry. In standard racing practise, each chariot held a single driver and was pulled by four horses, or sometimes two. Drivers and horses risked serious injury or death through collisions and crashes; this added to the excitement and interest for spectators. Most charioteers were slaves or contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaulish
Gaulish was an ancient Celtic language spoken in parts of Continental Europe before and during the period of the Roman Empire. In the narrow sense, Gaulish was the language of the Celts of Gaul (now France, Luxembourg, Belgium, most of Switzerland, Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the west bank of the Rhine). In a wider sense, it also comprises varieties of Celtic that were spoken across much of central Europe (" Noric"), parts of the Balkans, and Anatolia (" Galatian"), which are thought to have been closely related. The more divergent Lepontic of Northern Italy has also sometimes been subsumed under Gaulish. Together with Lepontic and the Celtiberian spoken in the Iberian Peninsula, Gaulish helps form the geographic group of Continental Celtic languages. The precise linguistic relationships among them, as well as between them and the modern Insular Celtic languages, are uncertain and a matter of ongoing debate because of their sparse att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), Roman Republic (509–27 BC) and Roman Empire (27 BC–476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian Peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually dominated the Italian Peninsula, assimilated the Greek culture of southern Italy (Magna Grecia) and the Etruscan culture and acquired an Empire that took in much of Europe and the lands and peoples surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. It was among the largest empires in the ancient world, with an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants, roughly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient History
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biga
Biga may refer to: Places * Biga, Çanakkale, a town and district of Çanakkale Province in Turkey * Sanjak of Biga, an Ottoman province * Biga Çayı, a river in Çanakkale Province * Biga Peninsula, a peninsula in Turkey, in the northwest part of Anatolia Other uses * Biga (bread baking), a type of pre-fermentation used in Italian baking * Biga and Busca, two political factions in the 15th century Catalan Civil War * Biga (typeface) * Biga (chariot), a two-horse chariot used in ancient Mediterranean countries * Bigha, a unit of land area used in North India * Biga language, an Austronesian language of West Papua, Indonesia See also * Bigeh Bigeh ( ar, بجح; Ancient Egyptian ''znmwt'') is an island and archaeological site situated along the Nile River in historic Nubia and within the Aswan Governorate of southern Egypt. The island has been situated in the reservoir of the Old As ..., an island in the River Nile * Biga Ranx (born 1988), French musician {{Disambi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triga (chariot)
The Trigarium was an equestrian training ground in the northwest corner of the Campus Martius ("Field of Mars") in ancient Rome. Its name was taken from the ''triga'', a three-horse chariot. The Trigarium was an open space located south of the bend of the Tiber River, near the present-day Via Giulia. It may be part of a larger field set aside as a public space for horse pasturage and military drill for youths, which was the original purpose of the Campus Martius. The earliest reference to the Trigarium dates to the time of Claudius, and the latest to the second half of the 4th century. To preserve its flexibility of purpose, the Trigarium had no permanent structures; it was used for chariot training and all forms of equestrian exercise. The faction headquarters of the professional charioteers were established nearby, with the Trigarium just northwest of the stables and clubhouse of the Green and Blue teams. An adjacent area where people played ball and hoop games and wres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |