|
Silicon Nanowires
Silicon nanowires, also referred to as SiNWs, are a type of semiconductor nanowire most often formed from a silicon precursor by etching of a solid or through catalyzed growth from a vapor or liquid phase. Such nanowires have promising applications in lithium ion batteries, thermoelectrics and sensors. Initial synthesis of SiNWs is often accompanied by thermal oxidation steps to yield structures of accurately tailored size and morphology. SiNWs have unique properties that are not seen in bulk (three-dimensional) silicon materials. These properties arise from an unusual quasi one-dimensional electronic structure and are the subject of research across numerous disciplines and applications. The reason that SiNWs are considered one of the most important one-dimensional materials is they could have a function as building blocks for nanoscale electronics assembled without the need for complex and costly fabrication facilities. SiNWs are frequently studied towards applications including pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanowire
A nanowire is a nanostructure in the form of a wire with the diameter of the order of a nanometre (10−9 metres). More generally, nanowires can be defined as structures that have a thickness or diameter constrained to tens of nanometers or less and an unconstrained length. At these scales, quantum mechanical effects are important—which coined the term "quantum wires". Many different types of nanowires exist, including superconducting (e.g. Yttrium barium copper oxide, YBCO), metallic (e.g. nickel, Ni, platinum, Pt, gold, Au, Ag), semiconducting (e.g. Silicon nanowire, silicon nanowires (SiNWs), indium phosphide, InP, gallium nitride, GaN) and insulating (e.g. Silicon dioxide, SiO2, Titanium dioxide, TiO2). Molecular nanowires are composed of repeating molecular units either organic (e.g. DNA) or inorganic (e.g. Mo6S9−xIx). Characteristics file:SnSe@SWCNT.jpg, upright=1.2, Crystalline 2×2-atom tin selenide nanowire grown inside a single-wall carbon nanotube (tube diamete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vapor–liquid–solid Method
The vapor–liquid–solid method (VLS) is a mechanism for the growth of one-dimensional structures, such as nanowires, from chemical vapor deposition. The growth of a crystal through direct adsorption of a gas phase on to a solid surface is generally very slow. The VLS mechanism circumvents this by introducing a catalytic liquid alloy phase which can rapidly adsorb a vapor to supersaturation levels, and from which crystal growth can subsequently occur from nucleated seeds at the liquid–solid interface. The physical characteristics of nanowires grown in this manner depend, in a controllable way, upon the size and physical properties of the liquid alloy. Historical background The VLS mechanism was proposed in 1964 as an explanation for silicon whisker growth from the gas phase in the presence of a liquid gold droplet placed upon a silicon substrate. The explanation was motivated by the absence of axial screw dislocations in the whiskers (which in themselves are a growth mechani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoelectronics
Nanoelectronics refers to the use of nanotechnology in electronic components. The term covers a diverse set of devices and materials, with the common characteristic that they are so small that inter-atomic interactions and quantum mechanical properties need to be studied extensively. Some of these candidates include: hybrid molecular/semiconductor electronics, one-dimensional nanotubes/nanowires (e.g. silicon nanowires or carbon nanotubes) or advanced molecular electronics. Nanoelectronic devices have critical dimensions with a size range between 1 nm and 100 nm. Recent silicon MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor, or MOS transistor) technology generations are already within this regime, including 22 nanometers CMOS (complementary MOS) nodes and succeeding 14 nm, 10 nm and 7 nm FinFET (fin field-effect transistor) generations. Nanoelectronics is sometimes considered as disruptive technology because present candidates are significantly different f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology, also shortened to nanotech, is the use of matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale for industrial purposes. The earliest, widespread description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabrication of macroscale products, also now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. A more generalized description of nanotechnology was subsequently established by the National Nanotechnology Initiative, which defined nanotechnology as the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). This definition reflects the fact that quantum mechanical effects are important at this quantum-realm scale, and so the definition shifted from a particular technological goal to a research category inclusive of all types of research and technologies that deal with the special properties of matter which occur below the given size threshold. It is therefore common to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Materials
Material is a substance or mixture of substances that constitutes an object. Materials can be pure or impure, living or non-living matter. Materials can be classified on the basis of their physical and chemical properties, or on their geological origin or biological function. Materials science is the study of materials, their properties and their applications. Raw materials can be processed in different ways to influence their properties, by purification, shaping or the introduction of other materials. New materials can be produced from raw materials by synthesis. In industry, materials are inputs to manufacturing processes to produce products or more complex materials. Historical elements Materials chart the history of humanity. The system of the three prehistoric ages (Stone Age, Bronze Age, Iron Age) were succeeded by historical ages: steel age in the 19th century, polymer age in the middle of the following century (plastic age) and silicon age in the second half of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrophoresis
Electrophoresis, from Ancient Greek ἤλεκτρον (ḗlektron, "amber") and φόρησις (phórēsis, "the act of bearing"), is the motion of dispersed particles relative to a fluid under the influence of a spatially uniform electric field. Electrophoresis of positively charged particles (cations) is sometimes called cataphoresis, while electrophoresis of negatively charged particles (anions) is sometimes called anaphoresis. The electrokinetic phenomenon of electrophoresis was observed for the first time in 1807 by Russian professors Peter Ivanovich Strakhov and Ferdinand Frederic Reuss at Moscow University, who noticed that the application of a constant electric field caused clay particles dispersed in water to migrate. It is ultimately caused by the presence of a charged interface between the particle surface and the surrounding fluid. It is the basis for analytical techniques used in chemistry for separating molecules by size, charge, or binding affinity. Electropho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical potential. It is possible to diffuse "uphill" from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration, like in spinodal decomposition. The concept of diffusion is widely used in many fields, including physics (particle diffusion), chemistry, biology, sociology, economics, and finance (diffusion of people, ideas, and price values). The central idea of diffusion, however, is common to all of these: a substance or collection undergoing diffusion spreads out from a point or location at which there is a higher concentration of that substance or collection. A gradient is the change in the value of a quantity, for example, concentration, pressure, or temperature with the change in another variable, usually distance. A change in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. There are two classes of redox reactions: * ''Electron-transfer'' – Only one (usually) electron flows from the reducing agent to the oxidant. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * ''Atom transfer'' – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides, other chemical species can serve the same function. In hydrogenation, C=C (and other) bonds ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
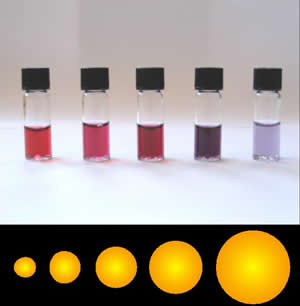
Colloidal Gold
Colloidal gold is a sol or colloidal suspension of nanoparticles of gold in a fluid, usually water. The colloid is usually either wine-red coloured (for spherical particles less than 100 nm) or blue/purple (for larger spherical particles or nanorods). Due to their optical, electronic, and molecular-recognition properties, gold nanoparticles are the subject of substantial research, with many potential or promised applications in a wide variety of areas, including electron microscopy, electronics, nanotechnology, materials science, and biomedicine. The properties of colloidal gold nanoparticles, and thus their potential applications, depend strongly upon their size and shape. For example, rodlike particles have both a transverse and longitudinal absorption peak, and anisotropy of the shape affects their self-assembly. History Used since ancient times as a method of staining glass colloidal gold was used in the 4th-century Lycurgus Cup, which changes color dependin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercritical Fluid
A supercritical fluid (SCF) is any substance at a temperature and pressure above its critical point, where distinct liquid and gas phases do not exist, but below the pressure required to compress it into a solid. It can effuse through porous solids like a gas, overcoming the mass transfer limitations that slow liquid transport through such materials. SCF are much superior to gases in their ability to dissolve materials like liquids or solids. Also, near the critical point, small changes in pressure or temperature result in large changes in density, allowing many properties of a supercritical fluid to be "fine-tuned". Supercritical fluids occur in the atmospheres of the gas giants Jupiter and Saturn, the terrestrial planet Venus, and probably in those of the ice giants Uranus and Neptune. Supercritical water is found on Earth, such as the water issuing from black smokers, a type of underwater hydrothermal vent. They are used as a substitute for organic solvents in a range of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Vapor Deposition
Physical vapor deposition (PVD), sometimes called physical vapor transport (PVT), describes a variety of vacuum deposition methods which can be used to produce thin films and coatings on substrates including metals, ceramics, glass, and polymers. PVD is characterized by a process in which the material transitions from a condensed phase to a vapor phase and then back to a thin film condensed phase. The most common PVD processes are sputtering and evaporation. PVD is used in the manufacturing of items which require thin films for optical, mechanical, electrical, acoustic or chemical functions. Examples include semiconductor devices such as thin-film solar cells, microelectromechanical devices such as thin film bulk acoustic resonator, aluminized PET film for food packaging and balloons, and titanium nitride coated cutting tools for metalworking. Besides PVD tools for fabrication, special smaller tools used mainly for scientific purposes have been developed. The source material i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |