|
Sibynophiinae
Sibynophiinae is a small subfamily of colubroid snakes, sometimes referred to as a family (Sibynophiidae). This group has also been called Scaphiodontophiinae but since the name Sibynophiinae is older, it has priority. They are commonly called hinged-teeth snakes. Sibynophiine snakes are between 30 and 100 cm in total length as adults, depending on the species. They have extremely long tails, up to half of the total length. They are non-venomous and eat mostly lizards. These snakes possess several unique features, including numerous small, spatulate, hinged maxillary teeth, a specialization that allows grasping and feeding on hard-bodied prey such as skinks, and the presence of fracture planes between caudal vertebrae that allow them to easily break parts of their tails in a fashion similar to many lizards (although they cannot regrow their tails). ''Scaphiodontophis'' are also unusual in being partial coral snake mimics: the front and sometimes the rear parts of their bodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colubroidea
Colubroidea is a superfamily of snakes in the clade Colubroides that includes Colubridae, with some studies splitting Colubridae into multiple families that make up Colubroidea. Historically, Colubroidea also included other caenophidian snakes such as cobras and vipers, as these snakes form a clade. However these groups are now divided into several distinct, but related, families. Zaher et al. (2009) proposed to redefine Colubroidea for colubrids and related families, while designating Colubroides as the group containing vipers and cobras as well as colubroids. The ReptileDatabase considers Colubroidea to be composed of Colubridae and the members of its sister group, Elapoidea, and does not recognize the division of Colubridae into multiple families. Classification Phylogeny Families and Subfamilies Usual taxonomy: * Family: Colubridae Oppel, 1811 ** Subfamily: Grayiinae Günther, 1858 ** Subfamily: Calamariinae Bonaparte, 1838 ** Subfamily: Ahaetullinae Figueroa, McKelvy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sibynophis
''Sibynophis'' is a genus of nonvenomous colubrid snakes, commonly called many-toothed snakes, which together with ''Scaphiodontophis'' make up the subfamily Sibynophiinae. Species The following nine species are recognized.Wikispecies * '' Sibynophis bistrigatus'' ( Günther, 1868) – Günther's many-toothed snake * ''Sibynophis bivittatus'' ( Boulenger, 1894) – white-striped snake * ''Sibynophis chinensis'' ( Günther, 1889) – Chinese many-toothed snake * '' Sibynophis collaris'' (Gray, 1853) – common many-toothed snake * '' Sibynophis geminatus'' ( H. Boie, 1826) – Boie's many-toothed snake * ''Sibynophis melanocephalus'' (Gray, 1835) – black-headed collared snake, Malayan many-toothed snake * ''Sibynophis sagittarius'' (Cantor, 1839) – Cantor's black-headed snake * ''Sibynophis subpunctatus'' ( A.M.C. Duméril, Bibron & A. Duméril, 1854) – Duméril's black-headed snake, Jerdon's many-toothed snake * '' Sibynophis triangularis'' Taylor Taylor, Taylors or Tayl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sibynophis Chinensis
''Sibynophis chinensis'', commonly known as the Chinese many-toothed snake, is a nonvenomous species of colubrid snake found in Vietnam, China, and Taiwan Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort .... References Sibynophis Reptiles of Vietnam Reptiles of China Reptiles of Taiwan Reptiles described in 1889 Taxa named by Albert Günther {{Colubrid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natricinae
The Natricinae are a subfamily of colubroid snakes, sometimes referred to as a family (Natricidae). The subfamily comprises 37 genera. Members include many very common snake species, such as the European grass snakes, and the North American water snakes and garter snakes. Some Old World members of the subfamily are known as keelbacks, because their dorsal scales exhibit strong keeling. Natricine snakes are found in Africa, Asia, Europe, North America, and Central America as far south as Costa Rica. A single species, '' Tropidonophis mairii'', reaches Australia. Although the highest diversity is in North America, the oldest members are in Asia and Africa, suggesting an Old World origin for the group. Most species are semiaquatic and feed on fish and amphibians, although a few are semifossorial or leaf-litter snakes that feed on invertebrates. Most species are harmless to humans, but a few (e.g., ''Thamnophis sirtalis'', '' Thamnophis elegans'') are capable of inflicting bites t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
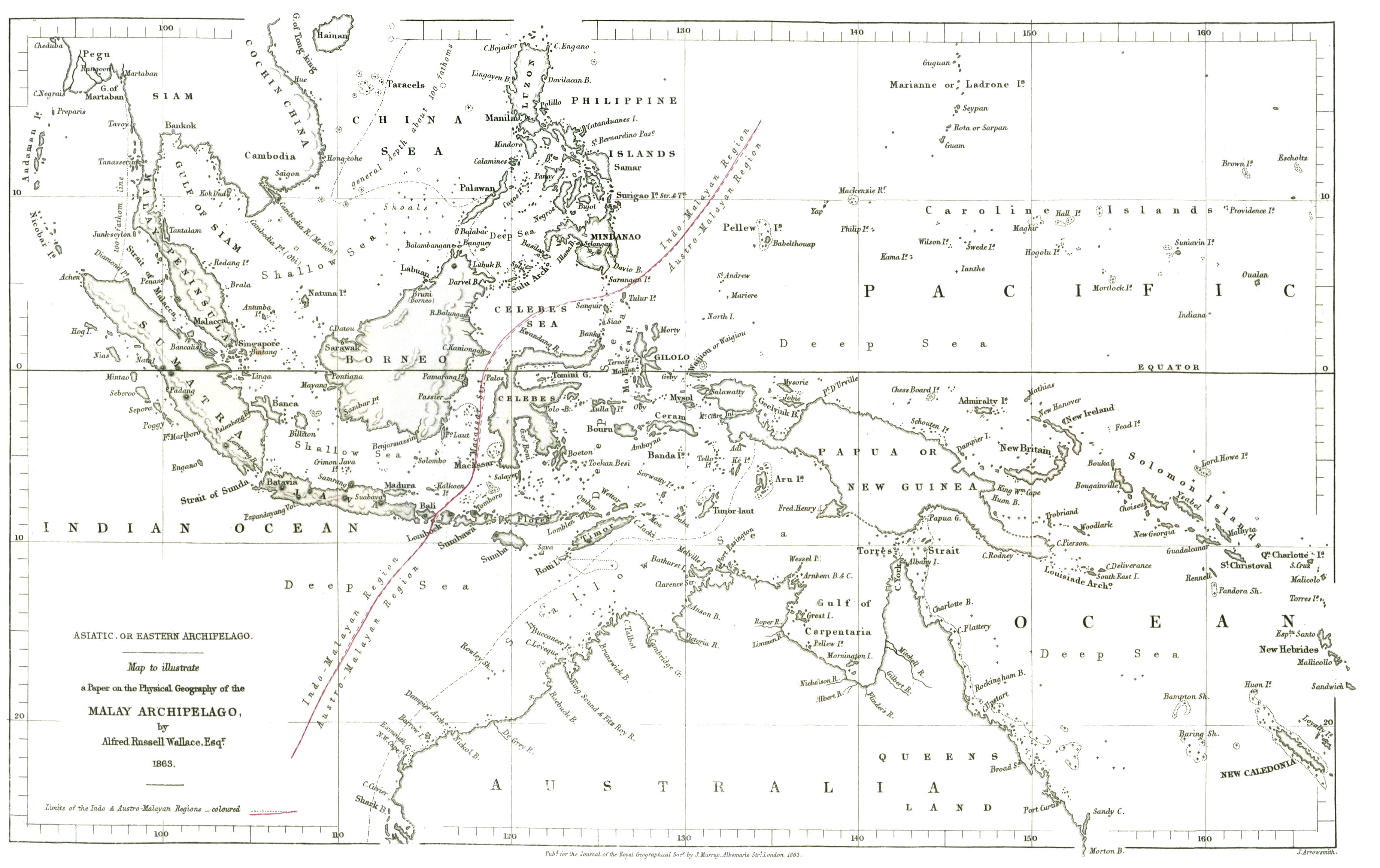
Wallace's Line
The Wallace Line or Wallace's Line is a faunal boundary line drawn in 1859 by the British naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace and named by English biologist Thomas Henry Huxley that separates the biogeographical realms of Asia and Wallacea, a transitional zone between Asia and Australia. West of the line are found organisms related to Asiatic species; to the east, a mixture of species of Asian and Australian origin is present. Wallace noticed this clear division during his travels through the East Indies in the 19th century. The line runs through Indonesia, between Borneo and Sulawesi (Celebes), and through the Lombok Strait between Bali and Lombok. The distance between Bali and Lombok is small, about . The distributions of many bird species observe the line, since many birds do not cross even the shortest stretches of open ocean water. Some bats have distributions that cross the line, but larger terrestrial mammals are generally limited to one side or the other; exceptions include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamprophiidae
The Lamprophiidae are a family of snakes found throughout much of Africa, including the Seychelles. There are 89 species as of July 2022. Biology Lamprophiids are a very diverse group of snakes. Many are terrestrial but some are fossorial (e.g. ''Amblyodipsas'') or semi-aquatic (e.g. ''Lycodonomorphus''). Some are fast-moving (e.g. ''Psammophis'') whereas others are slow (e.g. ''Duberria''). They are found in deserts, grasslands, tropical forests and mountains. Together they feed on mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish, and invertebrates. Some species use constriction to subdue their prey (e.g. ''Boaedon''). When other snake families were formerly included within the Lamprophiidae, they were considered even more diverse in biology, although this is now known to not be the case. Most species are oviparous. Classification Most lamprophiids were historically considered to be members of the subfamily Lamprophiinae in the family Colubridae. The following classification follows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liophidium
''Liophidium'' is a genus of snakes in the family Pseudoxyrhophiidae. The genus contains ten species, nine of which are endemic to the island of Madagascar and one to the island of Mayotte. All species of ''Liophidium'' are harmless to humans. Species The following species are recognized as being valid. *'' Liophidium apperti'' Domergue, 1984 *'' Liophidium chabaudi'' Domergue, 1984 *'' Liophidium maintikibo'' Franzen, Jones, Raselimanana, Nagy, D’Cruze, Glaw & Vences, 2009 *'' Liophidium mayottensis'' ( W. Peters, 1874) - Peters' brightsnake *'' Liophidium pattoni'' Vieites, Ratsoavina, Randrianiaina, Nagy, Glaw & Vences, 2010 *'' Liophidium rhodogaster'' (Schlegel, 1837) - gold-collared snake *'' Liophidium therezieni'' Domergue, 1984 *'' Liophidium torquatum'' (Boulenger, 1888) *'' Liophidium trilineatum'' Boulenger, 1896 - Madagascar three-lined snake *'' Liophidium vaillanti'' ( Mocquard, 1901) ''Nota bene'': A binomial authority In taxonomy, binomial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipsadinae
Dipsadinae is a large subfamily of colubroid snakes, sometimes referred to as a family (Dipsadidae). They are found in most of the Americas, including the West Indies, and are most diverse in South America. There are more than 700 species. Dipsadinae are an ecologically and morphologically diverse group of mostly small to moderate-sized snakes (typically less than in total length). Some are arboreal, but others are aquatic or terrestrial and may even burrow. Most are oviparous. Many eat frogs or lizards, and some consume mammals and birds. Several genera (e.g. '' Adelphicos'', '' Atractus'', ''Geophis'', ''Dipsas'', ''Ninia'', '' Sibon'', ''Sibynomorphus'', ''Tropidodipsas'') are specialized feeders on gooey and slimy prey, such as frog eggs, earthworms, snails, and slugs. Almost all species are completely harmless to humans, although a few genera (e.g. ''Borikenophis'', '' Cubophis'', ''Heterodon'', ''Hydrodynastes'', ''Philodryas'') have inflicted painful bites with local, no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crotalinae
The Crotalinae, commonly known as pit vipers,Mehrtens JM (1987). ''Living Snakes of the World in Color''. New York: Sterling Publishers. 480 pp. . crotaline snakes (from grc, κρόταλον ''krotalon'' castanet), or pit adders, are a subfamily of vipers found in Eurasia and the Americas. Like all other vipers, they are venomous. They are distinguished by the presence of a heat-sensing pit organ located between the eye and the nostril on both sides of the head. Currently, 23 genera and 155 species are recognized: These are also the only viperids found in the Americas. The groups of snakes represented here include rattlesnakes, lanceheads, and Asian pit vipers. The type genus for this subfamily is ''Crotalus'', of which the type species is the timber rattlesnake, ''C. horridus''. These snakes range in size from the diminutive hump-nosed viper, ''Hypnale hypnale'', that grows to a typical total length (including tail) of only , to the bushmaster, ''Lachesis muta'', a specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colubrinae
The Colubrinae are a subfamily of the family Colubridae of snakes. It includes numerous genera, and although taxonomic sources often disagree on the exact number, The Reptile Database lists 717 species in 92 genera as of September 2019. It is the second largest subfamily of colubrids, after Dipsadinae. Many of the most commonly known snakes are members of this subfamily, including rat snakes, king snakes, milk snakes, vine snakes, and indigo snakes. Colubrine snakes are distributed worldwide, with the highest diversity in North America, Asia, northern Africa, and the Middle East. There are relatively few species of colubrine snakes in Europe, South America, Australia, and southern Africa, and none in Madagascar, the Caribbean, or the Pacific Islands. Colubrine snakes are extremely morphologically and ecologically diverse. Many are terrestrial, and there are specialized fossorial (e.g. ''Tantilla'') and arboreal (e.g. ''Oxybelis'') groups, but no truly aquatic groups. Some of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |