|
Shussai-Iwano Ichirizuka
The is a historic Japanese distance marker akin to a milestone, comprising a pair of earthen mounds located in what is now part of the city of Izumo, Shimane Prefecture in the San'in region of Japan. It was designated a National Historic Site of Japan in 1937. Overview During the Edo period the Tokugawa shogunate established ''ichirizuka'' on major roads, enabling calculation both of distance travelled and of the charge for transportation by '' kago'' or palanquin. These mounds denoted the distance in '' ri'' () typically to Nihonbashi, the "Bridge of Japan", erected in Edo in 1603. They were typically planted with an ''enoki'' or Japanese red pine to provide shelter for travelers. Since the Meiji period, most of the ''ichirizuka'' have disappeared, having been destroyed by the elements, modern highway construction and urban encroachment. In 1876, the "Ichirizuka Abolition decree" was issued by the Meiji government and many were demolished at that time. Currently, 17 s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Izumo, Shimane
is a city in Shimane Prefecture, Japan. Izumo is known for noodles and the Izumo-taisha Shinto shrine. History Izumo Taisha is the oldest Shinto shrine in Japan. In 2008, the holy area was open to the public from 1 August until August 17, after which extensive renovation work began. The nearby Shimane Museum of Ancient Izumo, also located in Taisha Machi, has artifacts from the site. In 2009, a team of archaeologists announced that they likely discovered—at the Sunabara Remains in Taki-chō, Izumo City—the oldest stone tools ever found in Japan. The find totaled about 20 tools dating back an estimated 120,000 years: about 80,000 years earlier than previous estimates of when the first humans arrived in the Japanese archipelago. The stones were found directly across Route 9 from Kirara Taki beach on the Sea of Japan. The excavation team was led by Doshisha University professor Kazuto Matsufuji, and the first of the tools were unearthed by Toshiro Naruse, a professor emeritu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Red Pine
''Pinus densiflora'', also called the Japanese red pine, the Japanese pine, or Korean red pine, is a species of pine tree native to East Asia. Distribution and habitat ''P. densiflora'' has a home range that includes Japan, the Korean Peninsula, northeastern China (Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning, Shandong) and the extreme southeast of Russia (in Siberia, southern Primorsky Krai). Description The leaves are needle-like, long, with two per fascicle. The cones are long. It is closely related to Scots pine, differing in the longer, slenderer leaves which are mid-green without the glaucous-blue tone of Scots pine. This pine has become a popular ornamental and has several cultivars, but in the winter it becomes yellowish. The height of this tree is . The plant prefers full sun on well-drained, slightly acidic soil. Cultivation In Japan it is known as and . It is widely cultivated in Japan both for timber production and as an ornamental tree, and plays an important part in the classic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ijimi Ichirizuka
The is a historic Japanese distance marker akin to a milestone, comprising a pair of earthen mounds located in what is now the Shinji neighborhood of the city of Matsue, Shimane Prefecture in the San'in region of Japan. It was designated a National Historic Site of Japan in 1937. Overview During the Edo period the Tokugawa shogunate established ''ichirizuka'' on major roads, enabling calculation both of distance travelled and of the charge for transportation by '' kago'' or palanquin. These mounds denoted the distance in '' ri'' () typically to Nihonbashi, the "Bridge of Japan", erected in Edo in 1603. They were typically planted with an ''enoki'' or Japanese red pine to provide shelter for travelers. Since the Meiji period, most of the ''ichirizuka'' have disappeared, having been destroyed by the elements, modern highway construction and urban encroachment. In 1876, the "Ichirizuka Abolition decree" was issued by the Meiji government and many were demolished at that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yasugi, Shimane
is a city located in Shimane Prefecture, Japan. As of March 1, 2017, the city has an estimated population of 38,875 and a population density of 92 persons per km². The total area is . History The ruins of Gassantoda Castle are in Yasugi. According to legend, the goddess Izanami was buried here. In Shinto, both holy and negative concept exists. The city was an ancient steel-making (tatara) center. The Yasugi Steel brand name bears the name of the city, and was established by Hitachi Metals, Ltd. Yasugi was elevated to city status on April 4, 1954. On October 1, 2004, the towns of Hakuta and Hirose (both from Nogi District) were merged into Yasugi. Sightseeing The Adachi Museum of Art has a widely known Japanese garden and a collection of contemporary Japanese paintings, comprising approximately 1,300 of the country's most highly regarded paintings produced after the Meiji period and centering on the works of Yokoyama Taikan. In 2021, the gardens of the Adachi Museum wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yasugi Ichirizuka
The is a historic Japanese distance marker akin to a milestone, comprising a pair of earthen mounds located in what is now the Yasugi neighborhood of the city of Yasugi, Shimane Prefecture in the San'in region of Japan. It was designated a National Historic Site of Japan in 1936. Overview During the Edo period the Tokugawa shogunate established ''ichirizuka'' on major roads, enabling calculation both of distance travelled and of the charge for transportation by '' kago'' or palanquin. These mounds denoted the distance in '' ri'' () typically to Nihonbashi, the "Bridge of Japan", erected in Edo in 1603. They were typically planted with an ''enoki'' or Japanese red pine to provide shelter for travelers. Since the Meiji period, most of the ''ichirizuka'' have disappeared, having been destroyed by the elements, modern highway construction and urban encroachment. In 1876, the "Ichirizuka Abolition decree" was issued by the Meiji government and many were demolished at that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hōki Province
was an old province of Japan in the area that is today the western part of Tottori Prefecture. It was sometimes called . Hōki bordered on Inaba, Mimasaka, Bitchū, Bingo, and Izumo Provinces. The ancient capital was in the area that is now Kurayoshi, and a major castle town was at Yonago. Maps of Japan and Hōki Province were reformed in the 1870s when the prefecture system was introduced. At the same time, the province continued to exist for some purposes. For example, Hōki is explicitly recognized in treaties in 1894 (a) between Japan and the United States and (b) between Japan and the United Kingdom.US Department of State. (1906) ''A digest of international law as embodied in diplomatic discussions, treaties and other international agreements'' (John Bassett Moore, ed.), Vol. 5, p. 759 Historical districts * Tottori Prefecture ** Aimi District (会見郡) - merged with Aseri District to become Saihaku District (西伯郡) on March 29, 1896 ** Aseri District (� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Izumo Province
was an old province of Japan which today consists of the eastern part of Shimane Prefecture. It was sometimes called . The province is in the Chūgoku region. History During the early Kofun period (3rd century) this region was independent and constructed rectangular tumuli. But in the fourth century this region saw the construction of rectangular and key shaped tumuli. During the 6th or 7th century it was absorbed due to the expansion of the state of Yamato, within which it assumed the role of a sacerdotal domain. Today, the Izumo Shrine constitutes (as does the Grand Shrine of Ise) one of the most important sacred places of Shinto: it is dedicated to ''kami'', especially to Ōkuninushi (''Ō-kuni-nushi-no-mikoto''), mythical progeny of Susanoo and all the clans of Izumo. The mythological mother of Japan, the goddess Izanami, is said to be buried on Mt. Hiba, at the border of the old provinces of Izumo and Hōki, near modern-day Yasugi of Shimane Prefecture. By the Sengoku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matsue Castle
is a Japanese castle located in Matsue, Shimane Prefecture. Matsue Castle was constructed from 1607 to 1611 by Horio Yoshiharu, the first ''daimyō'' of the Matsue Domain, during the early Edo period. Ownership was passed to the Izumo branch of the Kyōgoku in 1633 and then the Matsudaira, a junior branch of the ruling Tokugawa clan, in 1637. The Matsudaira donated Matsue Castle to the city of Matsue in 1927. Matsue Castle is one of few remaining feudal Japanese castles in their original wooden form and not a modern concrete reconstruction. Built after the last great war of feudal Japan, the castle has survived earthquakes, fires, wars and other causes that destroyed or damaged other Japanese castles. Several castle buildings were demolished during the early Meiji period with only some of the original keep and stone walls existing today. Matsue Castle, standing on the shores of Lake Shinji, is one of Japan's Three Great Lake Castles and the heart of Matsue's central riverside d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matsue Domain
was a Japanese domain of the Edo period. It was associated with Izumo Province in modern-day Shimane Prefecture."Izumo Province" at JapaneseCastleExplorer.com retrieved 2013-4-27. In the , Matsue was a and abstraction based on periodic surveys and projected agricultural yields. In other wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
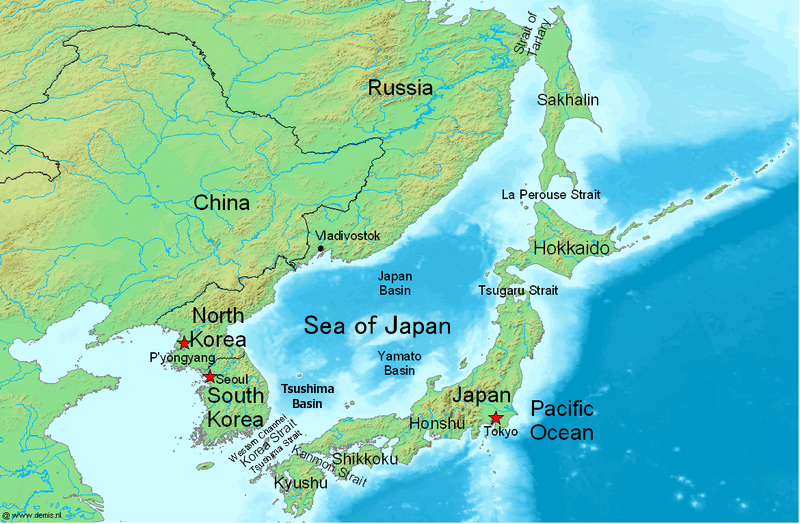
Sea Of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific Ocean. This isolation also affects faunal diversity and salinity, both of which are lower than in the open ocean. The sea has no large islands, bays or capes. Its water balance is mostly determined by the inflow and outflow through the straits connecting it to the neighboring seas and the Pacific Ocean. Few rivers discharge into the sea and their total contribution to the water exchange is within 1%. The seawater has an elevated concentration of dissolved oxygen that results in high biological productivity. Therefore, fishing is the dominant economic activity in the region. The intensity of shipments across the sea has been moderate owing to political issues, but it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the city had a population of 1.46 million. The city is the cultural anchor of a substantially larger metropolitan area known as Greater Kyoto, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) home to a census-estimated 3.8 million people. Kyoto is one of the oldest municipalities in Japan, having been chosen in 794 as the new seat of Japan's imperial court by Emperor Kanmu. The original city, named Heian-kyō, was arranged in accordance with traditional Chinese feng shui following the model of the ancient Chinese capital of Chang'an/Luoyang. The emperors of Japan ruled from Kyoto in the following eleven centuries until 1869. It was the scene of several key events of the Muromachi period, Sengoku period, and the Boshin War, such as the Ōnin War, the Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surrounding islands. Kyushu has a land area of and a population of 14,311,224 in 2018. In the 8th-century Taihō Code reforms, Dazaifu was established as a special administrative term for the region. Geography The island is mountainous, and Japan's most active volcano, Mount Aso at , is on Kyushu. There are many other signs of tectonic activity, including numerous areas of hot springs. The most famous of these are in Beppu, on the east shore, and around Mt. Aso in central Kyushu. The island is separated from Honshu by the Kanmon Straits. Being the nearest island to the Asian continent, historically it is the gateway to Japan. The total area is which makes it the 37th largest island in the world. It's slightly larger than Taiwan island . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |