|
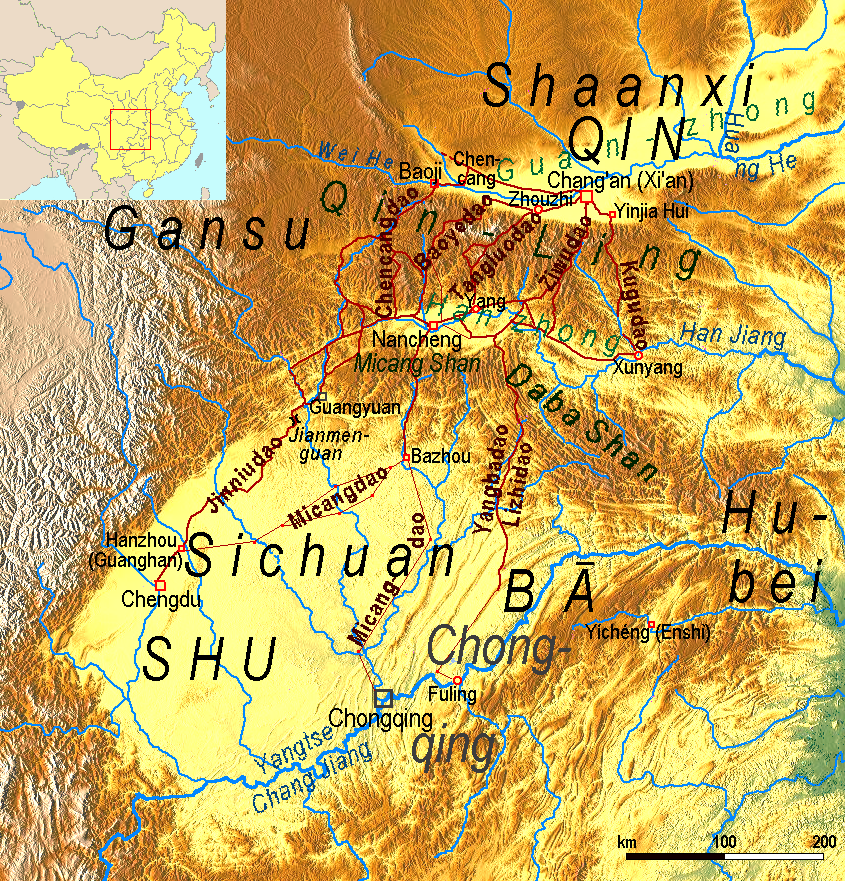
Shudao
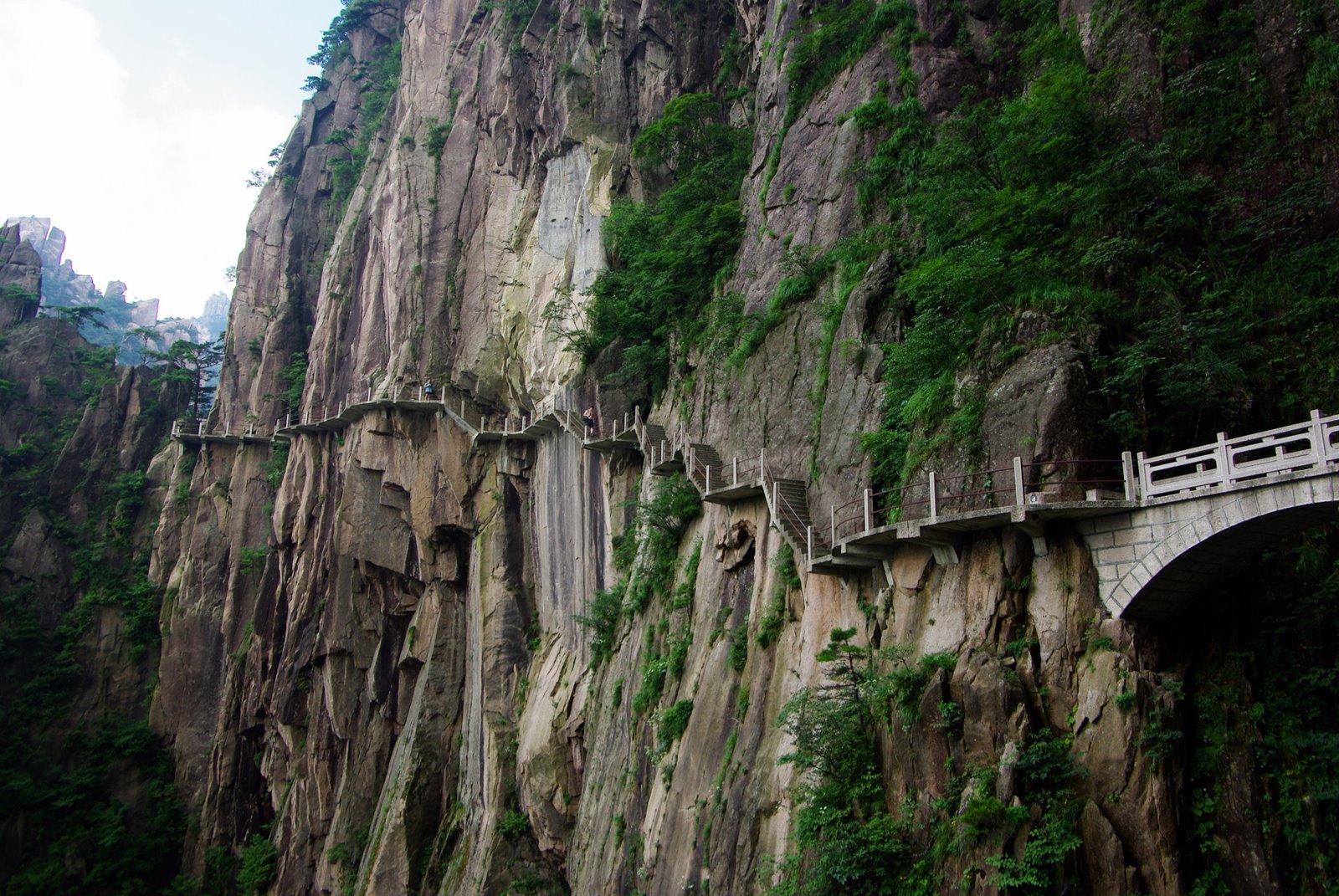
The Shudao (), or the Road(s) to Shu, is a system of mountain roads linking the Chinese province of Shaanxi with Sichuan (Shu), built and maintained since the 4th century BC. Technical highlights were the gallery roads, consisting of wooden planks erected on wooden or stone beams slotted into holes cut into the sides of cliffs. Geography The roads join three adjacent basins separated and surrounded by high mountains. The northern basin is called Guanzhong ("between the passes"). It is drained by the Yellow River. In ancient times it was the heart of the state of Qin, nowadays it is the central region of Shaanxi. To the south it is bounded by the Qinling Mountains. South of that range is the Hanzhong basin, drained by the Han River, a tributary of the Yangtze. The Hanzhong basin is divided from the Sichuan basin by mountain ranges called the Micang Shan (米倉山/米仓山, ''Mǐcāng Shān'', "Rice Granary Mountains") in the west and Daba Mountains in the east. The Sichuan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shudao
The Shudao (), or the Road(s) to Shu, is a system of mountain roads linking the Chinese province of Shaanxi with Sichuan (Shu), built and maintained since the 4th century BC. Technical highlights were the gallery roads, consisting of wooden planks erected on wooden or stone beams slotted into holes cut into the sides of cliffs. Geography The roads join three adjacent basins separated and surrounded by high mountains. The northern basin is called Guanzhong ("between the passes"). It is drained by the Yellow River. In ancient times it was the heart of the state of Qin, nowadays it is the central region of Shaanxi. To the south it is bounded by the Qinling Mountains. South of that range is the Hanzhong basin, drained by the Han River, a tributary of the Yangtze. The Hanzhong basin is divided from the Sichuan basin by mountain ranges called the Micang Shan (米倉山/米仓山, ''Mǐcāng Shān'', "Rice Granary Mountains") in the west and Daba Mountains in the east. The Sichuan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallery Road
The archaeological gallery roads () were roads through remote mountain areas of China. They consisted of wooden planks erected on holes cut into the sides of cliffs. They were most notably used in the Qin Mountains linking the Wei River and the Han River valleys. The first gallery roads were built during the Warring States period (476-221 BC) and used by Qin to invade Shu and Ba. They were fully consolidated into a thriving network during the Han Dynasty. Before the 20th century, very primitive versions were used in the western gorges of the Pamir Mountains. Introduction Gallery road, also known as cliff road, plank road, is a creative building in Chinese history. The main use of the gallery road is to establish a traffic route over a cliff in a steep mountainous area. The Shu Road is the most typical representative. It passes through some of the most rugged and desolate terrains in China, such as the Qinling Mountains and the Daba Mountain ranges, linking the Wei river v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanzhong
Guanzhong (, formerly romanised as Kwanchung) region, also known as the Guanzhong Basin, Wei River Basin, or uncommonly as the Shaanzhong region, is a historical region of China corresponding to the crescentic graben basin within present-day central Shaanxi, bounded between the Qinling Mountains in the south (known as Guanzhong's "South Mountains"), and the Huanglong Mountain, Meridian Ridge and Long Mountain ranges in the north (collectively known as its "North Mountains"). The central flatland area of the basin, known as the Guanzhong Plain, is made up of alluvial plains along the lower Wei River and its numerous tributaries and thus also called the Wei River Plain. The region is part of the Jin- Shaan Basin Belt, and is separated from its geological sibling — the Yuncheng Basin to its northeast — by the Yellow River section southwest of the Lüliang Mountains and north of the river's bend at the tri-provincial junction among Shaanxi, Shanxi and Henan. The name ''Guanzho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daba Mountains
The Daba Mountains, also known by their Chinese name as the Dabashan, are a mountain range in Central China between the watersheds of the Yellow and Yangtze Rivers. Part of the larger Qinling mountain range, it cuts through four provinces: Sichuan, Chongqing, Shaanxi, and Hubei. It is about long. Geography The Daba Mountains run in the general west-northwest to east-southeast direction, along the border between, on the one side (southwest and south) Sichuan and Chongqing, and on the other side (northeast and north) Shaanxi and Hubei. The mountains of Shennongjia are often considered the easternmost section of the Daba Range. The southern slope of the Daba Mountains drains into the Sichuan Basin or directly into the Yangtze via short streams that flow into the river in the Three Gorges area, such as the Shen Nong Stream. The northern side drains into the Han River, a major tributary of the Yangtze, which, however, does not join the Yangtze until some hundreds kilometers to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Cattle Road
The Stone Cattle Road () was an ancient Chinese road over the Qinling Mountains used by the state of Qin to conquer Sichuan in 316 BC. Story The story goes that King Huiwen of Qin on the Wei River wished to conquer the kingdom of Shu to the south over the impassable Qinling Mountains in the Sichuan Basin. Knowing of the King of Shu's fondness for treasure, he had his sculptors make five life-sized stone cows with gold tails and hindquarters with gold and placed them where the Shu ambassadors could see them. When the king of Shu heard of this, he thought it would be good to fertilize his treasury with golden cowpats, so he asked the king of Qin to send the cattle. The king of Qin replied that he was glad to do so, but the cattle were delicate and that to deliver them it would first be necessary to build a gallery road over the mountains. When this Stone Cattle Road was completed in 316 BC he used it to invade and conquer Shu. Sage gives a slightly different version of the story. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinling Mountains
The Qinling () or Qin Mountains, formerly known as the Nanshan ("Southern Mountains"), are a major east–west mountain range in southern Shaanxi Province, China. The mountains mark the divide between the drainage basins of the Yangtze and Yellow River systems, providing a natural boundary between North and South China and support a huge variety of plant and wildlife, some of which is found nowhere else on earth. To the north is the densely populated Wei River valley, an ancient center of Chinese civilization. To the south is the Han River valley. To the west is the line of mountains along the northern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. To the east are the lower Funiu and Dabie Shan which rise out of the coastal plain. The northern side of the range is prone to hot weather, however the physical barrier of the mountains mean that the land to the North has a semi-arid climate, with the lack of rich, fertile landscape that can not support a wealth of wildlife. The mountains also acted a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sichuan Basin
The Sichuan Basin (), formerly transliterated as the Szechwan Basin, sometimes called the Red Basin, is a lowland region in southwestern China. It is surrounded by mountains on all sides and is drained by the upper Yangtze River and its tributaries. The basin is anchored by Chengdu, the capital of Sichuan province, in the west, and the direct-administered municipality of Chongqing in the east. Due to its relative flatness and fertile soils, it is able to support a population of more than 100 million. In addition to being a dominant geographical feature of the region, the Sichuan Basin also constitutes a cultural sphere that is distinguished by its own unique customs, cuisine and dialects. It is famous for its rice cultivation and is often considered the breadbasket of China. In the 21st century its industrial base is expanding with growth in the high-tech, aerospace, and petroleum industries. Geography The Sichuan Basin is an expansive lowland region in China that is surr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Of Qin
Qin () was an ancient Chinese state during the Zhou dynasty. Traditionally dated to 897 BC, it took its origin in a reconquest of western lands previously lost to the Rong; its position at the western edge of Chinese civilization permitted expansion and development that was unavailable to its rivals in the North China Plain. Following extensive "Legalist" reform in the fourth century BC, Qin emerged as one of the dominant powers of the Seven Warring States and unified the seven states of China in 221 BC under Qin Shi Huang. It established the Qin dynasty, which was short-lived but greatly influenced later Chinese history. History Founding According to the 2nd century BC historical text ''Records of the Grand Historian'' by Sima Qian, the Qin state traced its origin to Zhuanxu, one of the legendary Five Emperors in ancient times. One of his descendants, Boyi, was granted the family name of Yíng by Emperor Shun. During the Xia and Shang dynasties, the Yíng clan spl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xianyang
Xianyang () is a prefecture-level city in central Shaanxi province, situated on the Wei River a few kilometers upstream (west) from the provincial capital of Xi'an. Once the capital of the Qin dynasty, it is now integrated into the Xi'an metropolitan area, one of the main urban agglomerations in northwestern China, with more than 7.17 million inhabitants, its built-up area made of 2 urban districts (Qindu and Weicheng) was 945,420 inhabitants at the 2010 census. It has a total area of . Xianyang is the seat of the Xi'an Xianyang International Airport, the main airport serving Xi'an and the largest airport in Northwest China, and one of the top 40th- busiest airports in the world. Xianyang is one of the top 500 cities in the world by scientific research outputs, as tracked by the Nature Index. It is home to the main campus of Northwest A&F University (NWAFU), one of the world's top universities in agriculture science related fields, and a member of "Project 985" club which is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xi'an
Xi'an ( , ; ; Chinese: ), frequently spelled as Xian and also known by #Name, other names, is the list of capitals in China, capital of Shaanxi, Shaanxi Province. A Sub-provincial division#Sub-provincial municipalities, sub-provincial city on the Guanzhong, Guanzhong Plain, the city is the third most populous city in Western China, after Chongqing and Chengdu, as well as the most populous city in Northwest China. Its total population was 12,952,907 as of the 2020 census. The total urban population was 9.28 million. Since the 1980s, as part of the China Western Development, economic growth of inland China especially for the central and northwest regions, Xi'an has re-emerged as a cultural, industrial, political and educational centre of the entire central-northwest region, with many facilities for research and development. Xi'an currently holds sub-provincial city in the People's Republic of China, sub-provincial status, administering 11 districts and 2 counties. In 2020, Xi'a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |