|
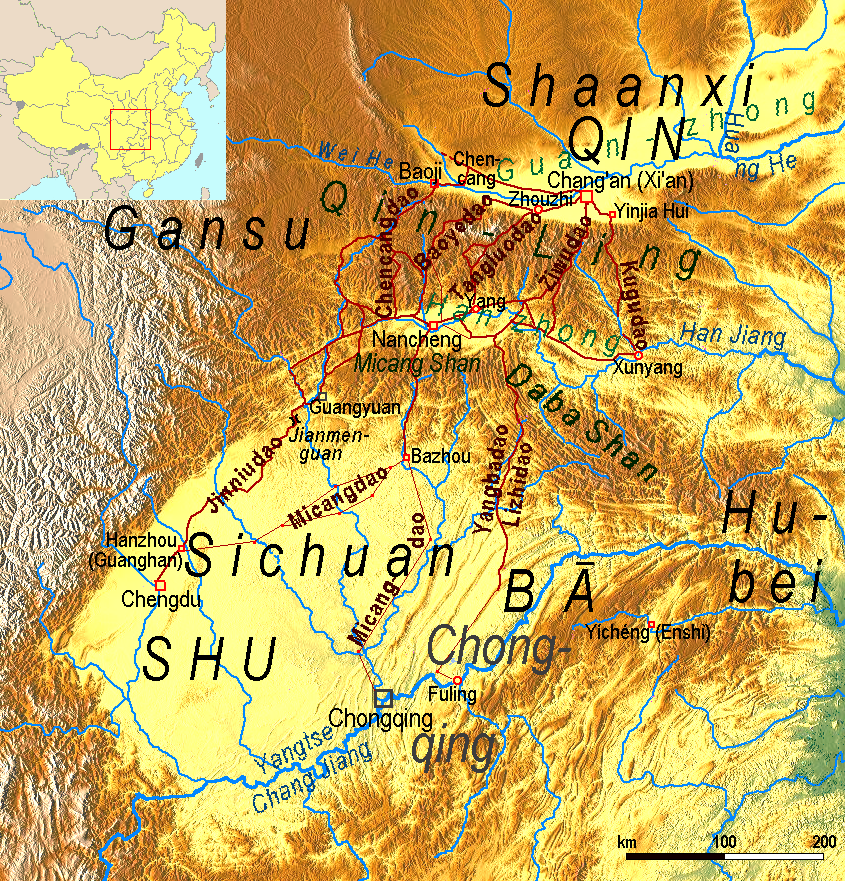
Stone Cattle Road
The Stone Cattle Road () was an ancient Chinese road over the Qinling Mountains used by the state of Qin to conquer Sichuan in 316 BC. Story The story goes that King Huiwen of Qin on the Wei River wished to conquer the kingdom of Shu to the south over the impassable Qinling Mountains in the Sichuan Basin. Knowing of the King of Shu's fondness for treasure, he had his sculptors make five life-sized stone cows with gold tails and hindquarters with gold and placed them where the Shu ambassadors could see them. When the king of Shu heard of this, he thought it would be good to fertilize his treasury with golden cowpats, so he asked the king of Qin to send the cattle. The king of Qin replied that he was glad to do so, but the cattle were delicate and that to deliver them it would first be necessary to build a gallery road over the mountains. When this Stone Cattle Road was completed in 316 BC he used it to invade and conquer Shu. Sage gives a slightly different version of the story. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinling Mountains
The Qinling () or Qin Mountains, formerly known as the Nanshan ("Southern Mountains"), are a major east–west mountain range in southern Shaanxi Province, China. The mountains mark the divide between the drainage basins of the Yangtze and Yellow River systems, providing a natural boundary between North and South China and support a huge variety of plant and wildlife, some of which is found nowhere else on earth. To the north is the densely populated Wei River valley, an ancient center of Chinese civilization. To the south is the Han River valley. To the west is the line of mountains along the northern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. To the east are the lower Funiu and Dabie Shan which rise out of the coastal plain. The northern side of the range is prone to hot weather, however the physical barrier of the mountains mean that the land to the North has a semi-arid climate, with the lack of rich, fertile landscape that can not support a wealth of wildlife. The mountains also acted a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; Simplified Chinese characters, simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), Chinese postal romanization, alternatively Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu, is a Sub-provincial division, sub-provincial city which serves as the Capital city, capital of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a population of 20,937,757 inhabitants during the 2020 Chinese census, it is the fourth most populous city in China, and it is the only city apart from the four Direct-administered municipalities of China, direct-administered municipalities with a population of over 20 million (the other three are Chongqing, Shanghai and Beijing). It is traditionally the hub in Southwest China. Chengdu is located in central Sichuan. The surrounding Chengdu Plain is known as the "Country of Heaven" () and the "Land of Abundance". Its prehistoric settlers included the Sanxingdui culture. The site of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Ancient China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the ''Book of Documents'' (early chapters, 11th century BC), the ''Bamboo Annals'' (c. 296 BC) and the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' (c. 91 BC) describe a Xia dynasty before the Shang, but no writing is known from the period, and Shang writings do not indicate the existence of the Xia. The Shang ruled in the Yellow River valley, which is commonly held to be the cradle of Chinese civilization. However, Neolithic civilizations originated at various cultural centers along both the Yellow River and Yangtze River. These Yellow River and Yangtze civilizations arose millennia before the Shang. With thousands of years of continuous history, China is among the world's oldest civilizations and is regarded as one of the cradles of civilization. The Zhou dynasty (1046–256 BC) suppla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the Sichuan Basin and the easternmost part of the Tibetan Plateau between the Jinsha River on the west, the Daba Mountains in the north and the Yungui Plateau to the south. Sichuan's capital city is Chengdu. The population of Sichuan stands at 83 million. Sichuan neighbors Qinghai to the northwest, Gansu to the north, Shaanxi to the northeast, Chongqing to the east, Guizhou to the southeast, Yunnan to the south, and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the west. In antiquity, Sichuan was the home of the ancient states of Ba and Shu. Their conquest by Qin strengthened it and paved the way for Qin Shi Huang's unification of China under the Qin dynasty. During the Three Kingdoms era, Liu Bei's state of Shu was based in Sichuan. The area was deva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Keay
John Stanley Melville Keay FRGS is a British historian, journalist, radio presenter and lecturer specialising in popular histories of India, the Far East and China, often with a particular focus on their colonisation and exploration by European ethnic groups, Europeans. In particular, he is widely seen as a pre-eminent historian of British India. He is known both for stylistic flair and meticulous research into archival primary sources, including centuries-old unpublished sources. The author of some twenty-five books, he also writes regularly for a number of prominent publications in Britain and Asia. He began his career with ''The Economist''. He has received several major honours including the Sir Percy Sykes Memorial Medal. In 2019, he received an honorary doctorate, presented by Princess Anne, from the University of the Highlands and Islands in Scotland. ''The Economist'' has called him "a gifted non-academic historian", the ''Yorkshire Post'' has called him "one of our ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
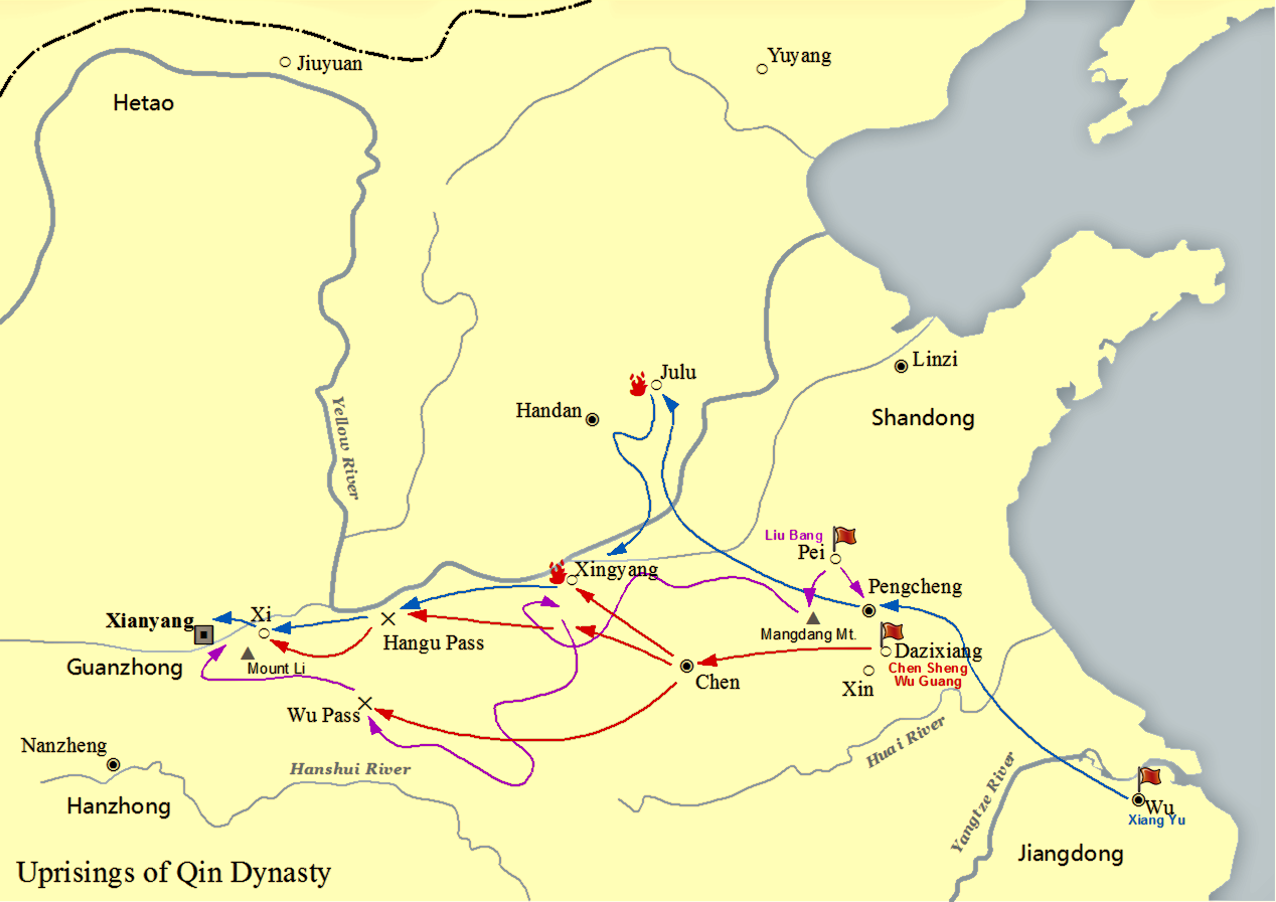
Liu Bang
Emperor Gaozu of Han (256 – 1 June 195 BC), born Liu Bang () with courtesy name Ji (季), was the founder and first emperor of the Han dynasty, reigning in 202–195 BC. His temple name was "Taizu" while his posthumous name was Emperor Gao, or Gaodi; "Gaozu of Han", derived from the ''Records of the Grand Historian'', is the common way of referring to this sovereign even though he was not accorded the temple name "Gaozu", which literally means "High Founder". Liu Bang was one of the few dynasty founders in Chinese history who was born into a peasant family. Prior to coming to power, Liu Bang initially served for the Qin dynasty as a minor law enforcement officer in his home town Pei County, within the conquered state of Chu. With the First Emperor's death and the Qin Empire's subsequent political chaos, Liu Bang renounced his civil service position and became an anti-Qin rebel leader. He won the race against fellow rebel leader Xiang Yu to invade the Qin heartland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanzhong
Hanzhong (; abbreviation: Han) is a prefecture-level city in the southwest of Shaanxi province, China, bordering the provinces of Sichuan to the south and Gansu to the west. The founder of the Han dynasty, Liu Bang, was once enfeoffed as the king of the Hanzhong region after overthrowing the Qin dynasty. During the Chu-Han contention, Liu Bang shortened his title to the King of Han (), and later used it as the name of his imperial dynasty. In this way, Hanzhong was responsible for the naming of the Han dynasty, which was later hailed as the first golden age in imperial Chinese history and lends its name to the principal ethnic group in China. Hanzhong is located at the modern headwater of the Han River, the largest tributary of the Yangtze River. Hanzhong city covers and is centered around the Hantai District. The prefecture-level city consists of two urban district and nine rural counties. As of the 2020 census, its population was 3,211,462, of whom 1,084,448 lived in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Taibai
Mount Taibai () is a mountain located on the border between Mei, Taibai and Zhouzhi counties in the south west of Shaanxi Province, China China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and .... The mount's highest point, Baxian Tower (), rises to a height of and is the tallest in the Qinling Range, as well as the watershed between the Han River (Yangtze River tributary), Han River and Wei River. Mount Taibai is also the highest mountain in Eastern China. History During the reign of the legendary, morally perfect Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors, Three Sovereigns (c. 2852–2070 BC) Mount Taibai was called Mountain of Rich Goods (Pinyin language, pinyin: ''Dun Wu Shān''). During the Xia dynasty, Xia Dynasty (c. 2070–1600 BC) it was known as Mount Tai Yi, referring to the brigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fengxiang County
Fengxiang District (), formerly, Fengxiang County and its ancient name is Yong county (雍县), is a district administered by Baoji City in the west of Shaanxi province, China. The county covers an area of and as of 2004 had a population of 510,000. The Fengxiang's government's seat is in Chengguan Town (). History The city of ''Yōng'' () located in Fengxiang District, was once the capital of the ancient State of Qin during the Zhou Dynasty (1046–256 BCE). As Yong's population expanded over time, the surrounding area became Yong County (). During the Tang Dynasty (618–907 CE), a prefectural seat of government was established and renamed Fengxiang County, although people continued to use the old name. Under the Tang, it also served as Xidu (), the "Western Capital" of the empire.Theobald, Ulrich. ''China Knowledge''.Chinese History - Tang Dynasty 唐 (618-907): Map and Geography. Accessed 19 Oct 2012. Fengxiang was the capital of the Qi Kingdom (907–924). Geography and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daba Mountains
The Daba Mountains, also known by their Chinese name as the Dabashan, are a mountain range in Central China between the watersheds of the Yellow and Yangtze Rivers. Part of the larger Qinling mountain range, it cuts through four provinces: Sichuan, Chongqing, Shaanxi, and Hubei. It is about long. Geography The Daba Mountains run in the general west-northwest to east-southeast direction, along the border between, on the one side (southwest and south) Sichuan and Chongqing, and on the other side (northeast and north) Shaanxi and Hubei. The mountains of Shennongjia are often considered the easternmost section of the Daba Range. The southern slope of the Daba Mountains drains into the Sichuan Basin or directly into the Yangtze via short streams that flow into the river in the Three Gorges area, such as the Shen Nong Stream. The northern side drains into the Han River, a major tributary of the Yangtze, which, however, does not join the Yangtze until some hundreds kilometers to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qin (state)
Qin () was an ancient Chinese state during the Zhou dynasty. Traditionally dated to 897 BC, it took its origin in a reconquest of western lands previously lost to the Rong; its position at the western edge of Chinese civilization permitted expansion and development that was unavailable to its rivals in the North China Plain. Following extensive "Legalist" reform in the fourth century BC, Qin emerged as one of the dominant powers of the Seven Warring States and unified the seven states of China in 221 BC under Qin Shi Huang. It established the Qin dynasty, which was short-lived but greatly influenced later Chinese history. History Founding According to the 2nd century BC historical text ''Records of the Grand Historian'' by Sima Qian, the Qin state traced its origin to Zhuanxu, one of the legendary Five Emperors in ancient times. One of his descendants, Boyi, was granted the family name of Yíng by Emperor Shun. During the Xia and Shang dynasties, the Yíng clan split ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |