|
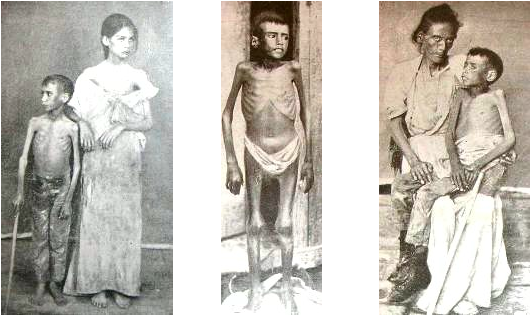
Shark Island Concentration Camp
Shark Island or "Death Island" was one of five concentration camps in German South West Africa. It was located on Shark Island off Lüderitz, in the far south-west of the territory which today is Namibia. It was used by the German Empire during the Herero and Namaqua genocide of 1904–08. Between 1,032 and 3,000 Herero and Namaqua men, women, and children died in the camp between March 1905 and its closing in April 1907. Background On 12 January 1904, the Herero people rebelled against German colonial rule under the leadership of Samuel Maharero. Origins of the Herero revolt date back to the 1890s when tribes settled in Namibia came under pressure from the growing number of German settlers wanting their land, cattle, and labor. Factors such as loss of property, increasing debt in an attempt to resettle lost herds, low wages on white-owned farms, and racial inequalities only intensified the hostility between the Herero and the Germans. When the Herero rebelled, they killed ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concentration Camp
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects". Thus, while it can simply mean imprisonment, it tends to refer to preventive confinement rather than confinement ''after'' having been convicted of some crime. Use of these terms is subject to debate and political sensitivities. The word ''internment'' is also occasionally used to describe a neutral country's practice of detaining belligerent armed forces and equipment on its territory during times of war, under the Hague Convention of 1907. Interned persons may be held in prisons or in facilities known as internment camps (also known as concentration camps). The term ''concentration camp'' originates from the Spanish–Cuban Ten Years' War when Spanish forces detained Cuban civilians in camps in order to more easily combat guerrilla forces. Over the following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internment
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects". Thus, while it can simply mean imprisonment, it tends to refer to preventive confinement rather than confinement ''after'' having been convicted of some crime. Use of these terms is subject to debate and political sensitivities. The word ''internment'' is also occasionally used to describe a neutral country's practice of detaining belligerent armed forces and equipment on its territory during times of war, under the Hague Convention of 1907. Interned persons may be held in prisons or in facilities known as internment camps (also known as concentration camps). The term ''concentration camp'' originates from the Spanish–Cuban Ten Years' War when Spanish forces detained Cuban civilians in camps in order to more easily combat guerrilla forces. Over the followin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugen Fischer
Eugen Fischer (5 July 1874 – 9 July 1967) was a German professor of medicine, anthropology, and eugenics, and a member of the Nazi Party. He served as director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute of Anthropology, Human Heredity, and Eugenics, and also served as rector of the Frederick William University of Berlin. Fischer's ideas informed the Nuremberg Laws of 1935 which served to justify the Nazi Party's belief in German racial superiority to other "races", and especially the Jews. Adolf Hitler read Fischer's work while he was imprisoned in 1923 and he used Fischer's eugenic notions in support of a pure Aryan society in his manifesto, ''Mein Kampf'' (''My Struggle''). Fischer was born in Karlsruhe, Grand Duchy of Baden, in 1874. He studied medicine, folkloristics, history, anatomy, and anthropology in Berlin, Freiburg and Munich. In 1918, he joined the Anatomical Institute in Freiburg, part of the University of Freiburg. In 1927, Fischer became the director of the Kaiser Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scurvy
Scurvy is a disease resulting from a lack of vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Early symptoms of deficiency include weakness, feeling tired and sore arms and legs. Without treatment, decreased red blood cells, gum disease, changes to hair, and bleeding from the skin may occur. As scurvy worsens there can be poor wound healing, personality changes, and finally death from infection or bleeding. It takes at least a month of little to no vitamin C in the diet before symptoms occur. In modern times, scurvy occurs most commonly in people with mental disorders, unusual eating habits, alcoholism, and older people who live alone. Other risk factors include intestinal malabsorption and dialysis. While many animals produce their own vitamin C, humans and a few others do not. Vitamin C is required to make the building blocks for collagen. Diagnosis is typically based on physical signs, X-rays, and improvement after treatment. Treatment is with vitamin C supplements taken by mouth. Improvemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Witbooi
Witbooi is an Afrikaans and Khoekhoe surname, common in Namibia and South Africa. Notable people with the surname include: * Hendrik Witbooi, Namaqua leader *Hendrik Samuel Witbooi, Oorlam Kaptein *Hendrik Witbooi (politician), former deputy prime minister of Namibia *Andile Witbooi, South African rugby player *Lucia Witbooi Lucia Witbooi (born 1961 in Gabes, Namibia, Gabes, ǁKaras Region) is a Namibian politician. A member of SWAPO, Witbooi was elected to the National Assembly of Namibia, Namibia's National Assembly in the 2009 Namibian general election, 2009 general ..., Namibian politician * Ryan Witbooi, Namibian rugby player {{surname Afrikaans-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schutztruppe Of German South West Africa
The Imperial Schutztruppe for German South west Africa (german: Kaiserliche Schutztruppe für Deutsch-Südwestafrika) was the official name of the military formation that maintained the German Empire in its colony of German South West Africa. The Schutztruppe are held responsible for numerous atrocities in the Herero and Nama uprising in 1904. During the First World War, the Schutztruppe was defeated by the troops of the Union of South Africa. Formation acquired the bay of Angra Pequena and five miles of hinterland for the Bremen tobacconist Adolf Lüderitz on 1 May 1883 from the Nama people in Bethanie. On April 24, 1884 Bismarck telegraphed the German consul in Cape Town that " is under the protection of the German Empire". Between October 1888 and July 1889, in the course of a dispute between the Witbooi and the Herero, there had been an expulsion of the German Commissariat and an interruption of German sovereignty in Okahandja. The German Colonial Society engaged ''Hauptm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Von Estorff
Ludwig Gustav Adolf von Estorff (25 December 1859 – 5 October 1943) was a German military officer who notably served as a Schutztruppe commander in Africa; and later as an Imperial German Army general in World War I. He also was a recipient of the Pour le Merite, Germany's highest military award. Early life and career Ludwig was the second child of later Generalmajor Eggert Ludwig von Estorff (1831–1903) and his wife Julie Bernhardine, née von Witzendorff (1836–1902). In 1878, after being a cadet in Berlin, Estorff was commissioned into the Prussian Army as a Lieutenant in the 31st (1st Thuringian) Infantry Regiment. In 1894, by now a Hauptmann, he left the army in order to join the Schutztruppe of German South West Africa. There he'd quickly see service in the First Witbooi Rebellion. After five years he briefly returned to Germany, then resumed service on various stations on the African continent. Herero Wars He resigned in 1903 but rejoined the Schutztruppe in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swakopmund
Swakopmund (german: Mouth of the Swakop) is a city on the coast of western Namibia, west of the Namibian capital Windhoek via the B2 main road. It is the capital of the Erongo administrative district. The town has 44,725 inhabitants and covers of land. The city is situated in the Namib Desert and is the fourth largest population centre in Namibia. Swakopmund is a beach resort and an example of German colonial architecture. It was founded in 1892 as the main harbour for German South West Africa. Buildings in the city include the '' Altes Gefängnis'', a prison designed by Heinrich Bause in 1909. The ''Woermannhaus'', built in 1906 with a prominent tower (Damara tower), is now a public library. Attractions in Swakopmund include a Swakopmund Museum, the National Marine Aquarium, a crystal gallery, and spectacular sand dunes near Langstrand south of the Swakop River. Outside the city, the Rossmund Desert Golf Course is one of only five all-grass desert golf courses in the world. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windhoek
Windhoek (, , ) is the capital and largest city of Namibia. It is located in central Namibia in the Khomas Highland plateau area, at around above sea level, almost exactly at the country's geographical centre. The population of Windhoek in 2020 was 431,000 which is growing continually due to an influx from all over Namibia. Windhoek is the social, economic, political, and cultural centre of the country. Nearly every Namibian national enterprise, governmental body, educational and cultural institution is headquartered there. The city developed at the site of a permanent hot spring known to the indigenous pastoral communities. It developed rapidly after Jonker Afrikaner, Captain of the Orlam, settled there in 1840 and built a stone church for his community. In the decades following, multiple wars and armed hostilities resulted in the neglect and destruction of the new settlement. Windhoek was founded a second time in 1890 by Imperial German Army Major Curt von François, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genocidal Rape
Genocidal rape, a form of wartime sexual violence, is the action of a group which has carried out acts of mass rape and gang rapes, against its enemy during wartime as part of a genocide, genocidal campaign. During the Armenian genocide, Armenian Genocide, the Nanjing massacre, second Sino-Japanese war, the Holocaust, the Bangladesh Liberation War, the Bosnian War, the Rwandan genocide, the Sexual violence in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Congolese conflicts, the Genocide of Yazidis by ISIL, Iraqi Civil War, the South Sudanese Civil War, the Rohingya genocide, the mass rapes that had been an integral part of those conflicts brought the concept of genocidal rape to international prominence. Although Wartime sexual violence, war rape has been a recurrent feature in conflicts throughout human history, it has usually been looked upon as a by-product of conflict and not an integral part of military policy. Genocide debate Some scholars argue that the Genocide Convention, Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sjambok
The sjambok () or litupa is a heavy leather whip. It is traditionally made from an adult hippopotamus or rhinoceros hide, but is also commonly made out of plastic. A strip of the animal's hide is cut and carved into a strip long, tapering from about thick at the handle to about at the tip. This strip is then rolled until reaching a tapered-cylindrical form. The resulting whip is both flexible and durable. A plastic version was made for the apartheid era South African Police, and used for riot control. Peter Hathaway Capstick describes a sjambok as a short swordlike whip made from rhino pizzle leather that could lay a man open like a straight razor. The sjambok was heavily used by the Voortrekkers driving their oxen while migrating from the Cape of Good Hope, and remains in use by herdsmen to drive cattle. They are widely available in South Africa from informal traders to regular stores from a variety of materials, lengths and thicknesses. Use by police In South Africa, us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Argus
The ''Cape Argus'' is a daily newspaper co-founded in 1857 by Saul Solomon and published by Sekunjalo in Cape Town, South Africa. It is commonly referred to as ''The Argus''. Although not the first English-language newspaper in South Africa, the ''Cape Argus'' was the first locally to use the telegraph for news gathering. As of 2012, the ''Argus'' had a daily readership of 294 000, according to the South African Advertising Research Foundation's All Media Products Survey (Amps) Newspaper Readership and Trends. Its circulation for the first quarter of 2013 was 33 247. Jermaine Craig is the executive editor of the ''Cape Argus''. He replaced Gasant Abarder, who resigned in early 2013 to take up a post at Primedia in the Western Cape. History The ''Cape Argus'' was founded on 3 January 1857, by the partners Saul Solomon, journalist Richard William Murray ("Limner") and the MP Bryan Henry Darnell. However, political differences immediately surfaced between the partners. Sau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |