Internment on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in
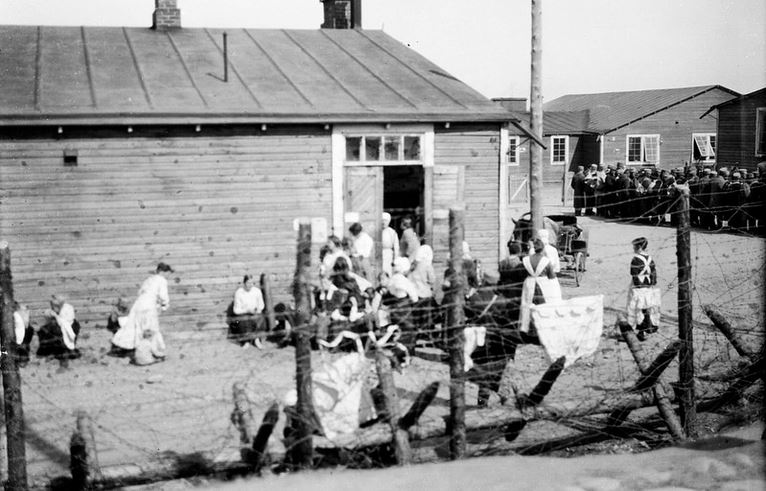
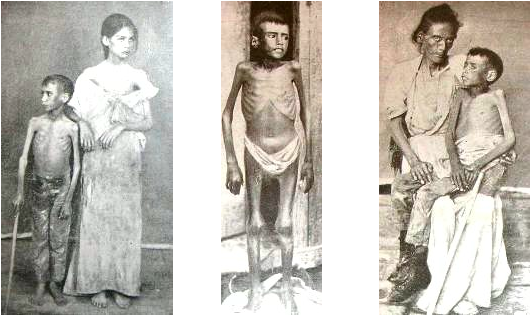


 The ''
The ''
 Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
time or of terrorism
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violen ...
suspects". Thus, while it can simply mean imprisonment, it tends to refer to preventive confinement rather than confinement ''after'' having been convicted of some crime. Use of these terms is subject to debate and political sensitivities. The word ''internment'' is also occasionally used to describe a neutral country's practice of detaining belligerent armed forces and equipment on its territory during times of war, under the Hague Convention of 1907
The Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907 are a series of international treaties and declarations negotiated at two international peace conferences at The Hague in the Netherlands. Along with the Geneva Conventions, the Hague Conventions were amo ...
.
Interned persons may be held in prison
A prison, also known as a jail, gaol (dated, standard English, Australian, and historically in Canada), penitentiary (American English and Canadian English), detention center (or detention centre outside the US), correction center, corre ...
s or in facilities known as internment camps (also known as concentration camps). The term ''concentration camp'' originates from the Spanish–Cuban Ten Years' War
The Ten Years' War ( es, Guerra de los Diez Años; 1868–1878), also known as the Great War () and the War of '68, was part of Cuba's fight for independence from Spain. The uprising was led by Cuban-born planters and other wealthy natives. O ...
when Spanish forces detained Cuban civilians in camps in order to more easily combat guerrilla forces. Over the following decades the British during the Second Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the South ...
and the Americans during the Philippine–American War also used concentration camps.
The term "concentration camp" or "internment camp" is used to refer to a variety of systems that greatly differ in their severity, mortality rate, and architecture; their defining characteristic is that inmates are held outside the rule of law. Extermination camp
Nazi Germany used six extermination camps (german: Vernichtungslager), also called death camps (), or killing centers (), in Central Europe during World War II to systematically murder over 2.7 million peoplemostly Jewsin the Holocaust. The v ...
s or death camps, whose primary purpose is killing, are also imprecisely referred to as "concentration camps".
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is an international document adopted by the United Nations General Assembly that enshrines the rights and freedoms of all human beings. Drafted by a UN committee chaired by Eleanor Roosevelt, ...
restricts the use of internment, with Article 9 stating, "No one shall be subjected to arbitrary arrest
Arbitrary arrest and arbitrary detention are the arrest or detention of an individual in a case in which there is no likelihood or evidence that they committed a crime against legal statute, or in which there has been no proper due process of ...
, detention or exile."
Defining internment and concentration camp



 The ''
The ''American Heritage Dictionary
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, p ...
'' defines the term ''concentration camp'' as: "A camp where persons are confined, usually without hearings and typically under harsh conditions, often as a result of their membership in a group which the government has identified as dangerous or undesirable."
Although the first example of civilian internment may date as far back as the 1830s, the English term ''concentration camp'' was first used in order to refer to the reconcentration camps (Spanish:''reconcentrados'') which were set up by the Spanish military
The Spanish Armed Forces are in charge of guaranteeing the sovereignty and independence of the Kingdom of Spain, defending its territorial integrity and the constitutional order, according to the functions entrusted to them by the Constitution o ...
in Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
during the Ten Years' War
The Ten Years' War ( es, Guerra de los Diez Años; 1868–1878), also known as the Great War () and the War of '68, was part of Cuba's fight for independence from Spain. The uprising was led by Cuban-born planters and other wealthy natives. O ...
(1868–1878). The label was applied yet again to camps set up by the United States during the Philippine–American War (1899–1902). And expanded usage of the ''concentration camp'' label continued, when the British set up camps during the Second Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the South ...
(1899–1902) in South Africa for interning Boer
Boers ( ; af, Boere ()) are the descendants of the Dutch-speaking Free Burghers of the eastern Cape frontier in Southern Africa during the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries. From 1652 to 1795, the Dutch East India Company controlled this are ...
s during the same time period.
During the 20th century, the arbitrary internment of civilians by the state reached its most extreme forms in the Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
Gulag system of concentration camps (1918–1991) and the Nazi concentration camps
From 1933 to 1945, Nazi Germany operated more than a thousand concentration camps, (officially) or (more commonly). The Nazi concentration camps are distinguished from other types of Nazi camps such as forced-labor camps, as well as con ...
(1933–1945). The Soviet system was the first applied by a government on its own citizens. The Gulag consisted in over 30,000 camps for most of its existence (1918–1991) and detained some 18 million from 1929 until 1953, which is only a third of its 73-year lifespan. The Nazi concentration camp system was extensive, with as many as 15,000 camps and . In this online site are the names of 149 camps and 814 subcamps, organized by country. and at least 715,000 simultaneous internees. The total number of casualties in these camps is difficult to determine, but the deliberate policy of extermination through labor
Extermination through labour (or "extermination through work", german: Vernichtung durch Arbeit) is a term that was adopted to describe forced labor in Nazi concentration camps in light of the high mortality rate and poor conditions; in some ...
in many of the camps was designed to ensure that the inmates would die of starvation, untreated disease and summary executions within set periods of time. Moreover, Nazi Germany established six extermination camp
Nazi Germany used six extermination camps (german: Vernichtungslager), also called death camps (), or killing centers (), in Central Europe during World War II to systematically murder over 2.7 million peoplemostly Jewsin the Holocaust. The v ...
s, specifically designed to kill millions of people, primarily by gassing.
As a result, the term "concentration camp" is sometimes conflated with the concept of an "extermination camp
Nazi Germany used six extermination camps (german: Vernichtungslager), also called death camps (), or killing centers (), in Central Europe during World War II to systematically murder over 2.7 million peoplemostly Jewsin the Holocaust. The v ...
" and historians debate whether the term "concentration camp" or the term "internment camp" should be used to describe other examples of civilian internment.
The former label continues to see expanded use for cases post-World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, for instance in relation to British camps in Kenya during the Mau Mau rebellion
The Mau Mau rebellion (1952–1960), also known as the Mau Mau uprising, Mau Mau revolt or Kenya Emergency, was a war in the British Kenya Colony (1920–1963) between the Kenya Land and Freedom Army (KLFA), also known as the ''Mau Mau'', ...
(1952–1960), and camps set up in Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
during the military dictatorship of Augusto Pinochet
Augusto José Ramón Pinochet Ugarte (, , , ; 25 November 1915 – 10 December 2006) was a Chilean general who ruled Chile from 1973 to 1990, first as the leader of the Military Junta of Chile from 1973 to 1981, being declared President of ...
(1973–1990). According to the United States Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD or DOD) is an executive branch department of the federal government charged with coordinating and supervising all agencies and functions of the government directly related to national sec ...
as many as 3 million Uyghurs
The Uyghurs; ; ; ; zh, s=, t=, p=Wéiwú'ěr, IPA: ( ), alternatively spelled Uighurs, Uygurs or Uigurs, are a Turkic ethnic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the general region of Central and East Asia. The Uyghur ...
and members of other Muslim minority groups are being held in China's re-education camps which are located in the Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
region and which American news reports often label as ''concentration camps''. The camps were established in late 2010s under General Secretary Xi Jinping
Xi Jinping ( ; ; ; born 15 June 1953) is a Chinese politician who has served as the general secretary of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and chairman of the Central Military Commission (CMC), and thus as the paramount leader of China, ...
's administration
Administration may refer to:
Management of organizations
* Management, the act of directing people towards accomplishing a goal
** Administrative Assistant, traditionally known as a Secretary, or also known as an administrative officer, admini ...
.
Examples
Active
* North Korean prison camps (1948–present) * Guantanamo Bay detention camp (2002–present) * Refugee detention centres in Libya (2011–present) * Uyghur re-education camps in China (2017–present) * Anti-gay detention camps in Chechnya (2017–present) *Trump administration migrant detentions
The Trump administration has Immigration detention in the United States, detained migrants attempting to enter the United States at the United States–Mexico border. Government reports from the Department of Homeland Security Office of Inspect ...
as part of immigration detention in the United States
The United States government holds tens of thousands of immigrants in detention under the control of Customs and Border Protection (CBP; principally the Border Patrol) and the Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE). Immigrants are detained for ...
(2018–present)
Closed
*American Civil War prison camps
Between 1861 and 1865, American Civil War prison camps were operated by the Union and the Confederacy to detain over 400,000 captured soldiers. From the start of the Civil War through to 1863 a parole exchange system saw most prisoners of war s ...
(1861–1865)
* Second Boer War in South Africa (1900–1902)
*Herero and Namaqua genocide
The Herero and Namaqua genocide or the Herero and Nama genocide was a campaign of ethnic extermination and collective punishment waged by the German Empire against the Herero (Ovaherero) and the Nama in German South West Africa (now Namibia). I ...
(1904–1907)
* Concentration of Armenians during the Armenian Genocide (1915–1916)
*Finnish Civil War
The Finnish Civil War; . Other designations: Brethren War, Citizen War, Class War, Freedom War, Red Rebellion and Revolution, . According to 1,005 interviews done by the newspaper ''Aamulehti'', the most popular names were as follows: Civil W ...
(1918)
* Italian concentration camps in Africa and Europe (1930–1944)
* German concentration camps before and during World War II (1933–1945)
* Japanese internment of prisoners of war and civilians during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
(ended 1945)
* Japanese-American internment camps in World War II (1942–1946)
*Japanese Canadian internment
From 1942 to 1949, Canada forcibly relocated and incarcerated over 22,000 Japanese Canadians—comprising over 90% of the total Japanese Canadian population—from British Columbia in the name of " national security". The majority were Canadi ...
(1942–1949)
*Cyprus internment camps
The Cyprus internment camps were camps maintained in Cyprus by the British government for the internment of Jews who had immigrated or attempted to immigrate to Mandatory Palestine, which was in violation of British policy. There were a total of ...
(1946–1949)
*Malayan New villages as part of the Briggs Plan
The Briggs Plan ( ms, Rancangan Briggs) was a military plan devised by British General Sir Harold Briggs shortly after his appointment in 1950 as Director of Operations during the Malayan Emergency (1948–1960). The plan aimed to defeat the Ma ...
during the Malayan Emergency (1950–1960)
*Deoli interment camp in India
IN, In or in may refer to:
Places
* India (country code IN)
* Indiana, United States (postal code IN)
* Ingolstadt, Germany (license plate code IN)
* In, Russia, a town in the Jewish Autonomous Oblast
Businesses and organizations
* Indepen ...
(1962-1967)
*Operation Demetrius
Operation Demetrius was a British Army operation in Northern Ireland on 9–10 August 1971, during the Troubles. It involved the mass arrest and internment (imprisonment without trial) of people suspected of being involved with the Irish Republi ...
in Northern Ireland (1971)
* Omarska camp in Bosnia, 1992
*Dretelj camp
The Dretelj camp or Dretelj prison was a prison camp run by the Croatian Defence Forces (HOS) and later by the Croatian Defence Council (HVO) during the Bosnian War.
The camp
The camp was located near Čapljina and Medjugorje in southern Bosnia ...
(1992–1995)
*Camp Bucca
Camp Bucca ( ar, سجن بوكا, Sijn Būkā) was a forward operating base that housed a theater internment facility maintained by the United States military in the vicinity of Umm Qasr, Iraq. After being taken over by the U.S. military (800th ...
in Iraq (2003–2009)
* Abu Ghraib prison in Iraq (1980–2014)
See also
*Civilian internee
A civilian internee is a civilian detained by a party to a war for security reasons. Internees are usually forced to reside in internment camps. Historical examples include Japanese American internment and internment of German Americans in the Un ...
*Extermination through labor
Extermination through labour (or "extermination through work", german: Vernichtung durch Arbeit) is a term that was adopted to describe forced labor in Nazi concentration camps in light of the high mortality rate and poor conditions; in some ...
*Extrajudicial detention
Administrative detention is arrest and detention of individuals by the state without trial. A number of jurisdictions claim that it is done for security reasons. Many countries claim to use administrative detention as a means to combat terrorism ...
*Gulag
The Gulag, an acronym for , , "chief administration of the camps". The original name given to the system of camps controlled by the GPU was the Main Administration of Corrective Labor Camps (, )., name=, group= was the government agency in ...
* New village
*Bantustan
A Bantustan (also known as Bantu homeland, black homeland, black state or simply homeland; ) was a territory that the National Party administration of South Africa set aside for black inhabitants of South Africa and South West Africa (now ...
* House arrest
* Labor camp
*Kwalliso
North Korea's political penal labor colonies, transliterated ''kwalliso'' or ''kwan-ri-so'', constitute one of three forms of political imprisonment in the country, the other two being what David Hawk translated as "short-term detention/for ...
(North Korean political penal labour colonies)
*Laogai
''Laogai'' (), short for ''laodong gaizao'' (), which means reform through labor, is a criminal justice system involving the use of penal labor and prison farms in the People's Republic of China (PRC) and North Korea (DPRK). ''Láogǎi'' i ...
(Chinese, "reform through labor")
*Military Units to Aid Production
Military Units to Aid Production or UMAPs (Unidades Militares de Ayuda a la Producción) were agricultural forced labor camps operated by the Cuban government from November 1965 to July 1968 in the province of Camagüey.Guerra, Lillian. ""Gender ...
* "Polish death camp" controversy
* Prison overcrowding
*Prisoner-of-war camp
A prisoner-of-war camp (often abbreviated as POW camp) is a site for the containment of enemy fighters captured by a belligerent power in time of war.
There are significant differences among POW camps, internment camps, and military prisons. ...
* Prisons in North Korea
*Quasi-criminal Quasi-criminal means a lawsuit or equity proceeding that has some, but not all, of the qualities of a criminal prosecution. It may appear in either a common law or a civil law jurisdiction. It refers to "a court's right to punish for actions or o ...
*
*Re-education camp (Vietnam)
Re-education camps ( vi, Trại cải tạo) were prison camps operated by the Communist government of Vietnam
The Government of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (), also known as the Vietnamese Government or the Government of Vietnam (), ...
*Re-education through labor
Re-education through labor (RTL; ), abbreviated ''laojiao'' () was a system of administrative detention on Mainland China. Active from 1957 to 2013, the system was used to detain persons who were accused of committing minor crimes such as pet ...
*Remand (detention)
Remand, also known as pre-trial detention, preventive detention, or provisional detention, is the process of detaining a person until their trial after they have been arrested and charged with an offence. A person who is on remand is held i ...
References
Further reading
* * * * Exhaustive history of the internment camps. Also available in German ()External links
* {{Authority control Total institutions