|
Shamosuchus
''Shamosuchus'' is an extinct genus of neosuchian crocodyliform that lived during the Late Cretaceous (Campanian) period in what is now the Djadokhta Formation of Mongolia, approximately 75 million to 71 million years ago. Paleobiology The eye and nasal openings were not raised above the skull as in modern crocodilians, so that the animal would have to raise its head completely out of the water to breathe. As this cranial morphology does not suit an ambush predator, it lends support to the idea of a diet of aquatic invertebrates. The teeth were adapted to crush bivalves, gastropods and other animals with a shell or exoskeleton. The genus was named in 1924 by Charles C. Mook. ''Shamosuchus'' reached up to in length. ''Paralligator'' was synonymized with ''Shamosuchus'' by several authors. However, recent cladistic analysis of Paralligatoridae Paralligatoridae is an extinct family of neosuchian crocodyliforms that existed during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. It inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shamosuchus
''Shamosuchus'' is an extinct genus of neosuchian crocodyliform that lived during the Late Cretaceous (Campanian) period in what is now the Djadokhta Formation of Mongolia, approximately 75 million to 71 million years ago. Paleobiology The eye and nasal openings were not raised above the skull as in modern crocodilians, so that the animal would have to raise its head completely out of the water to breathe. As this cranial morphology does not suit an ambush predator, it lends support to the idea of a diet of aquatic invertebrates. The teeth were adapted to crush bivalves, gastropods and other animals with a shell or exoskeleton. The genus was named in 1924 by Charles C. Mook. ''Shamosuchus'' reached up to in length. ''Paralligator'' was synonymized with ''Shamosuchus'' by several authors. However, recent cladistic analysis of Paralligatoridae Paralligatoridae is an extinct family of neosuchian crocodyliforms that existed during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. It inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paralligator
''Paralligator'' is an extinct genus of neosuchian crocodylomorph that lived during the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian-Maastrichtian) period in what is now the Bayan Shireh and Nemegt formations of Mongolia, approximately 96 million to 70 million years ago. Taxonomy Three species are recognized: Misassigned species ''"Paralligator" sungaricus'', described from the Early Cretaceous Nenjiang Formation of Jilin Province, China, is based on postcranial remains consisting of a few presacral vertebrae, dorsal osteoderms, a partial left femur, and the proximal part of a left tibia and fibula. However, the type material is too fragmentary to be considered diagnostic, and the species is a ''nomen dubium In binomial nomenclature, a ''nomen dubium'' (Latin for "doubtful name", plural ''nomina dubia'') is a scientific name that is of unknown or doubtful application. Zoology In case of a ''nomen dubium'' it may be impossible to determine whether a s ...''. References Late Cretaceous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
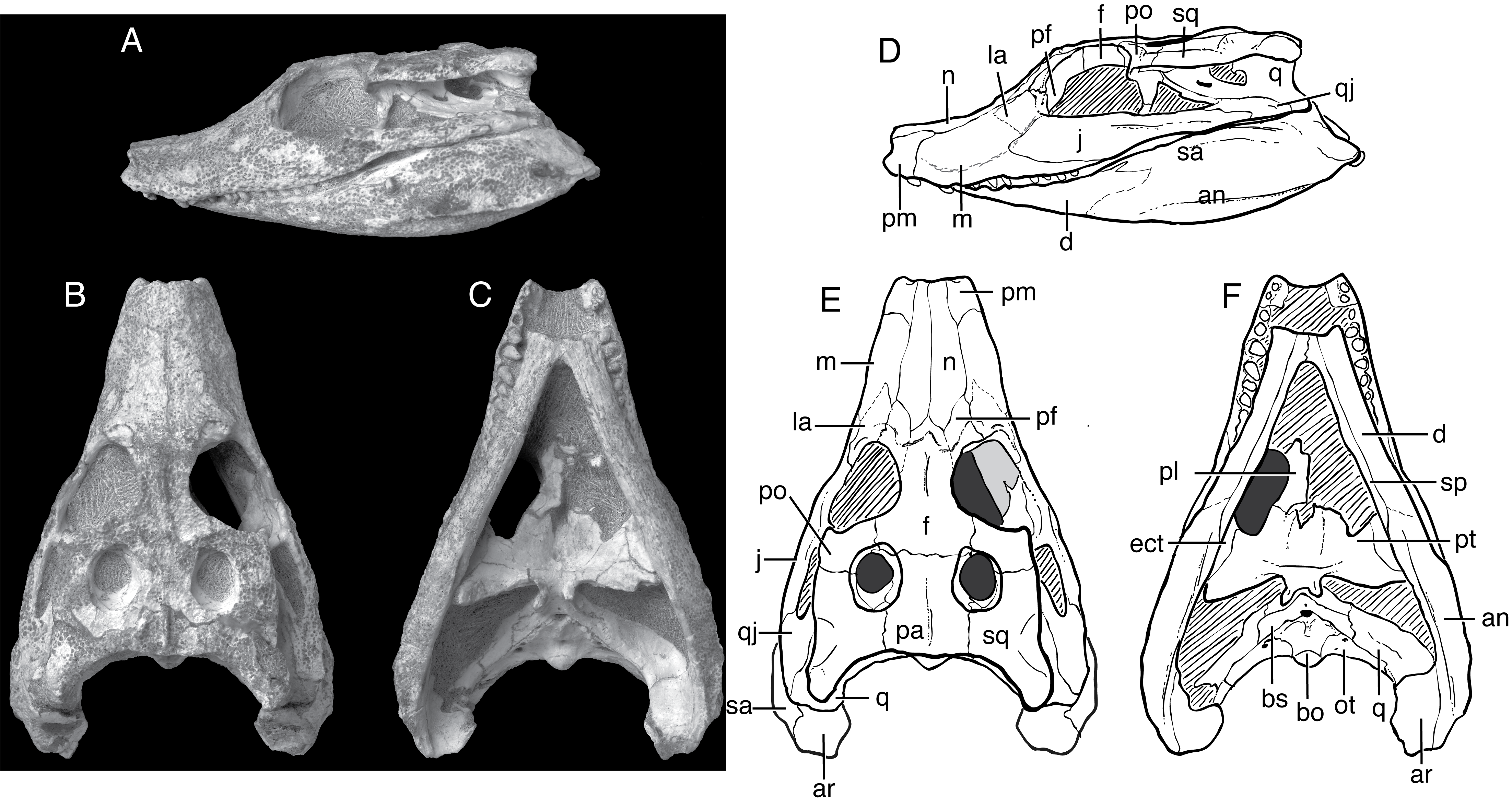
Paralligatoridae
Paralligatoridae is an extinct family of neosuchian crocodyliforms that existed during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. It includes the genera ''Paralligator'', '' Brillanceausuchus'', '' Kansajsuchus'', ''Shamosuchus'', ''Scolomastax'', ''Sabresuchus'', '' Rugosuchus'', '' Batrachomimus'' and '' Wannchampsus'', as well as the yet-unnamed "Glen Rose form". Evolution Phylogenetic analyses of crocodyliforms find Paralligatoridae to nest within Neosuchia, a large clade (evolutionary grouping) that also includes modern crocodylians. In crocodyliform phylogeny, paralligatorids are usually found near the base of Neosuchia, outside the clade Eusuchia, which includes crocodylians and their closest relatives. Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to d ... from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djadokhta Formation
The Djadochta Formation (sometimes transcribed and also known as Djadokhta, Djadokata, or Dzhadokhtskaya) is a highly fossiliferous geological formation situated in Central Asia, Gobi Desert, dating from the Late Cretaceous period, about 75 million to 71 million years ago. The type locality is the Bayn Dzak locality, famously known as the Flaming Cliffs. Dinosaur, mammal, and other reptile remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation. Excavation history The Djadochta Formation was first documented and explored—though only a single locality—during paleontological expeditions of the American Museum of Natural History in 1922–1925, which were part of the Central Asiatic Expeditions. The expeditions were led by Roy Chapman Andrews, in company of Walter Willis Granger as chief paleontologist and field team. The team did extensive exploration at the Bayn Dzak (formerly Shabarakh Usu) region, which they nicknamed Flaming Cliffs given that at sunset th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neosuchia
Neosuchia is a clade within Mesoeucrocodylia that includes all modern extant crocodilians and their closest fossil relatives. It is defined as the most inclusive clade containing all crocodylomorphs more closely related to ''Crocodylus niloticus'' (the Nile Crocodile) than to ''Notosuchus terrestris''. Members of Neosuchia generally share a crocodilian-like bodyform adapted to freshwater aquatic life, as opposed to the terrestrial habits of more basal crocodylomorph groups. The earliest neosuchian is suggested to be the Early Jurassic ''Calsoyasuchus'', which lived during the Sinemurian and Pliensbachian stages in North America. It is often identified as a member of Goniopholididae, though this is disputed, and the taxon may lie outside Neosuchia, which places the earliest records of the group in the Middle Jurassic. Characteristics A tooth notch between the maxilla and premaxilla is a basal characteristic of the Neosuchia, although it is lost in some more derived forms, most nota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the host) and parasitoidism (which always does, eventually). It is distinct from scavenging on dead prey, though many predators also scavenge; it overlaps with herbivory, as seed predators and destructive frugivores are predators. Predators may actively search for or pursue prey or wait for it, often concealed. When prey is detected, the predator assesses whether to attack it. This may involve ambush or pursuit predation, sometimes after stalking the prey. If the attack is successful, the predator kills the prey, removes any inedible parts like the shell or spines, and eats it. Predators are adapted and often highly specialized for hunting, with acute senses such as vision, hearing, or smell. Many predatory animals, both vertebrate and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous Crocodylomorphs Of Asia
Late may refer to: * LATE, an acronym which could stand for: ** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia ** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law ** Local average treatment effect, a concept in econometrics Music * ''Late'' (album), a 2000 album by The 77s * Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Grohl on his ''Pocketwatch'' album * Late (rapper), an underground rapper from Wolverhampton * "Late" (song), a song by Blue Angel * "Late", a song by Kanye West from ''Late Registration'' Other * Late (Tonga), an uninhabited volcanic island southwest of Vavau in the kingdom of Tonga * "Late" (''The Handmaid's Tale''), a television episode * LaTe, Oy Laivateollisuus Ab, a defunct shipbuilding company * Late may refer to a person who is Dead See also * * * ''Lates'', a genus of fish in the lates perch family * Later (other) * Tardiness * Tardiness (scheduling) In scheduling, tardiness is a measure of a delay in exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym (taxonomy)
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank - for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exoskeleton
An exoskeleton (from Greek ''éxō'' "outer" and ''skeletós'' "skeleton") is an external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to an internal skeleton (endoskeleton) in for example, a human. In usage, some of the larger kinds of exoskeletons are known as " shells". Examples of exoskeletons within animals include the arthropod exoskeleton shared by chelicerates, myriapods, crustaceans, and insects, as well as the shell of certain sponges and the mollusc shell shared by snails, clams, tusk shells, chitons and nautilus. Some animals, such as the turtle, have both an endoskeleton and an exoskeleton. Role Exoskeletons contain rigid and resistant components that fulfill a set of functional roles in many animals including protection, excretion, sensing, support, feeding and acting as a barrier against desiccation in terrestrial organisms. Exoskeletons have a role in defense from pests and predators, support and in providing an attachment framework f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastropod
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda (). This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. There are many thousands of species of sea snails and slugs, as well as freshwater snails, freshwater limpets, and land snails and slugs. The class Gastropoda contains a vast total of named species, second only to the insects in overall number. The fossil history of this class goes back to the Late Cambrian. , 721 families of gastropods are known, of which 245 are extinct and appear only in the fossil record, while 476 are currently extant with or without a fossil record. Gastropoda (previously known as univalves and sometimes spelled "Gasteropoda") are a major part of the phylum Mollusca, and are the most highly diversified class in the phylum, with 65,000 to 80,000 living snail and slug species. The anatomy, behavior, feeding, and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bivalve
Bivalvia (), in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. As a group, bivalves have no head and they lack some usual molluscan organs, like the radula and the odontophore. They include the clams, oysters, cockles, mussels, scallops, and numerous other families that live in saltwater, as well as a number of families that live in freshwater. The majority are filter feeders. The gills have evolved into ctenidia, specialised organs for feeding and breathing. Most bivalves bury themselves in sediment, where they are relatively safe from predation. Others lie on the sea floor or attach themselves to rocks or other hard surfaces. Some bivalves, such as the scallops and file shells, can swim. The shipworms bore into wood, clay, or stone and live inside these substances. The shell of a bivalve is composed of calc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_with_its_prey.jpg)

