Shamosuchus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Shamosuchus'' is an
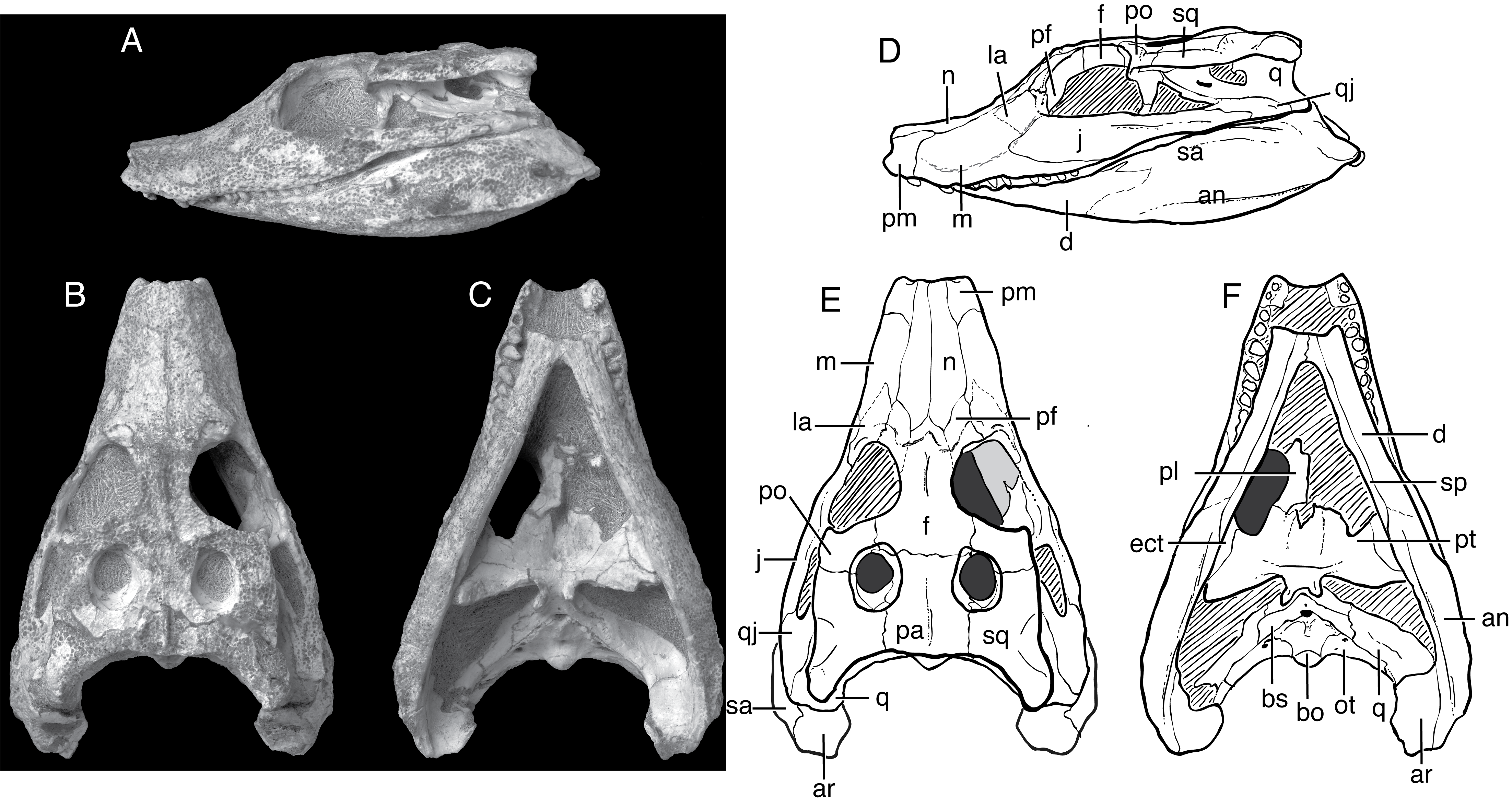 The eye and nasal openings were not raised above the skull as in modern
The eye and nasal openings were not raised above the skull as in modern
CRETÁCEO répteis e anfíbios
Late Cretaceous crocodylomorphs of Asia Neosuchians Prehistoric pseudosuchian genera Fossil taxa described in 1924 {{paleo-archosaur-stub
extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
of neosuchian crocodyliform
Crocodyliformes is a clade of crurotarsan archosaurs, the group often traditionally referred to as "crocodilians". They are the first members of Crocodylomorpha to possess many of the features that define later relatives. They are the only pseudo ...
that lived during the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ...
( Campanian) period in what is now the Djadokhta Formation of Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
, approximately 75 million to 71 million years ago.
Paleobiology
 The eye and nasal openings were not raised above the skull as in modern
The eye and nasal openings were not raised above the skull as in modern crocodilian
Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period ( Cenomanian stage) and are the closest living ...
s, so that the animal would have to raise its head completely out of the water to breathe. As this cranial morphology does not suit an ambush predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill th ...
, it lends support to the idea of a diet of aquatic invertebrates. The teeth were adapted to crush bivalve
Bivalvia (), in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. As a group, bival ...
s, gastropod
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda ().
This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. T ...
s and other animals with a shell or exoskeleton
An exoskeleton (from Greek ''éxō'' "outer" and ''skeletós'' "skeleton") is an external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to an internal skeleton (endoskeleton) in for example, a human. In usage, some of the ...
. The genus was named in 1924 by Charles C. Mook. ''Shamosuchus'' reached up to in length.
'' Paralligator'' was synonymized with ''Shamosuchus'' by several authors. However, recent cladistic analysis of Paralligatoridae found ''Paralligator'' distinct from ''Shamosuchus''.
References
External links
CRETÁCEO répteis e anfíbios
Late Cretaceous crocodylomorphs of Asia Neosuchians Prehistoric pseudosuchian genera Fossil taxa described in 1924 {{paleo-archosaur-stub