|
Serengeti-Dorobo Language
Serengeti-Dorobo (a nonce name) is an obscure " Dorobo" language, a few words of which were recorded in the late 19th century by Oscar Baumann. From the little data available, the language is not obviously related to any other, though the numeral system is Nilotic. It is not the only "Dorobo" language formerly spoken in the Serengeti. Vocabulary A few paragraphs were recorded by Baumann (1894, p. 366), but without any word-by-word translations. Numerals are as follows. Most resemble those of neighboring Nilotic languages The Nilotic languages are a group of related languages spoken across a wide area between South Sudan and Tanzania by the Nilotic peoples. Etymology The word Nilotic means of or relating to the Nile River or to the Nile region of Africa. Dem .... :1 ''napu'' (''kinavéta napó'' 'one cattle') f. Maasai fem. ''nabo'':2 ''ennya'' f. Datooga ''iyeny'', Omotik ''ainia'':3 ''uni'' f. Maasai fem. ''uni'':4 ''ongwan'' f. Maasai fem. ''ongwan'', Datooga, Oki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands and the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to the south; Zambia to the southwest; and Rwanda, Burundi, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west. Mount Kilimanjaro, Africa's highest mountain, is in northeastern Tanzania. According to the United Nations, Tanzania has a population of million, making it the most populous country located entirely south of the equator. Many important hominid fossils have been found in Tanzania, such as 6-million-year-old Pliocene hominid fossils. The genus Australopithecus ranged across Africa between 4 and 2 million years ago, and the oldest remains of the genus ''Homo'' are found near Lake Olduvai. Following the rise of '' Homo erectus'' 1.8 million years ago, humanity spread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorobo Peoples
Dorobo (or ''Ndorobo'', ''Wadorobo'', ''dorobo'', ''Torobo'') is a derogatory umbrella term for several unrelated hunter-gatherer groups of Kenya and Tanzania. They comprised client groups to the Maasai and did not practice cattle pastoralism. Etymology The term 'Dorobo' derives from the Maa expression ''il-tóróbò'' (singular ''ol-torróbònì'') 'hunters; the ones without cattle'. Living from hunting wild animals implies being primitive, and being without cattle implies being very poor in the pastoralist Maa culture. Classifications In the past it has been assumed that all Dorobo were of Southern Nilotic origin; accordingly, the term ''Dorobo'' was thought to denote several closely related ethnic groups. Groups that have been referred to as Dorobo include: *Kaplelach Okiek and Kipchornwonek Okiek (Nilotic; Rift Valley Province, Kenya) *Sengwer *Mukogodo-Maasai (the former Yaaku, sometimes Aramanik) (Yaaku language; Laikipia District, Rift Valley Province, Kenya) *Aasax (Aas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nilotic Languages
The Nilotic languages are a group of related languages spoken across a wide area between South Sudan and Tanzania by the Nilotic peoples. Etymology The word Nilotic means of or relating to the Nile River or to the Nile region of Africa. Demographics Nilotic peoples, who are the native speakers of the languages, originally migrated from the Gezira area in Sudan. Nilotic language speakers live in parts of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Kenya, Sudan, South Sudan, Tanzania and Uganda. Subdivisions According to linguist Joseph Greenberg, the language family is divided up into three subgroups: *Eastern Nilotic languages such as Turkana and Maasai *Southern Nilotic languages such as Kalenjin and Datooga *Western Nilotic languages such as Luo, Nuer and Dinka Before Greenberg's reclassification, Nilotic was used to refer to Western Nilotic alone, with the other two being grouped as related " Nilo-Hamitic" languages. Blench (2012) treats the Burun languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omaio Language
Omaio (Omaiyo) is an obscure Dorobo language of Tanzania. According to interviews with speakers, the people were expelled from the Serengeti in the 1950s to make way for the park. As of 2018, three speakers remember some words of the language, though it had not been spoken since they were children. Based on the few hundred words and phrases that have been collected, the language has not been classified. There is evidence of words that can be traced to contact with speakers of the Maa and Datooga languages, as well as older words from the Southern Nilotic family which may have been inherited or borrowed. See also * Serengeti Dorobo language Notes External linksOmaiyo Language Resources {{Languages of Tanzania Languages of Tanzania Unclassified languages of Africa Endangered unclassified languages Endangered languages of Africa Dorobo stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Tanzania
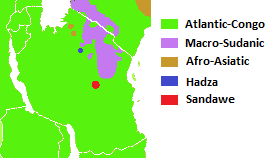
Tanzania is a multilingual country. There are many languages spoken in the country, but no one language is spoken natively by a majority or a large plurality of the population. Swahili and English, the latter of which was inherited from colonial rule (''see Tanganyika Territory''), are widely spoken as lingua francas. They serve as working languages in the country, with Swahili being the official national language. There are more speakers of Swahili than of English in Tanzania. Overview According to ''Ethnologue'', there are a total of 126 languages spoken in Tanzania. Two are institutional, 18 are developing, 58 are vigorous, 40 are endangered, and 8 are dying. There are also three languages that recently became extinct. Most languages spoken locally belong to two broad language families: Niger-Congo ( Bantu branch) and Nilo-Saharan ( Nilotic branch), spoken by the country's Bantu and Nilotic populations, respectively. Additionally, the Hadza and Sandawe hunter-gatherers s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unclassified Languages Of Africa
The languages of Africa are divided into several major language families: * Niger–Congo or perhaps Atlantic–Congo languages (includes Bantu and non-Bantu, and possibly Mande and others) are spoken in West, Central, Southeast and Southern Africa. *Afroasiatic languages are spread throughout Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa and parts of the Sahel. *Indo-European languages are spoken in South Africa and Namibia (Afrikaans, English, German) and are used as lingua francas in the former colonies of Britain and Liberia that was part of American Colonization Society (English), former colonies of France and of Belgium ( French), former colonies of Portugal (Portuguese), former colonies of Italy (Italian), former colonies of Spain (Spanish) and the current Spanish territories of Ceuta, Melilla and the Canary Islands and the current French territories of Mayotte and La Réunion. *Various families of Nilo-Saharan languages (unity debated) are spoken from Tanzania to E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Extinct In The 20th Century
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of methods, including spoken, sign, and written language. Many languages, including the most widely-spoken ones, have writing systems that enable sounds or signs to be recorded for later reactivation. Human language is highly variable between cultures and across time. Human languages have the properties of productivity and displacement, and rely on social convention and learning. Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between and . Precise estimates depend on an arbitrary distinction (dichotomy) established between languages and dialects. Natural languages are spoken, signed, or both; however, any language can be encoded into secondary media using auditory, visual, or tactile stimuli – for example, writing, whis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |