|
Languages Of Tanzania
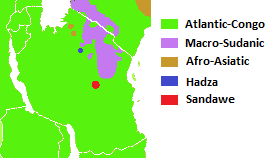
Tanzania is a multilingual country. There are many languages spoken in the country, but no one language is spoken natively by a majority or a large plurality of the population. Swahili and English, the latter of which was inherited from colonial rule (''see Tanganyika Territory''), are widely spoken as lingua francas. They serve as working languages in the country, with Swahili being the official national language. There are more speakers of Swahili than of English in Tanzania. Overview According to ''Ethnologue'', there are a total of 126 languages spoken in Tanzania. Two are institutional, 18 are developing, 58 are vigorous, 40 are endangered, and 8 are dying. There are also three languages that recently became extinct. Most languages spoken locally belong to two broad language families: Niger-Congo ( Bantu branch) and Nilo-Saharan ( Nilotic branch), spoken by the country's Bantu and Nilotic populations, respectively. Additionally, the Hadza and Sandawe hunter-gatherers s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swahili Language
Swahili, also known by its local name , is the native language of the Swahili people, who are found primarily in Tanzania, Kenya and Mozambique (along the East African coast and adjacent litoral islands). It is a Bantu language, though Swahili has borrowed a number of words from foreign languages, particularly Arabic, but also words from Portuguese, English and German. Around forty percent of Swahili vocabulary consists of Arabic loanwords, including the name of the language ( , a plural adjectival form of an Arabic word meaning 'of the coast'). The loanwords date from the era of contact between Arab slave traders and the Bantu inhabitants of the east coast of Africa, which was also the time period when Swahili emerged as a lingua franca in the region. The number of Swahili speakers, be they native or second-language speakers, is estimated to be approximately 200 million. Due to concerted efforts by the government of Tanzania, Swahili is one of three official languages (th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadza People
The Hadza, or Hadzabe (''Wahadzabe'' in Swahili), are a Tanzanian indigenous ethnic group mostly based in southwest Karatu District of Arusha Region. They live around Lake Eyasi in the central Rift Valley and in the neighboring Serengeti Plateau. There are, as of 2015, between 1,200 and 1,300 Hadza people living in Tanzania, however only around 400 Hadza still survive exclusively based on the traditional means of foraging. Additionally, the increasing impact of tourism and encroaching pastoralists pose serious threats to the continuation of their traditional way of life. Genetically, the Hadza are not closely related to any other people. Once classified among the Khoisan languages, primarily because it has clicks, the Hadza language (Hadzane) is actually thought to be an isolate, unrelated to any other. Hadzane is an entirely oral language, but it is not predicted to be in danger of extinction. UNESCO states that the language is not endangered but vulnerable because most child ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nilotic
The Nilotic peoples are people indigenous to the Nile Valley who speak Nilotic languages. They inhabit South Sudan, Sudan, Ethiopia, Uganda, Kenya, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania. Among these are the Burun-speaking peoples, Karo peoples, Luo peoples, Ateker peoples, Kalenjin peoples, Datooga, Dinka, Nuer, Atwot, Lotuko, and the Maa-speaking peoples. The Nilotes constitute the majority of the population in South Sudan, an area that is believed to be their original point of dispersal. After the Bantu peoples, they constitute the second-most numerous group of peoples inhabiting the African Great Lakes region around the East African Rift. They make up a notable part of the population of southwestern Ethiopia as well. The Nilotic peoples primarily adhere to Christianity and traditional faiths, including the Dinka religion. Some Nilotic peoples also adhere to Islam. Name The terms "Nilotic" and "Nilote"' were previously used as racial subcl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantu Peoples
The Bantu peoples, or Bantu, are an ethnolinguistic grouping of approximately 400 distinct ethnic groups who speak Bantu languages. They are native to 24 countries spread over a vast area from Central Africa to Southeast Africa and into Southern Africa. There are several hundred Bantu languages. Depending on the definition of "language" or "dialect", it is estimated that there are between 440 and 680 distinct languages. The total number of speakers is in the hundreds of millions, ranging at roughly 350 million in the mid-2010s (roughly 30% of the population of Africa, or roughly 5% of the total world population). About 60 million speakers (2015), divided into some 200 ethnic or tribal groups, are found in the Democratic Republic of the Congo alone. The larger of the individual Bantu groups have populations of several million, e.g. the people of Rwanda and Burundi (25 million), the Bagandapeople of Uganda (10 million as of 2019), the Shona of Zimbabwe (15 million ), the Zulu of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nilo-Saharan Languages
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of African languages spoken by some 50–60 million people, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari River, Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributaries of the Nile meet. The languages extend through 17 nations in the northern half of Africa: from Algeria to Benin in the west; from Libya to the Democratic Republic of the Congo in the centre; and from Egypt to Tanzania in the east. As indicated by its hyphenated name, Nilo-Saharan is a family of the African interior, including the greater Nile Basin and the Central Sahara Desert. Eight of its proposed constituent divisions (excluding Kunama languages, Kunama, Kuliak, and Songhai languages, Songhay) are found in the modern countries of Sudan and South Sudan, through which the Nile River flows. In his book ''The Languages of Africa'' (1963), Joseph Greenberg named the group and argued it was a genetic (linguistics), genetic family. It contains the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of methods, including spoken, sign, and written language. Many languages, including the most widely-spoken ones, have writing systems that enable sounds or signs to be recorded for later reactivation. Human language is highly variable between cultures and across time. Human languages have the properties of productivity and displacement, and rely on social convention and learning. Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between and . Precise estimates depend on an arbitrary distinction (dichotomy) established between languages and dialects. Natural languages are spoken, signed, or both; however, any language can be encoded into secondary media using auditory, visual, or tactile stimuli – for example, writing, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnologue
''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' (stylized as ''Ethnoloɠue'') is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It was first issued in 1951, and is now published by SIL International, an American Christian non-profit organization. Overview and content ''Ethnologue'' has been published by SIL International (formerly known as the Summer Institute of Linguistics), a Christian linguistic service organization with an international office in Dallas, Texas. The organization studies numerous minority languages to facilitate language development, and to work with speakers of such language communities in translating portions of the Bible into their languages. Despite the Christian orientation of its publisher, ''Ethnologue'' isn't ideologically or theologically biased. ''Ethnologue'' includes alternative names and autonyms, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bundesarchiv Bild 105-DOA0075, Deutsch-Ostafrika, Einheimisches Mädchen
The German Federal Archives or Bundesarchiv (BArch) (german: Bundesarchiv) are the National Archives of Germany. They were established at the current location in Koblenz in 1952. They are subordinated to the Federal Commissioner for Culture and the Media ( Claudia Roth since 2021) under the German Chancellery, and before 1998, to the Federal Ministry of the Interior. On 6 December 2008, the Archives donated 100,000 photos to the public, by making them accessible via Wikimedia Commons. History The federal archive for institutions and authorities in Germany, the first precursor to the present-day Federal Archives, was established in Potsdam, Brandenburg in 1919, a later date than in other European countries. This national archive documented German government dating from the founding of the North German Confederation in 1867. It also included material from the older German Confederation and the Imperial Chamber Court. The oldest documents in this collection dated back to the year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingua Franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups of people who do not share a native language or dialect, particularly when it is a third language that is distinct from both of the speakers' native languages. Lingua francas have developed around the world throughout human history, sometimes for commercial reasons (so-called "trade languages" facilitated trade), but also for cultural, religious, diplomatic and administrative convenience, and as a means of exchanging information between scientists and other scholars of different nationalities. The term is taken from the medieval Mediterranean Lingua Franca, a Romance-based pidgin language used especially by traders in the Mediterranean Basin from the 11th to the 19th centuries. A world language – a language spoken internationally and by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanganyika Territory
Tanganyika was a colonial territory in East Africa which was administered by the United Kingdom in various guises from 1916 to 1961. It was initially administered under a military occupation regime. From 20 July 1922, it was formalised into a League of Nations mandate under British rule. From 1946, it was administered by the UK as a United Nations trust territory. Before World War I, Tanganyika formed part of the German colony of German East Africa. It was gradually occupied by forces from the British Empire and Belgian Congo during the East Africa Campaign, although German resistance continued until 1918. After this, the League of Nations formalised the UK's control of the area, who renamed it "Tanganyika". The UK held Tanganyika as a League of Nations mandate until the end of World War II after which it was held as a United Nations trust territory. In 1961, Tanganyika gained its independence from the UK as Tanganyika. It became a republic a year later. Tanganyika now forms pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |