|
Sequoiafarm Kaldenkirchen
The Kaldenkirchen Sequoia Farm (german: Sequoiafarm Kaldenkirchen) is a German arboretum that has been used as a biological institute for many years. Part of the protected area in the city of Nettetal, it is situated in the "Kaldenkirchen Grenzwald" (forest bordering Germany and the Netherlands). Nettetal lies in the Lower Rhine region of Germany. History and use In 1946, Illa Martin and Ernst J. Martin, both dentists and dendrologists in Kaldenkirchen, founded an arboretum close to the Dutch border. There, and in a nearby laboratory-plantation several acres wide from 1952 on, they cultivated 1,500 giant sequoia (''Sequoiadendron giganteum'') seedlings from seeds of US origin from Martin's nephew Albert A. Martin of Santa Barbara, CA. The seeds were collected in Sequoia National Forest at different elevations, wrapped in burlap to preserve them and sent to Germany. They wanted to find out if the giant sequoia, which had existed in Germany before the ice age, could be int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nettetal
Nettetal is a municipality in the district of Viersen, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is situated in the Lower Rhine region. History Nettetal was founded on January 1, 1970, when the former townships Leuth, Breyell, Hinsbeck and former towns/cities Lobberich and Kaldenkirchen were merged. All five communities had developed around the river Nette. Nettetal originally contained five boroughs, until Schaag separated from Breyell in 1995, becoming the sixth borough. At the time of its formation, it was considered too problematic to try and combine all five coats of arms into one, so a new coat of arm was introduced in 1971. It shows a water lily before a blue blackground, symbolizing the predominance of nature and the variety of lakes. Five water lily leaves represent the five founding boroughs of Nettetal. Demographics Nettetal's six boroughs, with populations per its own census, as of December 2020: Geography Nettetal is located in the middle of the cross-border Maas-Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abies Grandis
''Abies grandis'' (grand fir, giant fir, lowland white fir, great silver fir, western white fir, Vancouver fir, or Oregon fir) is a fir native to the Pacific Northwest and Northern California of North America, occurring at altitudes of sea level to . It is a major constituent of the Grand Fir/Douglas Fir Ecoregion of the Cascade Range. The tree typically grows to in height, and may be the tallest ''Abies'' species in the world. There are two varieties, the taller coast grand fir, found west of the Cascade Mountains, and the shorter interior grand fir, found east of the Cascades. It was first described in 1831 by David Douglas. It is closely related to white fir. The bark was historically believed to have medicinal properties, and it is popular in the United States as a Christmas tree. Its lumber is a softwood, and it is harvested as a hem fir. It is used in paper-making, as well as construction for framing and flooring, where it is desired for its resistance to splitting a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Cologne
The University of Cologne (german: Universität zu Köln) is a university in Cologne, Germany. It was established in the year 1388 and is one of the most prestigious and research intensive universities in Germany. It was the sixth university to be established in Central Europe. It closed in 1798 before being re-established in 1919. It is now one of the largest universities in Germany with more than 48,000 students. The University of Cologne was a university of excellence as part of the German Universities Excellence Initiative from 2012 to 2019. As of 2021, 3 Nobel Prize winners have been affiliated with the university. Professors and former students have won 11 Leibniz Prizes, the most prestigious as well as the best-funded prize in Europe. History 1388–1798 The university of Cologne was established in 1388 as the fourth university in the Holy Roman Empire, after the Charles University of Prague (1348), the University of Vienna (1365) and the Ruprecht Karl University of H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nette (Niers)
The Nette is a small river in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, a left tributary of the Niers. It rises near Dülken, a borough of Viersen. The Nette flows through Viersen-Boisheim and Nettetal before reaching the Niers in Wachtendonk Wachtendonk at the confluence of Niers River and Nette River is a municipality in the district of Kleve in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located west of the Rhine half way between Duisburg and Venlo at the Dutch Dutch commonly refers .... Its total length is ; its drainage area is . Lakes The Nette passes nine lakes on its way to Wachtendonk * Kleiner Breyeller See c. 5.3 ha * Großer Breyeller See c. 9.2 ha * Nettebruch c. 13.2 ha * Windmühlenbruch c. 6 ha * Ferkensbruch c. 4.5 ha * Kleiner de Wittsee c. 4.5 ha * Großer de Wittsee c. 22.5 ha * Schrolik c. 15.5 ha * Poelvennsee c. 24.5 ha The Maas-Schwalm-Nette Nature Park is named after the river. References Rivers of North Rhine-Westphalia Rivers of Germany {{ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schwalm (Meuse)
The Schwalm (German) or Swalm (Dutch), is a small river in Germany and the Netherlands, tributary to the river Meuse. Its source is near Wegberg, in the district Heinsberg, south-west of Mönchengladbach, in North Rhine-Westphalia (Germany). The Schwalm flows through Wegberg and Brüggen before flowing into the Meuse across the border with the Netherlands, in Swalmen. Its total length is 45 km. Sources The original source region has since become an area of carr with poor water quality. The water of the Schwalm comes mainly from '' Rheinbraun's'' waste water pits. This brown coal open cast mine is required to feed the waste water into the surface water. Otherwise it would fill the mine, which is up to 230 metres deep.This is achieved by means of shafts (''Schlitzschächten'') through which the water flows back into the groundwater. If it were not for these shafts, the rivers Niers and Schwalm would long since have dried up. This would also destroy the mixed alder and ash ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meuse
The Meuse ( , , , ; wa, Moûze ) or Maas ( , ; li, Maos or ) is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a total length of . History From 1301 the upper Meuse roughly marked the western border of the Holy Roman Empire with the Kingdom of France, after Count Henry III of Bar had to receive the western part of the County of Bar (''Barrois mouvant'') as a French fief from the hands of King Philip IV. In 1408, a Burgundian army led by John the Fearless went to the aid of John III against the citizens of Liège, who were in open revolt. After the battle which saw the men from Liège defeated, John ordered the drowning in the Meuse of suspicious burghers and noblemen in Liège. The border remained stable until the annexation of the Three Bishoprics Metz, Toul and Verdun by King Henry II in 1552 and the occupation of the Duchy of Lorraine by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Nursery
A nursery is a place where plants are propagated and grown to a desired size. Mostly the plants concerned are for gardening, forestry or conservation biology, rather than agriculture. They include retail nurseries, which sell to the general public, wholesale nurseries, which sell only to businesses such as other nurseries and to commercial gardeners, and private nurseries, which supply the needs of institutions or private estates. Some will also work in plant breeding. A nurseryman is a person who owns or works in a nursery. Some nurseries specialize in certain areas, which may include: propagation and the selling of small or bare root plants to other nurseries, growing out plant materials to a saleable size, or retail sales. Nurseries may also specialize in one type of plant: e.g., groundcovers, shade plants, or rock garden plants. Some produce bulk stock, whether seedlings or grafted, of particular varieties for purposes such as fruit trees for orchards, or timber tree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanical Garden accepts 187 species names of pines as current, together with more synonyms. The American Conifer Society (ACS) and the Royal Horticultural Society accept 121 species. Pines are commonly found in the Northern Hemisphere. ''Pine'' may also refer to the lumber derived from pine trees; it is one of the more extensively used types of lumber. The pine family is the largest conifer family and there are currently 818 named cultivars (or trinomials) recognized by the ACS. Description Pine trees are evergreen, coniferous resinous trees (or, rarely, shrubs) growing tall, with the majority of species reaching tall. The smallest are Siberian dwarf pine and Potosi pinyon, and the tallest is an tall ponderosa pine located in southern Oregon's Rogue Riv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Beech
''Nothofagus'', also known as the southern beeches, is a genus of 43 species of trees and shrubs native to the Southern Hemisphere in southern South America (Chile, Argentina) and Australasia (east and southeast Australia, New Zealand, New Guinea, and New Caledonia). The species are ecological dominants in many temperate forests in these regions. Some species are reportedly naturalised in Germany and Great Britain. The genus has a rich fossil record of leaves, cupules, and pollen, with fossils extending into the late Cretaceous period and occurring in Australia, New Zealand, Antarctica, and South America. Description The leaves are toothed or entire, evergreen or deciduous. The fruit is a small, flattened or triangular nut, borne in cupules containing one to seven nuts. Reproduction Many individual trees are extremely old, and at one time, some populations were thought to be unable to reproduce in present-day conditions where they were growing, except by suckering (clonal repr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dawn Redwood
''Metasequoia glyptostroboides'', the dawn redwood, is a fast-growing, endangered deciduous conifer. It is the sole living species of the genus ''Metasequoia'', one of three genera in the subfamily Sequoioideae of the family Cupressaceae. It now survives only in wet lower slopes and montane river and stream valleys in the border region of Hubei and Hunan provinces and Chongqing municipality in south-central China, notably in Lichuan county in Hubei. Although the shortest of the redwoods, it can grow to in height. In 1941, the genus ''Metasequoia'' was reported by paleobotanist Shigeru Miki as a widely distributed extinct genus based on fossils, before attracting considerable attention a few years later when small populations were found alive in central China. It is a particularly well-known example of a living fossil species. The tree faces considerable risks of extinction in its wild range due to deforestation, however it has been planted extensively in arboreta worldwide, wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
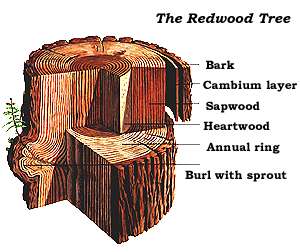
Coast Redwood
''Sequoia sempervirens'' ()''Sunset Western Garden Book,'' 1995:606–607 is the sole living species of the genus '' Sequoia'' in the cypress family Cupressaceae (formerly treated in Taxodiaceae). Common names include coast redwood, coastal redwood, and California redwood. It is an evergreen, long-lived, monoecious tree living 1,200–2,200 years or more. This species includes the tallest living trees on Earth, reaching up to in height (without the roots) and up to in diameter at breast height. These trees are also among the oldest living things on Earth. Before commercial logging and clearing began by the 1850s, this massive tree occurred naturally in an estimated along much of coastal California (excluding southern California where rainfall is not sufficient) and the southwestern corner of coastal Oregon within the United States. The name sequoia sometimes refers to the subfamily Sequoioideae, which includes ''S. sempervirens'' along with ''Sequoiadendron'' (gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia (german: Nordrhein-Westfalen, ; li, Noordrien-Wesfale ; nds, Noordrhien-Westfalen; ksh, Noodrhing-Wäßßfaale), commonly shortened to NRW (), is a States of Germany, state (''Land'') in Western Germany. With more than 18 million inhabitants, it is the List of German states by population, most populous state of Germany. Apart from the city-states, it is also the List of German states by population density, most densely populated state in Germany. Covering an area of , it is the List of German states by area, fourth-largest German state by size. North Rhine-Westphalia features 30 of the 81 German municipalities with over 100,000 inhabitants, including Cologne (over 1 million), the state capital Düsseldorf, Dortmund and Essen (all about 600,000 inhabitants) and other cities predominantly located in the Rhine-Ruhr metropolitan area, the largest urban area in Germany and the fourth-largest on the European continent. The location of the Rhine-Ruhr at the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)




.jpg)