|
Scottsbluff, Nebraska
Scottsbluff is a city in Scotts Bluff County, Nebraska, United States, in the Great Plains region. The population was 14,436 at the 2020 census. Scottsbluff is the largest city in the Nebraska Panhandle, and the 13th-most-populous city in Nebraska. Scottsbluff was founded in 1899 across the North Platte River from its namesake, a bluff that is now protected by the National Park Service as Scotts Bluff National Monument. The monument was named after Hiram Scott, a fur trader with the Rocky Mountain Fur Company who was found dead in the vicinity on the return trip from a fur expedition. The smaller town of Gering had been founded south of the river in 1887. The two cities have since grown together to form the 7th-largest urban area (the Scottsbluff Micropolitan Statistical Area) in Nebraska. History Scottsbluff was founded in 1899 by the Lincoln Land Company, a subsidiary of the Burlington Railroad. By 1900, the Burlington Railroad laid tracks into the town and placed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City
A city is a human settlement of a substantial size. The term "city" has different meanings around the world and in some places the settlement can be very small. Even where the term is limited to larger settlements, there is no universally agreed definition of the lower boundary for their size. In a narrower sense, a city can be defined as a permanent and Urban density, densely populated place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, Public utilities, utilities, land use, Manufacturing, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organisations, government organizations, and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving the efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiram Scott
Hiram Scott (c. 1805–1828) was an American mountain man, trapper, and pelt trader who trapped and took part in expeditions throughout the western United States during the 1820s. Born in Missouri, Scott joined the Rocky Mountain Fur Company in 1822 and took part in the first fur trade expedition at the Great Salt Lake in Utah. He died at age 23 near a cliff along the North Platte River in Nebraska which was named in his honor. The circumstances leading to his demise have given rise to many diverse accounts and theories. Early life and career Hiram Scott was born in 1805 in St. Charles County, Missouri. Described as an abnormally towering and strapping figure with a dark complexion, in 1822 Scott was employed by William Henry Ashley and Andrew Henry's Rocky Mountain Fur Company, a pioneering enterprise which funded explorations into the western United States' wilderness. The company's Superintendent of Indian Affairs William Clark had granted Ashley and Henry a license to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
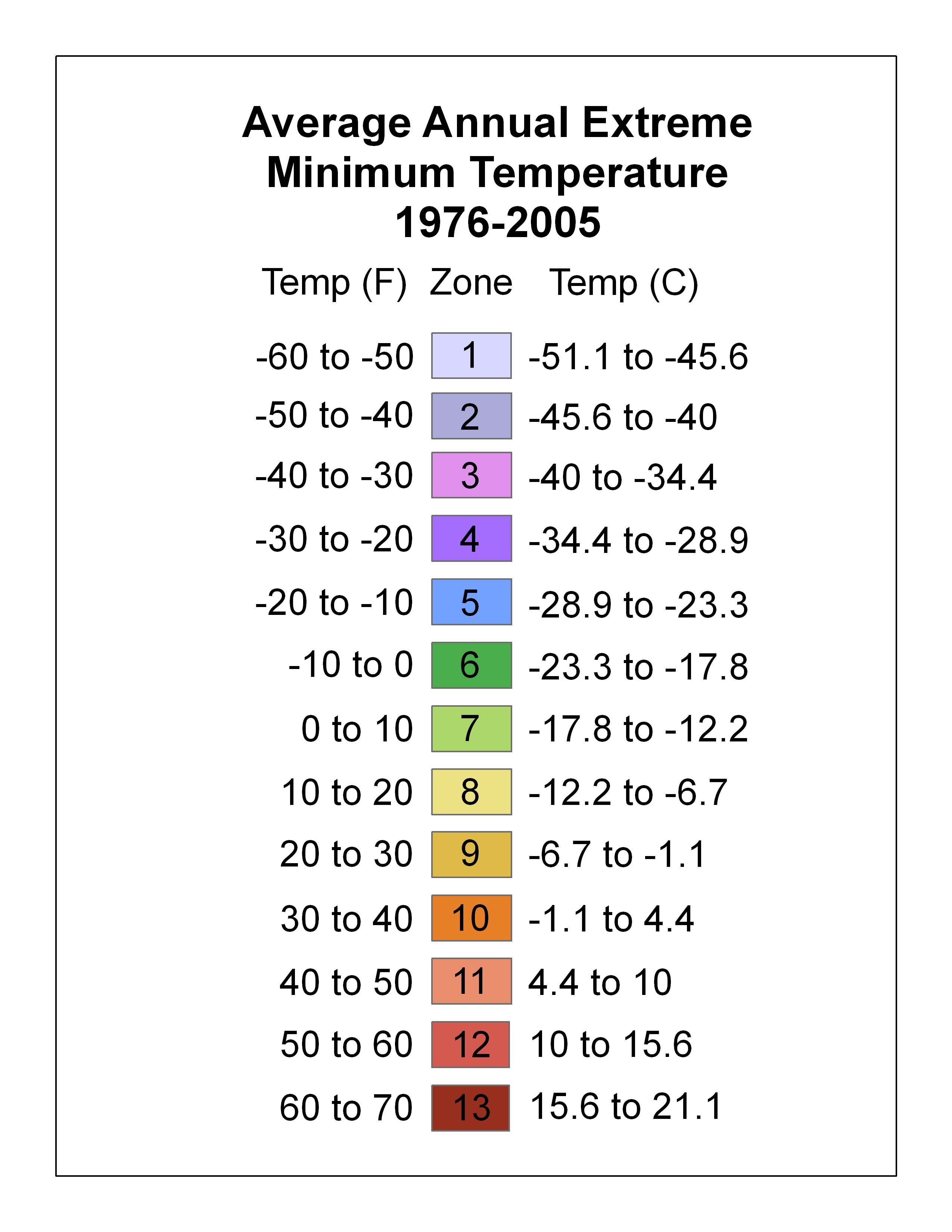
Hardiness Zone
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most widely used system, developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) as a rough guide for landscaping and gardening, defines 13 zones by long-term average annual extreme minimum temperatures. It has been adapted by and to other countries (such as Canada) in various forms. A plant may be described as "hardy to zone 10": this means that the plant can withstand a minimum temperature of . Unless otherwise specified, in American contexts "hardiness zone" or simply "zone" usually refers to the USDA scale. However, some confusion can exist in discussing buildings and HVAC, where "climate zone" can refer to the International Energy Conservation Code zones, where Zone 1 is warm and Zone 8 is cold. Other hardiness rating schemes have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
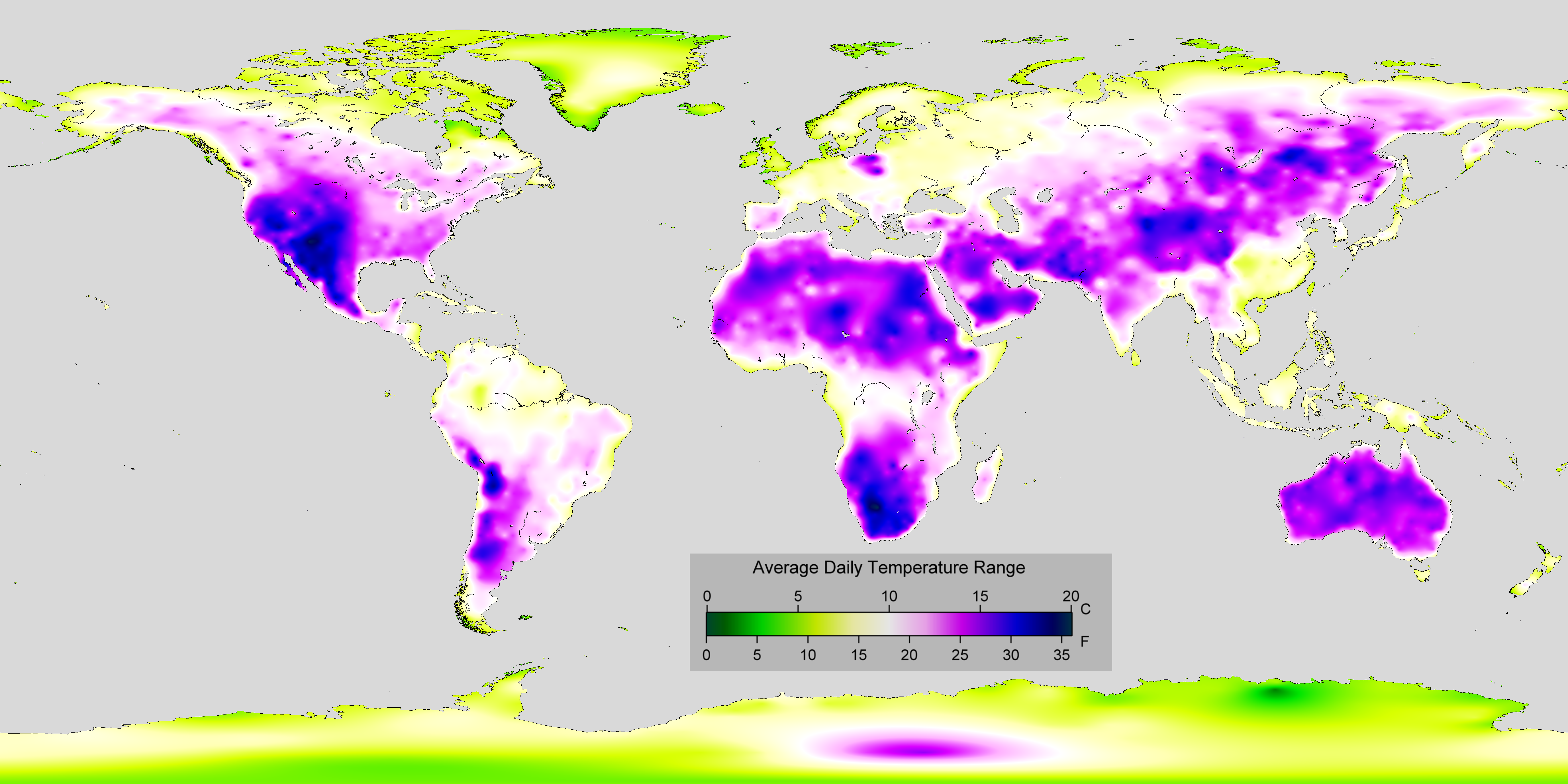
Diurnal Temperature Variation
In meteorology, diurnal temperature variation is the variation between a high air temperature and a low temperature that occurs during the same day. Temperature lag Temperature lag, also known as thermal inertia, is an important factor in diurnal temperature variation. Peak daily temperature generally occurs ''after'' noon, as air keeps absorbing net heat for a period of time from morning through noon and some time thereafter. Similarly, minimum daily temperature generally occurs substantially after midnight, indeed occurring during early morning in the hour around dawn, since heat is lost all night long. The analogous annual phenomenon is seasonal lag. As solar energy strikes the Earth's surface each morning, a shallow layer of air directly above the ground is heated by conduction. Heat exchange between this shallow layer of warm air and the cooler air above is very inefficient. On a warm summer's day, for example, air temperatures may vary by from just above the ground t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humid Continental Climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers, and cold (sometimes severely cold in the northern areas) and snowy winters. Precipitation is usually distributed throughout the year, but often these regions do have dry seasons. The definition of this climate in terms of temperature is as follows: the mean temperature of the coldest month must be below or depending on the isotherm, and there must be at least four months whose mean temperatures are at or above . In addition, the location in question must not be semi-arid or arid. The cooler ''Dfb'', ''Dwb'', and ''Dsb'' subtypes are also known as hemiboreal climates. Although amount of snowfall is not a factor used in defining the humid continental climate, snow during the winter in this type of climate is almost a guarantee, either intermitte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indicates a tropical rainforest climate. The system assigns a temperature subgroup for all groups other than those in the ''A'' group, indicated by the third letter for climates in ''B'', ''C'', ''D'', and the second letter for climates in ''E''. Other examples include: ''Cfb'' indicating an oceanic climate with warm summers as indicated by the ending ''b.'', while ''Dwb'' indicates a semi-Monsoon continental climate, monsoonal continental climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Semi-arid Climate
Cold is the presence of low temperature, especially in the atmosphere. In common usage, cold is often a subjective perception. A lower bound to temperature is absolute zero, defined as 0.00K on the Kelvin scale, an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. This corresponds to on the Celsius scale, on the Fahrenheit scale, and on the Rankine scale. Since temperature relates to the thermal energy held by an object or a sample of matter, which is the kinetic energy of the random motion of the particle constituents of matter, an object will have less thermal energy when it is colder and more when it is hotter. If it were possible to cool a system to absolute zero, all motion of the particles in a sample of matter would cease and they would be at complete rest in the classical sense. The object could be described as having zero thermal energy. Microscopically in the description of quantum mechanics, however, matter still has zero-point energy even at absolute zero, beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal statistical system, U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and American economy, economy. The U.S. Census Bureau is part of the United States Department of Commerce, U.S. Department of Commerce and its Director of the United States Census Bureau, director is appointed by the president of the United States. Currently, Ron S. Jarmin is the acting director of the U.S. Census Bureau. The Census Bureau's primary mission is conducting the United States census, U.S. census every ten years, which allocates the seats of the United States House of Representatives, U.S. House of Representatives to the U.S. state, states based on their population. The bureau's various censuses and surveys help allocate over $675 billion in federal funds every year and it assists states, local communities, and businesses in making informed decisions. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abalone
Abalone ( or ; via Spanish , from Rumsen language, Rumsen ''aulón'') is a common name for any small to very large marine life, marine gastropod mollusc in the family (biology), family Haliotidae, which once contained six genera but now contains only one genus, ''Haliotis''. Other common names are ear shells, sea ears, and, now rarely, muttonfish or muttonshells in parts of Australia, ormer in the United Kingdom, perlemoen in South Africa, and pāua in New Zealand. The number of abalone species recognized worldwide ranges between 30 and 130 with over 230 species-level taxa described. The most comprehensive treatment of the family considers 56 species valid, with 18 additional subspecies. The gastropod shell, shells of abalone have a low, open spiral structure, and are characterized by several open respiratory pores in a row near the shell's outer edge. The thick inner layer of the shell is composed of nacre, which in many species is highly iridescence, iridescent, giving rise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platte River
The Platte River () is a major American river, in the state of Nebraska. It is about long; measured to its farthest source via its tributary, the North Platte River, it flows for over . The Platte River is a tributary of the Missouri River, which itself is a tributary of the Mississippi River, which flows to the Gulf of Mexico. The Platte over most of its length is a broad, shallow, meandering stream with a sandy bottom and many islands—a braided stream. The Platte is one of the most significant tributary systems in the watershed of the Missouri, draining a large portion of the central Great Plains in Nebraska and the eastern Rocky Mountains in Colorado and Wyoming. The river valley played an important role in the westward expansion of the United States, providing the route for several major emigrant trails, including the Oregon, California, Mormon and Bozeman trails. The first Europeans to see the Platte were French explorers and fur trappers about 1714; they first call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakota Language
Lakota ( ), also referred to as Lakhota, Teton or Teton Sioux, is a Siouan languages, Siouan language spoken by the Lakota people of the Sioux tribes. Lakota is mutually intelligible with the two dialects of the Dakota language, especially Dakota language#Comparison of the dialects, Western Dakota, and is one of the three major variety (linguistics), varieties of the Sioux language. Speakers of the Lakota language make up one of the largest Native American language speech communities in the United States, with approximately 2,000 speakers, who live mostly in the northern plains states of North Dakota and South Dakota. Many communities have immersion programs for both children and adults. Like many indigenous languages, the Lakota language did not have a written form traditionally. However, efforts to develop a written form of Lakota began, primarily through the work of Christian missionaries and linguists, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The orthography has since evol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago, Burlington And Quincy Railroad
The Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad was a railroad that operated in the Midwest, Midwestern United States. Commonly referred to as the Burlington Route, the Burlington, CB&Q, or as the Q, it operated extensive trackage in the states of Colorado, Illinois, Iowa, Missouri, Nebraska, Wisconsin, Wyoming, and also in Texas through subsidiaries Colorado and Southern Railway, Fort Worth and Denver Railway, and Burlington-Rock Island Railroad. Its primary connections included Chicago, Minneapolis–Saint Paul, St. Louis, Kansas City, Missouri, Kansas City, and Denver. Because of this extensive trackage in the midwest and mountain states, the railroad used the advertising slogans "Everywhere West", "Way of the ''Zephyrs''", and "The Way West". In 1967, it reported 19,565 million net ton-miles of revenue freight and 723 million passenger miles; corresponding totals for C&S were 1,100 and 10 and for FW&D were 1,466 and 13. At the end of the year, CB&Q operated 8,538 route-miles, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |