|
Sarcophaga Bercaea
''Sarcophaga'' is a genus of true flies and the type genus of the flesh-fly family (Sarcophagidae). The members of this cosmopolitan genus are frequently known as common flesh flies. This genus occurs essentially worldwide. These flies are generally well-sized and of a greyish color; like many of their relatives, the typical patterns are lengthwise darker stripes on the thorax and dark and light square dots on the abdomen. Many have conspicuous red compound eyes. These are set further apart in females than in males; the females are also larger on average. As typical for this family, it is almost impossible to tell the species apart from their outward appearance, and many can only be reliably identified by microscopic examination of the males' genitalia. As the common name implies, their larvae typically feed on decaying meat. Some, however, instead eat the bacteria and other small organisms living on carrion. Many species have adapted to humans, and while they are usually nuisa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcophaga Africa
''Sarcophaga (Bercaea) africa'' is a species of fly belonging to the family Sarcophagidae, the flesh-flies. It is the best known species in its genus. ''S. africa'' feeds on living and dead tissue, including snails, and other decomposing matter, and feces. ''Sarcophaga africa'' is a synanthropic species known to cause myiasis in humans and livestock. The species is considered useful in forensic entomology Forensic entomology is the scientific study of the colonization of a dead body by arthropods. This includes the study of insect types commonly associated with cadavers, their respective life cycles, their ecological presences in a given environme ... due to this quality. ''S. africa'' is coprophagus, lays eggs in feces, and can be cultured from human and animal feces. The fly also lays eggs in decaying flesh and can be cultured from the decaying matter. References Sarcophagidae Forensic entomology Insects described in 1824 {{Oestroidea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcophaga Aldrichi
The friendly fly or large flesh fly, ''Sarcophaga aldrichi'', is a fly that is a parasitoid of the forest tent caterpillar. It strongly resembles the house fly but is in a different family, the Sarcophagidae, or flesh-flies. It is a little larger than the house fly, and has the same three black stripes on its thorax. It has red eyes, a grayish body, and a checkered abdomen. In early summer it emerges from pupae in the ground and seeks out forest tent caterpillar cocoons, where it deposits live larvae which bore into the cocoons and feed on the pupating insects, killing them. Eventually the fly maggot A maggot is the larva of a fly (order Diptera); it is applied in particular to the larvae of Brachycera flies, such as houseflies, cheese flies, and blowflies, rather than larvae of the Nematocera, such as mosquitoes and crane flies. ...s drop to the ground and pupate and go dormant over the winter. Population explosions of this species usually occur during the sum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcophaga Crassipalpis
''Sarcophaga crassipalpis'' is a species of flesh flies (insects in the family Sarcophagidae. It is a common laboratory animal used in the study of gene expression and the study of diapause in insects. ''Sarcophaga crassipalpis'' conforms to the basic bilateral symmetry body plan for arthropods and insects by possessing jointed-appendages, a sclerotized external cuticle, and an internal muscular system that functions as levers for movement. The six legs possess a tarsus, or foot, with a pair of claws for gripping rough surfaces. Beneath the claws is a fleshy, glandular adhesive pad called a pulvillus, which is used on smooth surfaces. ''Sarcophaga crassipalpis'' is an insect in the order Diptera, meaning “two-winged”. As with other flies, ''S. crassipalpis'' has one pair of wings used for flying. Posterior to the wings is a small pair of knob-like structures (called halteres), which function as organs of balance. Like other dipterans, ''S. crassipalpis'' reproduces utiliz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcophaga Bullata
''Sarcophaga bullata'', or the grey flesh fly, is a species of fly belonging to the family Sarcophagidae. It varies in size from small to large, 8 to 17 millimeters in length and is very similar in appearance and behavior to a closely related species, ''Sarcophaga haemorrhoidalis''. ''S. bullata'' is a common scavenger species in the Eastern United States, but is found throughout the Nearctic region. Identification down to the species level in the family Sarcophagidae is notably difficult and relies primarily on the male genitalia. Though limited information is available regarding ''S. bullata'', it has gained increasing recognition in the field of forensic entomology as a forensically-relevant fly species, as it may be among the first species to colonize human remains. In these instances, recovered maggots may be analyzed for post-mortem interval (PMI) estimations, which may be used as evidence in courts of law. Current studies regarding ''S. bullata'' have revealed a maternal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orchard
An orchard is an intentional plantation of trees or shrubs that is maintained for food production. Orchards comprise fruit- or nut-producing trees which are generally grown for commercial production. Orchards are also sometimes a feature of large gardens, where they serve an aesthetic as well as a productive purpose. A fruit garden is generally synonymous with an orchard, although it is set on a smaller non-commercial scale and may emphasize berry shrubs in preference to fruit trees. Most temperate-zone orchards are laid out in a regular grid, with a grazed or mown grass or bare soil base that makes maintenance and fruit gathering easy. Most modern commercial orchards are planted for a single variety of fruit. While the importance of introducing biodiversity is recognized in forest plantations, it would seem to be beneficial to introduce some genetic diversity in orchard plantations as well by interspersing other trees through the orchard. Genetic diversity in an orchard would p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forestry
Forestry is the science and craft of creating, managing, planting, using, conserving and repairing forests, woodlands, and associated resources for human and environmental benefits. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands. The science of forestry has elements that belong to the biological, physical, social, political and managerial sciences. Forest management play essential role of creation and modification of habitats and affect ecosystem services provisioning. Modern forestry generally embraces a broad range of concerns, in what is known as multiple-use management, including: the provision of timber, fuel wood, wildlife habitat, natural water quality management, recreation, landscape and community protection, employment, aesthetically appealing landscapes, biodiversity management, watershed management, erosion control, and preserving forests as " sinks" for atmospheric carbon dioxide. Forest ecosystems have come to be seen as the most important componen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caterpillar
Caterpillars ( ) are the larval stage of members of the order Lepidoptera (the insect order comprising butterflies and moths). As with most common names, the application of the word is arbitrary, since the larvae of sawflies (suborder Symphyta) are commonly called caterpillars as well. Both lepidopteran and symphytan larvae have eruciform body shapes. Caterpillars of most species eat plant material ( often leaves), but not all; some (about 1%) eat insects, and some are even cannibalistic. Some feed on other animal products. For example, clothes moths feed on wool, and horn moths feed on the hooves and horns of dead ungulates. Caterpillars are typically voracious feeders and many of them are among the most serious of agricultural pests. In fact, many moth species are best known in their caterpillar stages because of the damage they cause to fruits and other agricultural produce, whereas the moths are obscure and do no direct harm. Conversely, various species of caterpi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitoid
In evolutionary ecology, a parasitoid is an organism that lives in close association with its host (biology), host at the host's expense, eventually resulting in the death of the host. Parasitoidism is one of six major evolutionarily stable strategy, evolutionary strategies within parasitism, distinguished by the fatal prognosis for the host, which makes the strategy close to predation. Among parasitoids, strategies range from living inside the host (''endoparasitism''), allowing it to continue growing before emerging as an adult, to Paralysis, paralysing the host and living outside it (''ectoparasitism''). Hosts can include other parasitoids, resulting in hyperparasitism; in the case of oak galls, up to five levels of parasitism are possible. Some parasitoids Behavior-altering parasite, influence their host's behaviour in ways that favour the propagation of the parasitoid. Parasitoids are found in a variety of Taxon, taxa across the insect superorder Endopterygota, whose compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
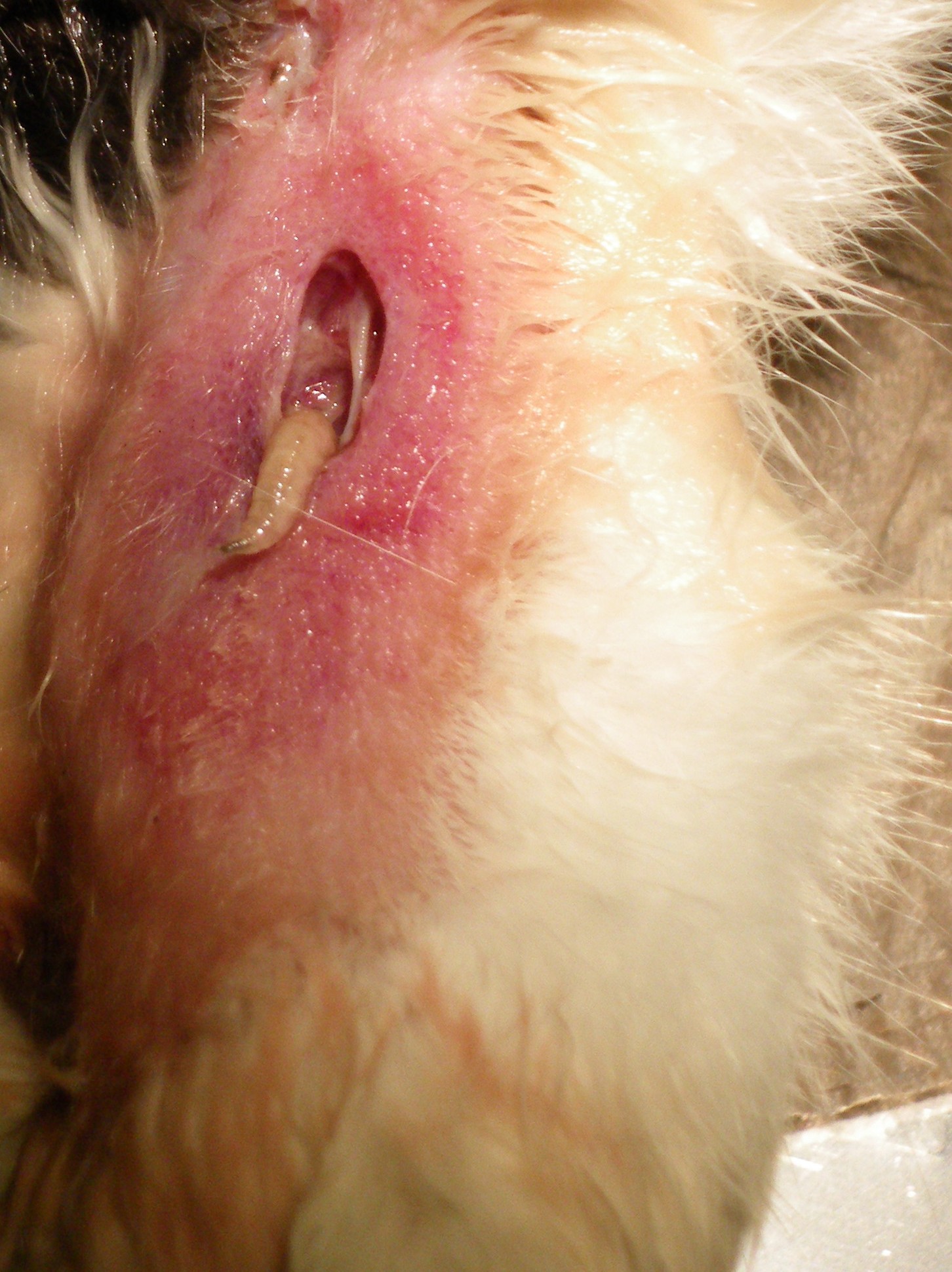
Myiasis
Myiasis is the parasitic infestation of the body of a live animal by fly larvae (maggots) which grow inside the host while feeding on its tissue. Although flies are most commonly attracted to open wounds and urine- or feces-soaked fur, some species (including the most common myiatic flies—the botfly, blowfly, and screwfly) can create an infestation even on unbroken skin and have been known to use moist soil and non-myiatic flies (such as the common housefly) as vector agents for their parasitic larvae. Because some animals (particularly non-native domestic animals) cannot react as effectively as humans to the causes and effects of myiasis, such infestations present a severe and continuing problem for livestock industries worldwide, causing severe economic losses where they are not mitigated by human action. Although typically a far greater issue for animals, myiasis is also a relatively frequent disease for humans in rural tropical regions where myiatic flies thrive, and of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ. The term ''pathogen'' came into use in the 1880s. Typically, the term ''pathogen'' is used to describe an ''infectious'' microorganism or agent, such as a virus, bacterium, protozoan, prion, viroid, or fungus. Small animals, such as helminths and insects, can also cause or transmit disease. However, these animals are usually referred to as parasites rather than pathogens. The scientific study of microscopic organisms, including microscopic pathogenic organisms, is called microbiology, while parasitology refers to the scientific study of parasites and the organisms that host them. There are several pathways through which pathogens can invade a host. The principal pathways have different episodic time frames, but soil has the longest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector (epidemiology)
In epidemiology, a disease vector is any living agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen to another living organism; agents regarded as vectors are organisms, such as parasites or microbes. The first major discovery of a disease vector came from Ronald Ross in 1897, who discovered the malaria pathogen when he dissected a mosquito. Arthropods Arthropods form a major group of pathogen vectors with mosquitoes, flies, sand flies, lice, fleas, ticks, and mites transmitting a huge number of pathogens. Many such vectors are haematophagous, which feed on blood at some or all stages of their lives. When the insects feed on blood, the pathogen enters the blood stream of the host. This can happen in different ways. The ''Anopheles'' mosquito, a vector for malaria, filariasis, and various arthropod-borne-viruses (arboviruses), inserts its delicate mouthpart under the skin and feeds on its host's blood. The parasites the mosquito carries are usually located in its salivary gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |