|
Saprock
Saprolite is a chemically weathered rock. Saprolites form in the lower zones of soil profiles and represent deep weathering of the bedrock surface. In most outcrops its color comes from ferric compounds. Deeply weathered profiles are widespread on the continental landmasses between latitudes 35°N and 35°S. Conditions for the formation of deeply weathered regolith include a topographically moderate relief flat enough to prevent erosion and to allow leaching of the products of chemical weathering. A second condition is long periods of tectonic stability; tectonic activity and climate change can cause erosion. The third condition is humid tropical to temperate climate. Poorly weathered saprolite grit aquifers are capable of producing groundwater, often suitable for livestock. Deep weathering causes the formation of many secondary and supergene ores – bauxite, iron ores, saprolitic gold, supergene copper, uranium and heavy minerals in residual accumulations. Definition, des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regolith
Regolith () is a blanket of unconsolidated, loose, heterogeneous superficial deposits covering solid rock. It includes dust, broken rocks, and other related materials and is present on Earth, the Moon, Mars, some asteroids, and other terrestrial planets and moons. Etymology The term ''regolith'' combines two Greek words: (), 'blanket', and (), 'rock'. The American geologist George P. Merrill first defined the term in 1897, writing: Earth Earth's regolith includes the following subdivisions and components: * soil or pedolith * alluvium and other transported cover, including that transported by aeolian, glacial, marine, and gravity flow processes. * "saprolith'", generally divided into the ** ''upper saprolite'': completely oxidised bedrock ** ''lower saprolite'': chemically reduced partially weathered rocks ** ''saprock'': fractured bedrock with weathering restricted to fracture margins * volcanic ash and lava flows that are interbedded with unconsolidated material * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weakly radioactive because all isotopes of uranium are unstable; the half-lives of its naturally occurring isotopes range between 159,200 years and 4.5 billion years. The most common isotopes in natural uranium are uranium-238 (which has 146 neutrons and accounts for over 99% of uranium on Earth) and uranium-235 (which has 143 neutrons). Uranium has the highest atomic weight of the primordially occurring elements. Its density is about 70% higher than that of lead, and slightly lower than that of gold or tungsten. It occurs naturally in low concentrations of a few parts per million in soil, rock and water, and is commercially extracted from uranium-bearing minerals such as uraninite. In nature, uranium is found as uranium-238 (99. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grus (geology)
Grus is an accumulation of angular, coarse-grained fragments (particles of sand and gravel) resulting from the granular disintegration by the processes of chemical and mechanical weathering of crystalline rocks (most notably granitoids) generally in an arid or semiarid region. Grus sand, when cemented into a sandstone, will form an arkose. Within a European context most of the saprolite mantles of Late Cenozoic age are made up grus, contrasting with Mesozoic and Early Cenozoic saprolites made up of kaolinitic and ferrallitic Ferrallitisation is the process in which rock is changed into a soil consisting of clay ( kaolinite) and sesquioxides, in the form of hydrated oxides of iron and aluminium. In humid tropical areas, with consistently high temperatures and rainfall fo ... material. See also * * References Deposition (geology) Regolith Weathering {{geology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Dating
Relative dating is the science of determining the relative order of past events (i.e., the age of an object in comparison to another), without necessarily determining their absolute age (i.e., estimated age). In geology, rock or superficial deposits, fossils and lithologies can be used to correlate one stratigraphic column with another. Prior to the discovery of radiometric dating in the early 20th century, which provided a means of absolute dating, archaeologists and geologists used relative dating to determine ages of materials. Though relative dating can only determine the ''sequential order'' in which a series of events occurred, not ''when'' they occurred, it remains a useful technique. Relative dating by biostratigraphy is the preferred method in paleontology and is, in some respects, more accurate. The Law of Superposition, which states that older layers will be deeper in a site than more recent layers, was the summary outcome of 'relative dating' as observed in geology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrain
Terrain or relief (also topographical relief) involves the vertical and horizontal dimensions of land surface. The term bathymetry is used to describe underwater relief, while hypsometry studies terrain relative to sea level. The Latin word (the root of ''terrain'') means "earth." In physical geography, terrain is the lay of the land. This is usually expressed in terms of the elevation, slope, and orientation of terrain features. Terrain affects surface water flow and distribution. Over a large area, it can affect weather and climate patterns. Importance The understanding of terrain is critical for many reasons: * The terrain of a region largely determines its suitability for human settlement: flatter alluvial plains tend to have better farming soils than steeper, rockier uplands. * In terms of environmental quality, agriculture, hydrology and other interdisciplinary sciences; understanding the terrain of an area assists the understanding of watershed boundaries, dra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorological variables that are commonly measured are temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, and precipitation. In a broader sense, climate is the state of the components of the climate system, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere and biosphere and the interactions between them. The climate of a location is affected by its latitude/longitude, terrain, altitude, land use and nearby water bodies and their currents. Climates can be classified according to the average and typical variables, most commonly temperature and precipitation. The most widely used classification scheme was the Köppen climate classification. The Thornthwaite system, in use since 1948, incorporates evapotranspiration along with temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goethite
Goethite (, ) is a mineral of the diaspore group, consisting of iron(III) oxide-hydroxide, specifically the "α" polymorph. It is found in soil and other low-temperature environments such as sediment. Goethite has been well known since ancient times for its use as a pigment (brown ochre). Evidence has been found of its use in paint pigment samples taken from the caves of Lascaux in France. It was first described in 1806 based on samples found in the Hollertszug Mine in Herdorf, Germany. The mineral was named after the German polymath and poet Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1749–1832). Composition Goethite is an iron oxyhydroxide containing ferric iron. It is the main component of rust and bog iron ore. Goethite's hardness ranges from 5.0 to 5.5 on the Mohs Scale, and its specific gravity varies from 3.3 to 4.3. The mineral forms prismatic needle-like crystals ("needle ironstone") but is more typically massive. Feroxyhyte and lepidocrocite are both polymorphs of the iron oxy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in front of oxygen (32.1% and 30.1%, respectively), forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust. In its metallic state, iron is rare in the Earth's crust, limited mainly to deposition by meteorites. Iron ores, by contrast, are among the most abundant in the Earth's crust, although extracting usable metal from them requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching or higher, about higher than that required to smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BCE and the use of iron tools and weapons began to displace copper alloys, in some regions, only around 1200 BCE. That event is considered the transition from the Bronze Age to the Iron A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saprolite On Aranmore, Sept 2019
Saprolite is a chemically weathered rock. Saprolites form in the lower zones of soil profiles and represent deep weathering of the bedrock surface. In most outcrops its color comes from ferric compounds. Deeply weathered profiles are widespread on the continental landmasses between latitudes 35°N and 35°S. Conditions for the formation of deeply weathered regolith include a topographically moderate relief flat enough to prevent erosion and to allow leaching of the products of chemical weathering. A second condition is long periods of tectonic stability; tectonic activity and climate change can cause erosion. The third condition is humid tropical to temperate climate. Poorly weathered saprolite grit aquifers are capable of producing groundwater, often suitable for livestock. Deep weathering causes the formation of many secondary and supergene ores – bauxite, iron ores, saprolitic gold, supergene copper, uranium and heavy minerals in residual accumulations. Definition, des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has a great affinity towards oxygen, and forms a protective layer of oxide on the surface when exposed to air. Aluminium visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, non-magnetic and ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al; this isotope is very common, making aluminium the twelfth most common element in the Universe. The radioactivity of 26Al is used in radiodating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ is small and highly charged; as such, it is polarizing, and bonds aluminium forms tend towards covalency. The strong affinity tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
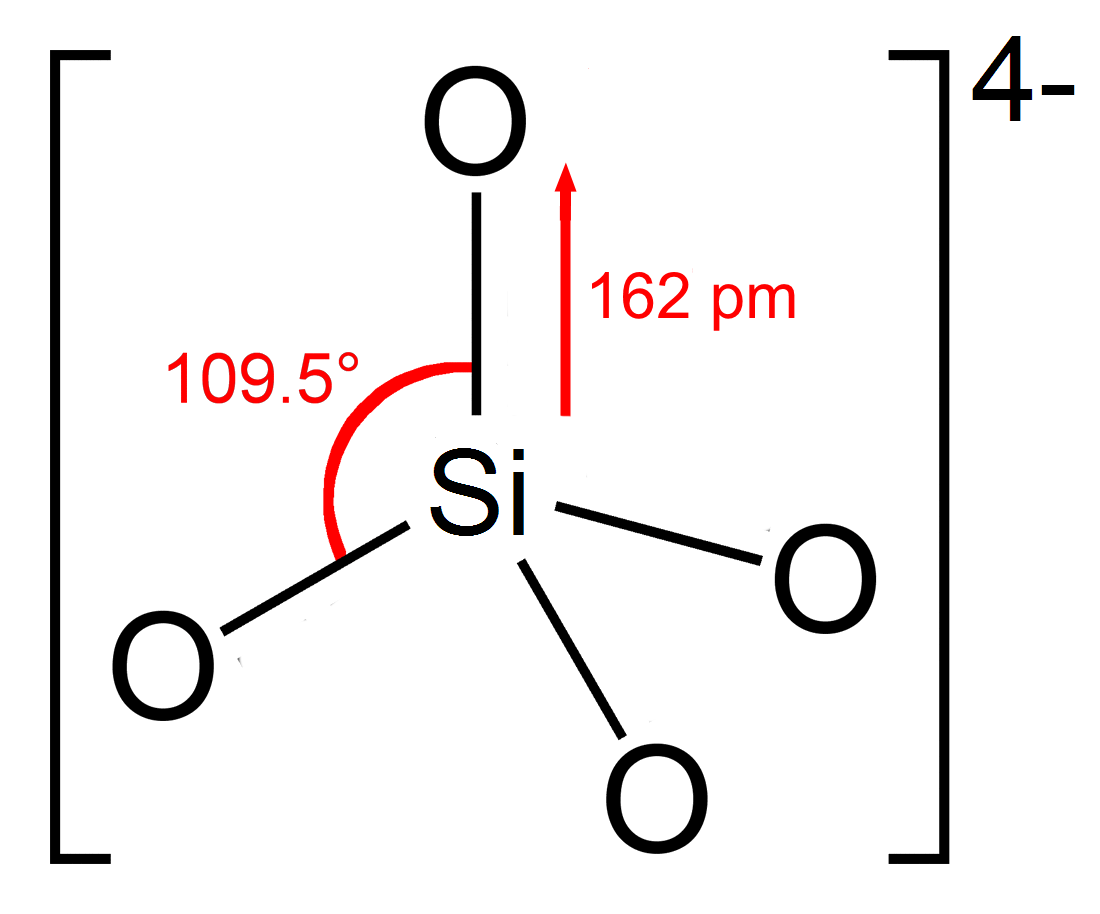
Silicate
In chemistry, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used for any salt of such anions, such as sodium metasilicate; or any ester containing the corresponding chemical group, such as tetramethyl orthosilicate. The name "silicate" is sometimes extended to any anions containing silicon, even if they do not fit the general formula or contain other atoms besides oxygen; such as hexafluorosilicate .Most commonly, silicates are encountered as silicate minerals. For diverse manufacturing, technological, and artistic needs, silicates are versatile materials, both natural (such as granite, gravel, and garnet) and artificial (such as Portland cement, ceramics, glass, and waterglass). Structural principles In all silicates, silicon atom occupies the center of an idealized tetrahedron whose corner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |