|
Relative Dating
Relative dating is the science of determining the relative order of past events (i.e., the age of an object in comparison to another), without necessarily determining their absolute age (i.e., estimated age). In geology, rock or superficial deposits, fossils and lithologies can be used to correlate one stratigraphic column with another. Prior to the discovery of radiometric dating in the early 20th century, which provided a means of absolute dating, archaeologists and geologists used relative dating to determine ages of materials. Though relative dating can only determine the ''sequential order'' in which a series of events occurred, not ''when'' they occurred, it remains a useful technique. Relative dating by biostratigraphy is the preferred method in paleontology and is, in some respects, more accurate. The Law of Superposition, which states that older layers will be deeper in a site than more recent layers, was the summary outcome of 'relative dating' as observed in g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surveying
Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the land, terrestrial Plane (mathematics), two-dimensional or Three-dimensional space#In Euclidean geometry, three-dimensional positions of Point (geometry), points and the Euclidean distance, distances and angles between them. These points are usually on the surface of the Earth, and they are often used to establish maps and boundaries for ownership, locations, such as the designated positions of structural components for construction or the surface location of subsurface features, or other purposes required by government or civil law, such as property sales. A professional in land surveying is called a land surveyor. Surveyors work with elements of geodesy, geometry, trigonometry, regression analysis, physics, engineering, metrology, programming languages, and the law. They use equipment, such as total stations, robotic total stations, theodolites, Satellite navigation, GNSS receivers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
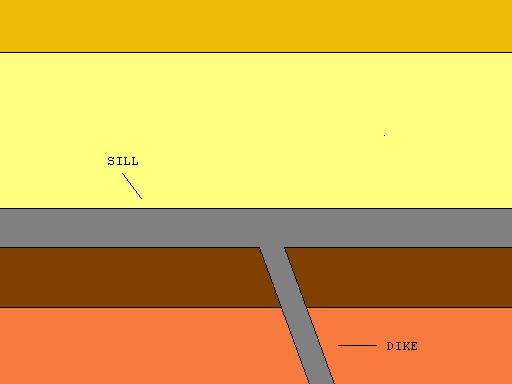
Dike (geology)
In geology, a dike or dyke is a sheet of rock that is formed in a fracture of a pre-existing rock body. Dikes can be either magmatic or sedimentary in origin. Magmatic dikes form when magma flows into a crack then solidifies as a sheet intrusion, either cutting across layers of rock or through a contiguous mass of rock. Clastic dikes are formed when sediment fills a pre-existing crack.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak Magmatic dikes A magmatic dike is a sheet of igneous rock that cuts across older rock beds. It is formed when magma fills a fracture in the older beds and then cools and solidifies. The dike rock is usually more resistant to weathering than the surrounding rock, so that erosion exposes the dike as a natural wall or ridge. It is from these natural walls that dikes get their name. Dikes preserve a record of the fissures through which most mafic magma (fluid magma low in silica) reaches the surface. They are studied by geologists for the clues they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sill (geology)
In geology, a sill is a tabular sheet intrusion that has intruded between older layers of sedimentary rock, beds of volcanic lava or tuff, or along the direction of foliation in metamorphic rock. A sill is a ''concordant intrusive sheet'', meaning that it does not cut across preexisting rock beds. Stacking of sills builds a sill complex. and a large magma chamber at high magma flux. In contrast, a dike is a discordant intrusive sheet, which does cut across older rocks. Formation Sills are fed by dikes, except in unusual locations where they form in nearly vertical beds attached directly to a magma source. The rocks must be brittle and fracture to create the planes along which the magma intrudes the parent rock bodies, whether this occurs along preexisting planes between sedimentary or volcanic beds or weakened planes related to foliation in metamorphic rock. These planes or weakened areas allow the intrusion of a thin sheet-like body of magma paralleling the existi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batholith
A batholith () is a large mass of intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock (also called plutonic rock), larger than in area, that forms from cooled magma deep in the Earth's crust. Batholiths are almost always made mostly of felsic or intermediate composition, intermediate rock types, such as granite, quartz monzonite, or diorite (see also ''granite dome''). Formation Although they may appear uniform, batholiths are in fact structures with complex histories and compositions. They are composed of multiple masses, or ''plutons'', bodies of igneous rock of irregular dimensions (typically at least several kilometers) that can be distinguished from adjacent igneous rock by some combination of criteria including age, composition, texture, or mappable structures. Individual plutons are solidified from magma that traveled toward the surface from a zone of partial melting near the base of the Earth's crust. Traditionally, these plutons have been considered to form by ascent of relative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laccolith
A laccolith is a body of intrusive rock with a dome-shaped upper surface and a level base, fed by a conduit from below. A laccolith forms when magma (molten rock) rising through the Earth's crust begins to spread out horizontally, prying apart the host rock strata. The pressure of the magma is high enough that the overlying strata are forced upward, giving the laccolith its dome-like form. Over time, erosion can expose the solidified laccolith, which is typically more resistant to weathering than the host rock. The exposed laccolith then forms a hill or mountain. The Henry Mountains of Utah, US, are an example of a mountain range composed of exposed laccoliths. It was here that geologist Grove Karl Gilbert carried out pioneering field work on this type of intrusion. Laccolith mountains have since been identified in many other parts of the world. Description A laccolith is a type of igneous intrusion, formed when magma forces its way upwards through the Earth's crust but cool ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentary Rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock formed by the cementation (geology), cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or deposited at Earth's surface. Sedimentation is any process that causes these particles to settle in place. Geological detritus originates from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or Mass wasting, mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus is formed by bodies and parts (mainly shells) of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies (marine snow). Sedimentation may also occur when dissolved minerals precipitate from aqueous solution, water solution. The sedimentary rock cover of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igneous Rocks
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main Rock (geology)#Classification, rock types, the others being sedimentary rock, sedimentary and metamorphic rock, metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. The magma can be derived from Partial melting, partial melts of existing rocks in either a Terrestrial planet, planet's mantle (geology), mantle or crust (geology), crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Solidification into rock occurs either below the surface as intrusive rocks or on the surface as extrusive (geology), extrusive rocks. Igneous rock may form with crystallization to form granular, crystalline rocks, or without crystallization to form Volcanic glass, natural glasses. Igneous rocks occur in a wide range of geological settings: shields, platforms, orogens, basins, large igneous provinces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrusive Rock
Intrusive rock is formed when magma penetrates existing rock, crystallizes, and solidifies underground to form ''Igneous intrusion, intrusions'', such as batholiths, dike (geology), dikes, Sill (geology), sills, laccoliths, and volcanic necks.Intrusive RocksIntrusive rocks accessdate: March 27, 2017.Igneous intrusive rocks, accessdate: March 27, 2017.Britannica.comintrusive rock , geology , Britannica.com accessdate: March 27, 2017. Intrusion is one of the two ways igneous rock can form. The other is extrusive rock, extrusion, such as a Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruption or similar event. An intrusion is any body of intrusive igneous rock, formed from magma that cools and solidifies within the crust of the planet. In contrast, an ''extrusion'' consists of extrusive rock, formed above the surface of the crust. Some geologists use the term plutonic rock synonymously with intrusive rock, but other geologists subdivide intrusive rock, by crystal size, into coarse-grai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Hutton
James Hutton (; 3 June Old Style and New Style dates, O.S. 1726 – 26 March 1797) was a Scottish geologist, Agricultural science, agriculturalist, chemist, chemical manufacturer, Natural history, naturalist and physician. Often referred to as the "Father of Modern Geology," he played a key role in establishing geology as a modern science. Hutton advanced the idea that the physical world's history of Earth, remote history can be inferred from evidence in present-day rocks. Through his study of features in the landscape and coastlines of his native Scottish lowlands, such as Salisbury Crags or Siccar Point, he developed the theory that geological features could not be static but underwent continuing transformation over indefinitely long periods of time. From this he argued, in agreement with many other early geologists, that the Earth could not be young. He was one of the earliest proponents of what in the 1830s became known as uniformitarianism, the science which explains feat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EJ Brill
Brill Academic Publishers () is a Dutch international academic publisher of books, academic journals, and databases founded in 1683, making it one of the oldest publishing houses in the Netherlands. Founded in the South Holland city of Leiden, it maintains its headquarters there, while also operating offices in Boston, Paderborn, Vienna, Singapore, and Beijing. Since 1896, Brill has been a public limited company (). Brill is especially known for its work in subject areas such as Oriental studies, classics, religious studies, Jewish studies, Islamic studies, Asian studies, international law, and human rights. The publisher offers traditional print books, academic journals, primary source materials online, and publications on microform. In recent decades, Brill has expanded to digital publishing with ebooks and online resources including databases and specialty collections varying by discipline. History Founding by Luchtmans, 1683–1848 On 17 May 1683, the Leiden booksell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principle Of Uniformitarianism
Uniformitarianism, also known as the Doctrine of Uniformity or the Uniformitarian Principle, is the assumption that the same natural laws and processes that operate in our present-day scientific observations have always operated in the universe in the past and apply everywhere in the universe., "''The assumption of spatial and temporal invariance of natural laws is by no means unique to geology since it amounts to a warrant for inductive inference'' which, as Bacon showed nearly four hundred years ago, is ''the basic mode of reasoning in empirical science. Without assuming this spatial and temporal invariance, we have no basis for extrapolating from the known to the unknown'' and, therefore, no way of reaching general conclusions from a finite number of observations." It refers to invariance in the metaphysical principles underpinning science, such as the constancy of cause and effect throughout space-time, but has also been used to describe spatiotemporal invariance of physical l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |