|
Sandy Bridge (microarchitecture)
Sandy Bridge is the codename for Intel's 32 nm microarchitecture used in the second generation of the Intel Core processors ( Core i7, i5, i3). The Sandy Bridge microarchitecture is the successor to Nehalem and Westmere microarchitecture. Intel demonstrated an A1 stepping Sandy Bridge processor in 2009 during Intel Developer Forum (IDF), and released first products based on the architecture in January 2011 under the Core brand. Sandy Bridge is manufactured in the 32 nm process and has a soldered contact with the die and IHS (Integrated Heat Spreader), while Intel's subsequent generation Ivy Bridge uses a 22 nm die shrink and a TIM (Thermal Interface Material) between the die and the IHS. Technology Intel demonstrated a Sandy Bridge processor with A1 stepping at 2 GHz during the Intel Developer Forum in September 2009. Upgraded features from Nehalem include: CPU * Intel Turbo Boost 2.0 * 32 KB data + 32 KB instruction L1 cache and 256 KB L2 c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Intel Sandy Bridge-based Xeon Microprocessors
Intel Sandy Bridge-based Xeon microprocessors (often referred to as Sandy Bridge-E) are microprocessors based on the Intel's 32 nm Sandy Bridge architecture for servers, workstations, and high-end desktops. It succeeds the six-core Gulftown/Westmere-EP processor which used the older LGA 1366 package, and uses LGA 2011, LGA 1356 and LGA 1155 socket depending on the package. Overview There are five different families of Xeon processors that were based on Sandy Bridge architecture: * Sandy Bridge-E (LGA 2011) targeted high-end desktop (HEDT) enthusiast segment. It was branded as Core i7 Extreme Edition and Core i7 processors, despite sharing many similarities with Xeon models. * Sandy Bridge-EP (LGA 2011) branded as Xeon E5 models aimed at high-end servers and workstations. It supported motherboards equipped with up to 4 sockets. * Sandy Bridge-EN ( LGA 1356) uses a smaller socket for low-end and dual-processor servers on certain Xeon E5 and Pentium branded models. * Sandy Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
AES Instruction Set
An Advanced Encryption Standard instruction set (AES instruction set) is a set of instructions that are specifically designed to perform AES encryption and decryption operations efficiently. These instructions are typically found in modern processors and can greatly accelerate AES operations compared to software implementations. An AES instruction set includes instructions for key expansion, encryption, and decryption using various key sizes (128-bit, 192-bit, and 256-bit). The instruction set is often implemented as a set of instructions that can perform a single round of AES along with a special version for the last round which has a slightly different method. When AES is implemented as an instruction set instead of as software, it can have improved security, as its side channel attack surface is reduced. x86 architecture processors AES-NI (or the Intel Advanced Encryption Standard New Instructions; AES-NI) was the first major implementation. AES-NI is an extension to the x8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Haswell (microarchitecture)
Haswell is the List of Intel codenames, codename for a Central processing unit, processor microarchitecture developed by Intel as the "fourth-generation core" successor to the Ivy Bridge (microarchitecture), Ivy Bridge (which is a die shrink/Tick–tock model, tick of the Sandy Bridge, Sandy Bridge microarchitecture). Intel officially announced CPUs based on this microarchitecture on June 4, 2013, at Computex Taipei 2013, while a working Haswell chip was demonstrated at the 2011 Intel Developer Forum. Haswell was the last generation of Intel processor to have socketed processors on mobile. With Haswell, which uses a 22 nm process, Intel also introduced low-power processors designed for convertible or "hybrid" ultrabooks, designated by the "U" suffix. Haswell began shipping to manufacturers and Original equipment manufacturer, OEMs in mid-2013, with its desktop chips officially launched in September 2013. Haswell CPUs are used in conjunction with the Intel 8 Series chipsets, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ivy Bridge (microarchitecture)
Ivy Bridge is the codename for Intel's 22 nm microarchitecture used in the third generation of the Intel Core processors ( Core i7, i5, i3). Ivy Bridge is a die shrink to 22 nm process based on FinFET ("3D") Tri-Gate transistors, from the former generation's 32 nm Sandy Bridge microarchitecture—also known as tick–tock model. The name is also applied more broadly to the Xeon and Core i7 Extreme Ivy Bridge-E series of processors released in 2013. Ivy Bridge processors are backward compatible with the Sandy Bridge platform, but such systems might require a firmware update (vendor specific). In 2011, Intel released the 7-series Panther Point chipsets with integrated USB 3.0 and SATA 3.0 to complement Ivy Bridge. Volume production of Ivy Bridge chips began in the third quarter of 2011. Quad-core and dual-core-mobile models launched on April 29, 2012 and May 31, 2012 respectively. Core i3 desktop processors, as well as the first 22 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Westmere (microarchitecture)
Westmere (formerly Nehalem-C) is the code name given to the 32 nanometer, 32 nm die shrink of ''Nehalem (microarchitecture), Nehalem''. While sharing the same CPU sockets, Westmere included Intel HD Graphics, while Nehalem did not. The first ''Westmere''-based processors were launched on January 7, 2010, by Intel Corporation. The Westmere architecture has been available under the Intel brands of List of Intel Core i3 microprocessors, Core i3, List of Intel Core i5 microprocessors, Core i5, List of Intel Core i7 microprocessors, Core i7, List of Intel Pentium microprocessors, Pentium, List of Intel Celeron microprocessors, Celeron and Xeon, and includes directX 10.1, and openGL 2.1. Technology Westmere's feature improvements from Nehalem, as reported: * Native six-core (Gulftown (microprocessor), Gulftown) and ten-core (Westmere-EX) processors. * A new set of instructions that gives over 3x the encryption and decryption rate of Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) processes co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nehalem (microarchitecture)
Nehalem is the codename for Intel's 45 nm microarchitecture released in November 2008. It was used in the first generation of the Intel Core i5 and i7 processors, and succeeds the older Core microarchitecture used on Core 2 processors. The term "Nehalem" comes from the Nehalem River. Nehalem is built on the 45 nm process, is able to run at higher clock speeds without sacrificing efficiency, and is more energy-efficient than Penryn microprocessors. Hyper-threading is reintroduced, along with a reduction in L2 cache size, as well as an enlarged L3 cache that is shared among all cores. Nehalem is an architecture that differs radically from NetBurst, while retaining some of the latter's minor features. Nehalem later received a die-shrink to 32 nm with Westmere, and was fully succeeded by "second-generation" Sandy Bridge in January 2011. Technology * Cache line block on L2/L3 cache was reduced from 128 bytes in NetBurst & Merom/Penryn to 64 bytes per line in this gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Socket G2
Socket G2, also known as rPGA 988B is Intel's CPU socket used with their line of mobile Core i7, the successor to the Core 2 line, and also with several mobile Core i5 and Core i3 processors. It is based on Intel's Sandy Bridge and Ivy Bridge architecture. Like its predecessor, socket G1 systems, it can only run in dual-channel memory mode, but with data rates up to 1600 MHz (as opposed to the triple-channel mode which is unique to the LGA-1366 platform and subsequent Xeon sockets). Socket G2 CPUs are also known as FCPGA988 socket processors, which should be pin compatible with PPGA988. Although nearly all motherboards using this socket are intended for mobile products like laptops, a few desktop boards using this do exist. Supermicro, for example, produced a number of mini ITX motherboards using the QM77 chipset. Technical specifications * Pins arranged in a 35×36 grid array (it is incompatible with G1 socket due to different placing of one pin) * 18×15 size grid rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
LGA 1356
LGA 1356, also called Socket B2, is an Intel microprocessor socket released in Q1 2012 with 1356 Land Grid Array pins. It launched alongside LGA 2011 to replace its predecessor, LGA 1366 (Socket B) and LGA 1567. It's compatible with Intel Sandy Bridge-EN (also known as Romley-EN) and Ivy Bridge-EN microprocessors. Description LGA 1356 has 1356 protruding pins to make contact with the pads on the processor. Processors of LGA 1356 and LGA 1366 sockets are not compatible with each other since they have different socket notches. While LGA 2011 was designed for high-end desktops and high-performance servers, LGA 1356 was designed for the dual-processor and low-end segment of the server market. It supports 64-bit wide DDR3 triple channel memory, and equipped with 1 Intel QPI connection and 24 PCI Express lanes. Meanwhile LGA 2011 supports quad channel memory, 2 QPI connections and 40 PCIe lanes. Socket LGA 1155, desktop socket of the same generation supports dual channel m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
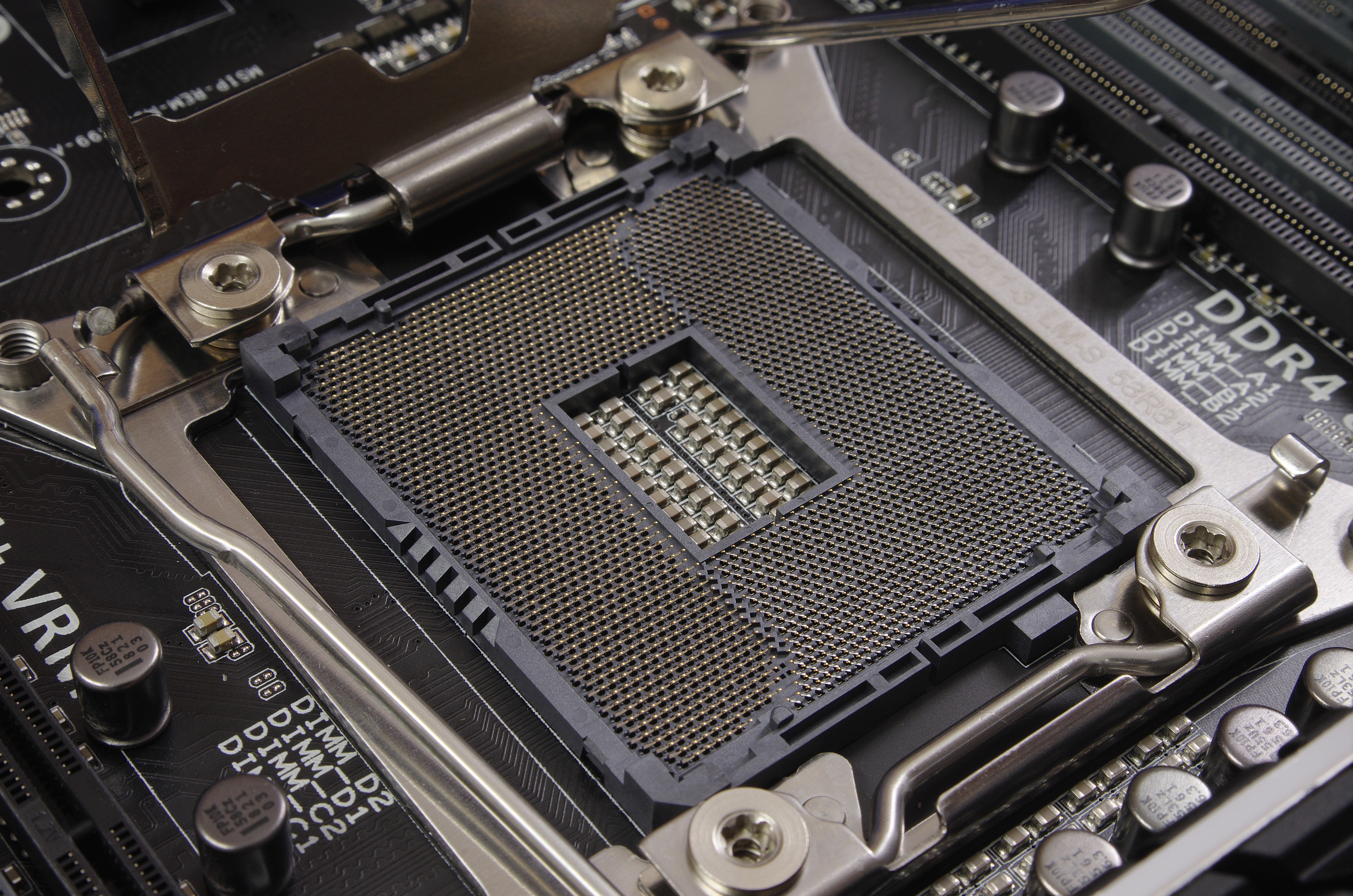
LGA 2011
LGA 2011, also called ''Socket R'', is a CPU socket by Intel released on November 14, 2011. It launched along with LGA 1356 to replace its predecessor, LGA 1366 (Socket B) and LGA 1567. While LGA 1356 was designed for dual-processor or low-end servers, LGA 2011 was designed for high-end desktops and high-performance servers. The socket has 2011 protruding pins that touch contact points on the underside of the processor. The LGA 2011 socket uses Intel QuickPath Interconnect, QPI to connect the CPU to additional CPUs. Direct Media Interface, DMI 2.0 is used to connect the processor to the Platform Controller Hub, PCH. The memory controller and 40 PCI Express (PCIe) lanes are integrated into the CPU. On a secondary processor an extra ×4 PCIe interface replaces the DMI interface. As with its predecessor LGA 1366, there is no provisioning for integrated graphics. This socket supports four DDR3 SDRAM, DDR3 or DDR4 SDRAM, DDR4 SDRAM memory channels with up to three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |